JDBC从入门到放弃
06-JDBC的批处理
当有成批插入或者更新记录的需求时,可以采用JDBC的批量更新机制,这一机制允许多条语句一次性的提交给数据库批量处理。通常情况下比单独处理要更有效率。
批量处理一般流程。
假设我们有100000条数据要插入的数据库,采用批处理,每10000条批量插入一次。
①先不执行sql,可以积累起来,每10000条执行一次
stat.addBatch(); // 积累起来, 暂时不执行
if(i%10000==0) {
stat.executeBatch(); //批量处理
stat.clearBatch(); //清空前面的等待sql的记录
}
②//sql总条数不是批量的整数倍,循环外面,还要在执行一次
if(100000%10000!=0) {
stat.executeBatch(); //批量处理
stat.clearBatch(); //清空前面的等待sql的记录
}
下面我们来演示批处理的处理。
分别采用statement和preparedStatement以及批处理来进行插入,我们测试一下每种操作运行的总时间。
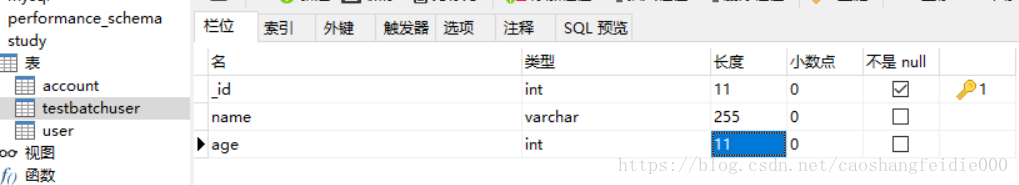
为了测试结果的准确性,我们新建一张表,每次操作之前,清空表中的数据。
delete from testbatchuser;
采用statement进行插入
|
/** * 测试statement不使用Batch的情况下进行大量数据插入 */ @Test public void testNoBatchStatement() { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Connection con = null; Statement statement = null; try { // 1:获取数据库里欧按揭 con = DBUtils.getConnection(); for(int i = 0;i<100000;i++) { String userName= "用户:"+i; int age = i; // 2:准备插入数据库语句 String sql = "INSERT INTO testbatchuser(name,age)" + " VALUES('" + userName + "'," + age +");"; // 3:执行数据库插入语句 statement = con.createStatement(); statement.executeUpdate(sql); } } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally { DBUtils.close(con, statement, null); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("总耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms"); } |
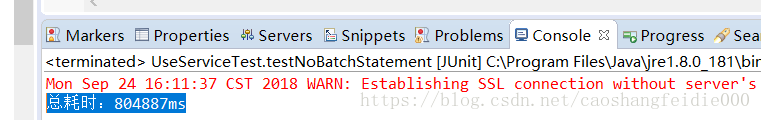
总耗时:804887ms
采用preparedStatement进行插入
|
/** * 测试statement不使用Batch的情况下进行大量数据插入 */ @Test public void testNoBatchPreparedStatement() { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Connection con = null; PreparedStatement pst = null; try { // 1:获取数据库里欧按揭 con = DBUtils.getConnection(); // 2:准备插入数据库语句 String sql ="INSERT INTO testbatchuser(name,age)" + " VALUES(?,?);"; pst = con.prepareStatement(sql); for(int i = 0;i<100000;i++) { String userName= "用户:"+i; int age = i; pst.setString(1, userName); pst.setInt(2, age); // 3:执行数据库插入语句 pst.executeUpdate(); } } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally { DBUtils.close(con, pst, null); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("总耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms"); } |
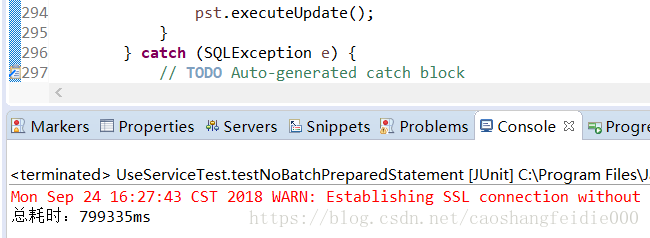
总耗时:799335ms
采用batch批量进行插入
|
/** * 测试preparedstatement使用Batch的情况下进行大量数据插入 */ @Test public void testBatchPreparedStatement() { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Connection con = null; PreparedStatement pst = null; try { // 1:获取数据库里欧按揭 con = DBUtils.getConnection(); con.setAutoCommit(false); // 2:准备插入数据库语句 String sql = "INSERT INTO testbatchuser(name,age)" + " VALUES(?,?);"; pst = con.prepareStatement(sql); int totleLength = 100000; int stepLenth = 10000; for (int i = 1; i < totleLength + 1; i++) { String userName = "用户:" + (i - 1); int age = i - 1; pst.setString(1, userName); pst.setInt(2, age); pst.addBatch();// 把每一条不一样的sql暂存起来 if (i % stepLenth == 0) {// 先不执行sql,可以积累起来,每stepLenth条执行一次 // 3:执行数据库插入语句 pst.executeBatch(); pst.clearBatch(); // 清空前面的等待sql的记录 con.commit(); } } if (totleLength % stepLenth != 0) { pst.executeBatch(); // 批量处理 pst.clearBatch(); // 清空前面的等待sql的记录 con.commit(); } } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } finally { DBUtils.close(con, pst, null); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("总耗时:" + (end - start) + "ms"); } |
查看插入结果,结果正确。
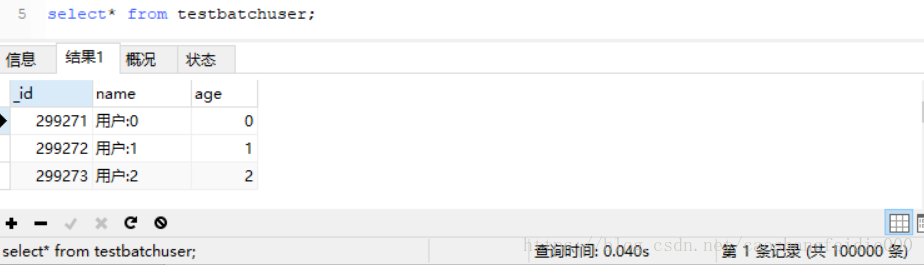
总耗时:9729ms
在本机上测试,从结果上看,批量插入比preparedStatement的和Statement的要快很多。





 本文对比了使用JDBC的Statement、PreparedStatement及批处理方式进行大量数据插入的性能。通过实验发现,采用批处理机制批量更新数据库,相较于逐条插入,能显著提升效率,尤其是在处理大规模数据集时优势更为明显。
本文对比了使用JDBC的Statement、PreparedStatement及批处理方式进行大量数据插入的性能。通过实验发现,采用批处理机制批量更新数据库,相较于逐条插入,能显著提升效率,尤其是在处理大规模数据集时优势更为明显。
















 973
973

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








