在springboot构建的项目启动后,想让程序自动执行一些任务,我们可以使用CommandLineRunner或ApplicationRunner实现。首先,我们来看看简单的源码。
/**
* Interface used to indicate that a bean should <em>run</em> when it is contained within
* a {@link SpringApplication}. Multiple {@link CommandLineRunner} beans can be defined
* within the same application context and can be ordered using the {@link Ordered}
* interface or {@link Order @Order} annotation.
* <p>
* If you need access to {@link ApplicationArguments} instead of the raw String array
* consider using {@link ApplicationRunner}.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @see ApplicationRunner
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface CommandLineRunner {
/**
* Callback used to run the bean.
* @param args incoming main method arguments
* @throws Exception on error
*/
void run(String... args) throws Exception;
}简单吧,就一个函数式接口。来看看注释:在一个SpringApplication项目中,此接口被用于标明一个实现类的bean应执行run方法。在同一个应用上下文,可以定义多个CommandLineRunner实现类的bean,并且这些bean可以使用Ordered接口或@Order注释进行排序。如果需要访问ApplicationArguments而不是原始的String数组,请考虑使用ApplicationRunner。怎么样,我翻译的还行吧。:D 现在,来看看官网https://spring.io
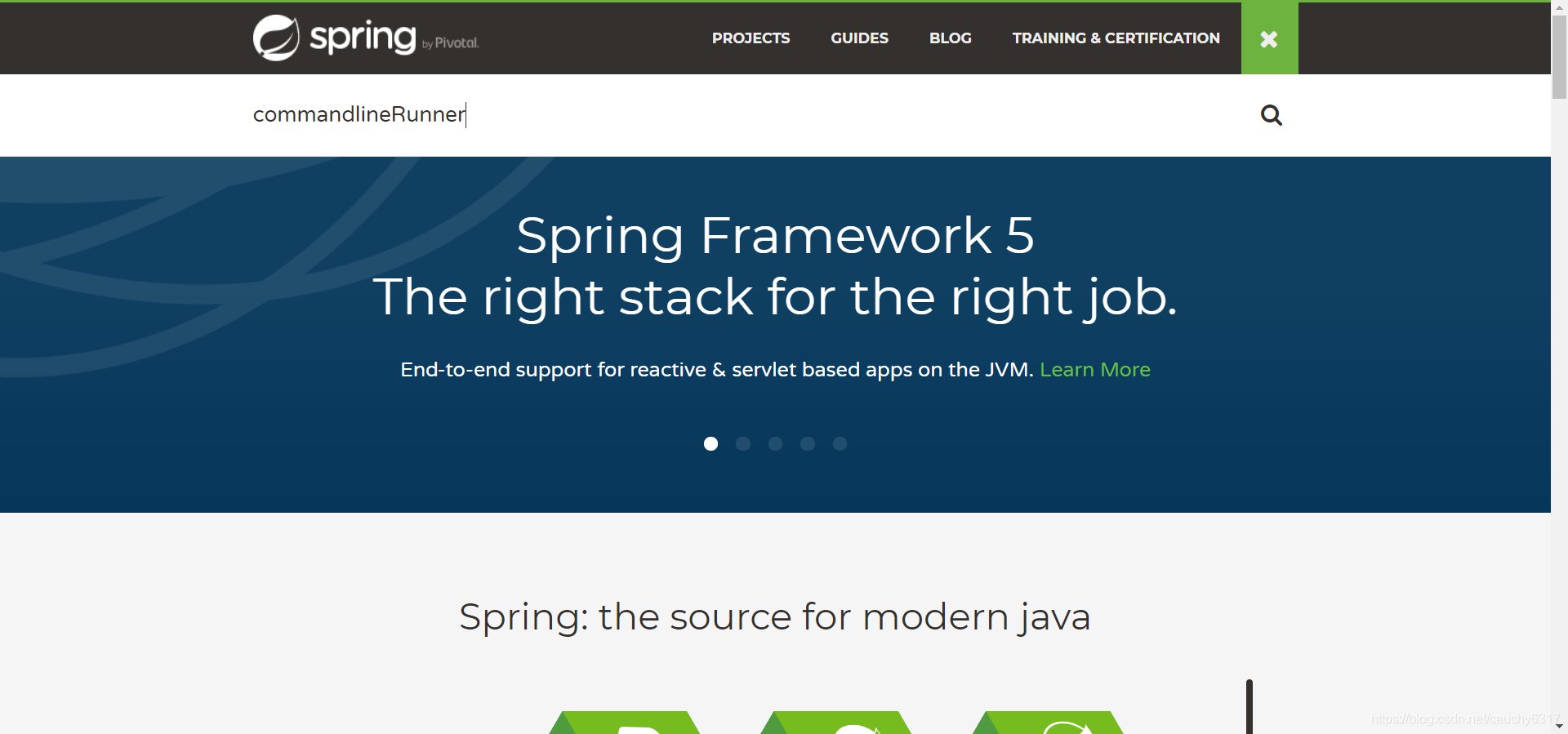
直接搜索CommandLineRunner就行啦。查询结果如下:
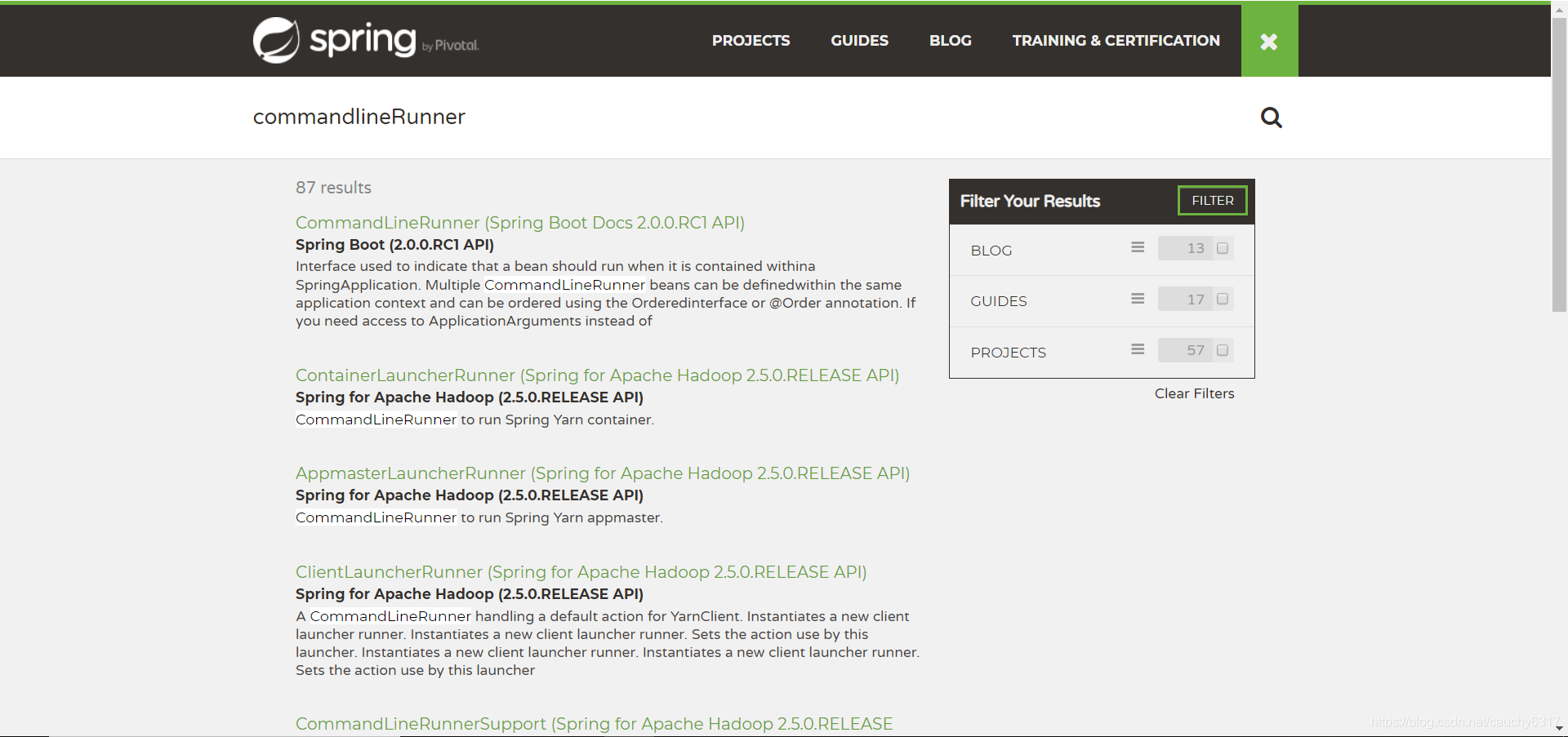
选择第一个点进去,可以看到javadoc文档。当然了,你可以使用Google的翻译成中文(右击网页)。现在,你可以对比一下翻译结果和我的翻译结果,哪个更容易理解。我想你心中已有答案了。:D
接下来,我们看看该如何使用CommandLineRunner。使用Intellij IDEA构建一个Maven的Web项目,这很简单,动手试试。
如果你已经完成了,那我们继续接下来的学习啦。在你的启动类所在包下新建一个CommandLineRunnerStudy 类,并且实现run接口(Ctrl + o 快捷键),简单地打印一句"Hello CommandLineRunner!"。注意:使用@Component注解,这样该实现类才能作为一个bean注入到spring Ioc 容器中。
/**
* @author Cheng Jun
* @version 1.0
* @Description:
* @date 2019/8/5 17:55
*/
@Component
public class CommandLineRunnerStudy implements CommandLineRunner {
/**
* Callback used to run the bean.
*
* @param args incoming main method arguments
* @throws Exception on error
*/
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Hello CommandLineRunner!");
}
}好了,大功告成!启动你的程序,可以看到控制台打印出了"Hello CommandLineRunner!"。现在让我们再来看看,String... args参数该如何使用。这个可变参数就是启动类中的String[] args,也就是我们传入启动类的参数可以直接在该方法中使用。那么该如何向启动类的main方法传入参数呢?在Intellij IDEA中我们可以这样做,点击菜单栏Run->Edit Configurations->Environment(默认为 collapse all),在Program arguments中输入你想设置的数组。然后在CommandLineRunnerStudy的run方法中添加"System.out.println(args[0]);"就可以打印出来了。
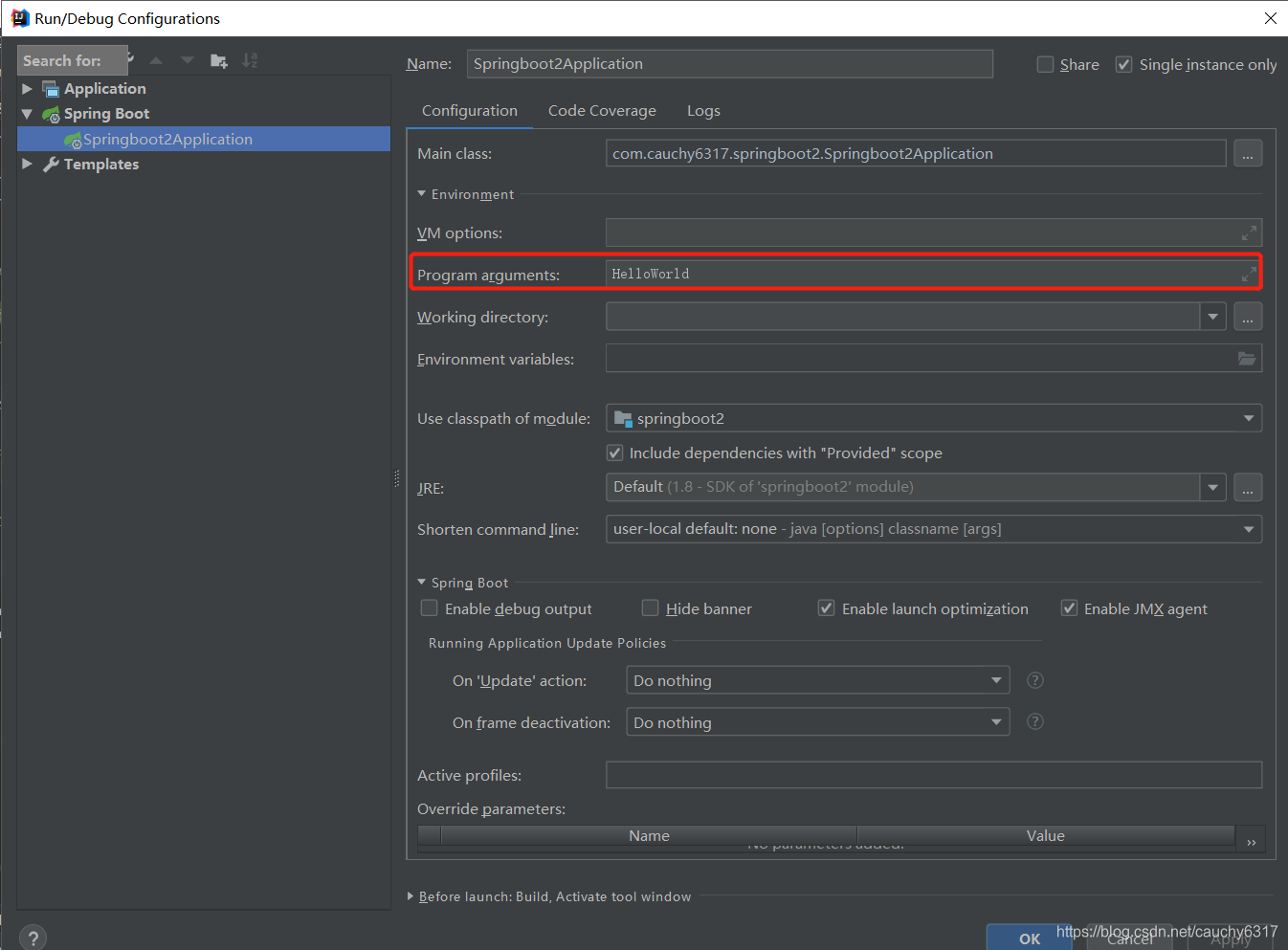
恭喜你,获得了CommandLineRunner的使用技巧。ApplicationRunner的使用和CommandLineRunner相同,只是在方法的参数有些区别。如果你想更进一步学习,我推荐你看看这篇博客https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/zongzhankui/article/details/78681942
如果对你有帮助,请点赞关注博主!





















 441
441

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








