博客🔗:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/cPen_web
视频🔗:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1vK4y1o7jH
变量和标签
变量
- 视图函数中可以将Python变量封装到 字典 中传递到模板上
样例:
def xxx_view(request):
dic = {
"变量1": "值1",
"变量2": "值2",
}
return render(request, 'xxx.html', dic)
- 能传递到模板中的 数据类型
str-字符串 int-整型
list-数组 tuple-元组
dict-字典 func-方法
obj-类实例化的对象
- 在模板中使用变量语法
- {
{ 变量名 }}
- {
{ 变量名.index }}
- {
{ 变量名.key }}
- {
{ 对象.方法 }}
- {
{ 函数名 }}
- 演示:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/test_html_param

# mysite1/mysite1/urls.py
urlpatterns = [
...
path('test_html', views.test_html)
]
# mysite1/mysite1/views.py
def test_html_param(request):
dic = {
}
dic['int'] = 88
dic['str'] = 'peng'
dic['lst'] = ['Tom', 'Jack', 'Lily']
dic['dict'] = {
'a':9, 'b':8}
dic['func'] = say_hi
dic['class_obj'] = Dog()
dic['script'] = '<script>alert(1111)</script>'
return render(request, 'test_html_param.html', dic)
def say_hi():
return 'hahaha'
class Dog:
def say(self):
return 'wangwang'
# mysite1/templates/test_html_param.html
<h3>int 是 {
{
int|add:"2" }}</h3>
<h3>str 是 {
{
str|upper }}</h3>
<h3>lst 是 {
{
lst }}</h3>
<h3>lst 是 {
{
lst.0 }}</h3>
<h3>dict 是 {
{
dict }}</h3>
<h3>dict['a'] 是 {
{
dict.a }}</h3>
<h3>function 是 {
{
func }}</h3>
<h3>class_obj 是 {
{
class_obj.say }}</h3>
<h3>script 是 {
{
script|safe }}</h3>
标签
模板标签
- 作用:将一些服务器端的功能嵌入到模板中,例如流程控制等
- 标签语法:
{% 标签 %}
...
{% 结束标签 %}
if标签
- 语法:
{% if 条件表达式1 %}
...
{% elif 条件表达式2 %}
...
{% elif 条件表达式3 %}
...
{% else %}
...
{% endif %} - 需要有结束标签
- 注意:
- if条件表达式里可以用的运算符 ==, !=, <, > , <=, >=, in, not in, is, is not, not、and、or
- 在if标记中使用实际括号是无效的语法。如果需要它们指示优先级,则应使用嵌套的if标记。
官方文档:https://docs.djangoproject.com/zh-hans/2.2/ref/templates/builtins/#if
- 演示:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/test_if_for
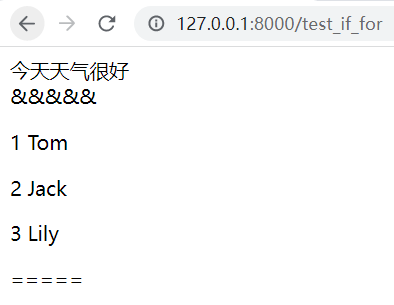
# mysite1/mysite1/urls.py
urlpatterns = [
...
path('test_if_for', views.test_if_for),
]
# mysite1/mysite1/views.py
def test_if_for(request):
dic = {
}
dic['x'] = 20
dic['lst'] = [




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 17
17

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










