
目录
1. 用栈实现队列 ★★
2. 单词搜索 II ★★★
3. 直线上最多的点数 ★★★
1. 用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 推到队列的末尾int pop()从队列的开头移除并返回元素int peek()返回队列开头的元素boolean empty()如果队列为空,返回true;否则,返回false
说明:
- 你只能使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有
push to top,peek/pop from top,size, 和is empty操作是合法的。 - 你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
进阶:
- 你能否实现每个操作均摊时间复杂度为
O(1)的队列?换句话说,执行n个操作的总时间复杂度为O(n),即使其中一个操作可能花费较长时间。
示例:
输入: ["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []] 输出: [null, null, null, 1, 1, false] 解释: MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue(); myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1] myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue) myQueue.peek(); // return 1 myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2] myQueue.empty(); // return false
提示:
1 <= x <= 9- 最多调用
100次push、pop、peek和empty - 假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用
pop或者peek操作)
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class MyQueue
{
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
stack<int> a, b;
MyQueue()
{
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x)
{
while (!b.empty())
{
a.push(b.top());
b.pop();
}
b.push(x);
while (!a.empty())
{
b.push(a.top());
a.pop();
}
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop()
{
int res = b.top();
b.pop();
return res;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek()
{
return b.top();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty()
{
return b.empty();
}
};
int main()
{
MyQueue myQueue = MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
cout << myQueue.peek() << endl; // return 1
cout << myQueue.pop() << endl; // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
return 0;
}输出:
1
1
2. 单词搜索 II
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个单词(字符串)列表 words,找出所有同时在二维网格和字典中出现的单词。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过 相邻的单元格 内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母在一个单词中不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:
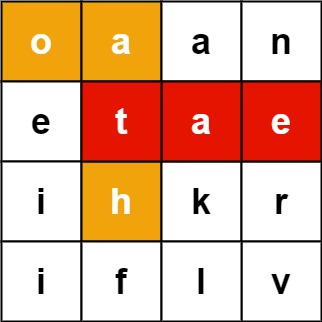
输入:board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"] 输出:["eat","oath"]
示例 2:
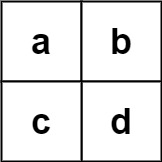
输入:board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"] 输出:[]
提示:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 12board[i][j]是一个小写英文字母1 <= words.length <= 3 * 10^41 <= words[i].length <= 10words[i]由小写英文字母组成words中的所有字符串互不相同
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
struct Node
{
bool isflag = false;
Node *next[27] = {};
};
set<string> res;
vector<string> ans;
Node *root;
vector<int> dirx{0, 0, 1, -1};
vector<int> diry{1, -1, 0, 0};
bool flag;
void createtree(vector<string> &words)
{
root = new Node();
for (auto w : words)
{
Node *p = root;
for (int i = 0; i < w.length(); i++)
{
if (p->next[w[i] - 'a'] == NULL)
{
p->next[w[i] - 'a'] = new Node();
}
p = p->next[w[i] - 'a'];
}
p->isflag = true;
}
}
void backtrack(vector<vector<char>> &board, vector<vector<bool>> visited, int row, int col, Node *roott, string cur)
{
cur += board[row][col];
roott = roott->next[board[row][col] - 'a'];
if (!roott)
return;
if (roott->isflag == true)
{
res.insert(cur);
flag = true;
}
visited[row][col] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nx = row + dirx[i];
int ny = col + diry[i];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= board.size() || ny >= board[0].size())
continue;
if (visited[nx][ny] == false)
{
backtrack(board, visited, nx, ny, roott, cur);
}
}
}
vector<string> findWords(vector<vector<char>> &board, vector<string> &words)
{
if (board.size() == 0 || words.size() == 0)
return ans;
createtree(words);
for (int i = 0; i < board.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < board[i].size(); j++)
{
Node *p = root;
flag = false;
if (p->next[board[i][j] - 'a'])
{
vector<vector<bool>> visited{board.size(), vector<bool>(board[0].size(), false)};
backtrack(board, visited, i, j, p, "");
}
}
}
set<string>::iterator it;
for (it = res.begin(); it != res.end(); it++)
ans.push_back(*it);
return ans;
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
vector<vector<char>> board = {
{'o','a','a','n'},
{'e','t','a','e'},
{'i','h','k','r'},
{'i','f','l','v'}};
vector<string> words = {"oath","pea","eat","rain"};
for (auto str: s.findWords(board, words))
cout << str << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}输出:
eat oath
3. 直线上最多的点数
给你一个数组 points ,其中 points[i] = [xi, yi] 表示 X-Y 平面上的一个点。求最多有多少个点在同一条直线上。
示例 1:
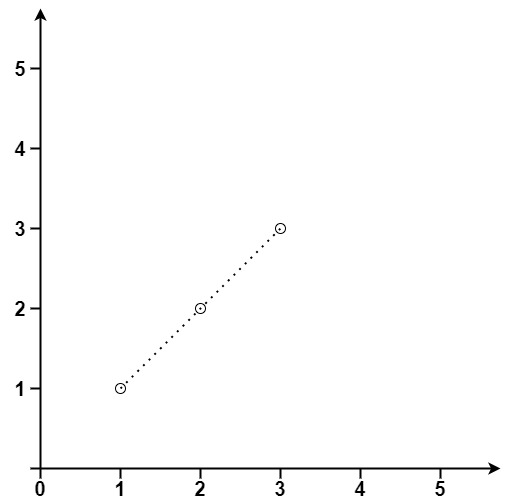
输入:points = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]] 输出:3
示例 2:
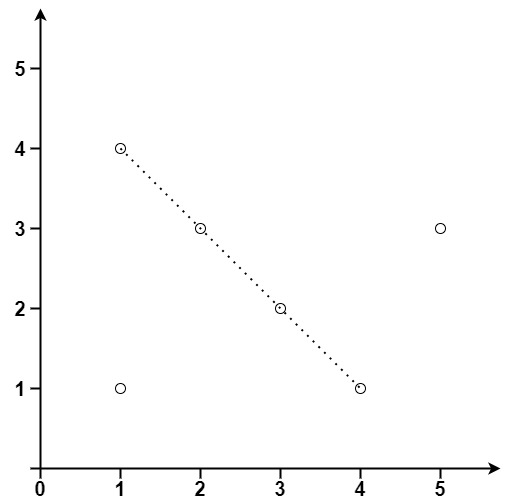
输入:points = [[1,1],[3,2],[5,3],[4,1],[2,3],[1,4]] 输出:4
提示:
1 <= points.length <= 300points[i].length == 2-10^4 <= xi, yi <= 10^4points中的所有点 互不相同
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Point
{
int x;
int y;
Point() : x(0), y(0) {}
Point(int a, int b) : x(a), y(b) {}
};
class Solution
{
public:
int maxPoints(vector<Point> &points)
{
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); ++i)
{
map<pair<int, int>, int> m;
int p = 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < points.size(); ++j)
{
if (points[i].x == points[j].x && (points[i].y == points[j].y))
{
++p;
continue;
}
int dx = points[j].x - points[i].x;
int dy = points[j].y - points[i].y;
int d = gcd(dx, dy);
++m[{dx / d, dy / d}];
}
ans = max(ans, p);
for (auto it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); ++it)
{
ans = max(ans, it->second + p);
}
}
return ans;
}
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return (b == 0) ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
};
int main()
{
Solution s;
vector<Point> points = {{1,1},{2,2},{3,3}};
cout << s.maxPoints(points) << endl;
points = {{1,1},{3,2},{5,3},{4,1},{2,3},{1,4}};
cout << s.maxPoints(points) << endl;
return 0;
}输出:
3
4
🌟 每日一练刷题专栏
✨ 持续,努力奋斗做强刷题搬运工!
👍 点赞,你的认可是我坚持的动力!
★ 收藏,你的青睐是我努力的方向!
✏️ 评论,你的意见是我进步的财富!
 | C/C++ 每日一练 专栏 |
 | Python 每日一练 专栏 |
























 2223
2223












