一、什么是OpenResty
-
OpenResty® 是一个基于 Nginx 与 Lua 的高性能 Web 平台,用于方便地搭建能够处理超高并发、扩展性极高的动态 Web应用、Web 服务和动态网关。通过汇聚各种设计精良的 Nginx 模块,从而将 Nginx 有效地变成一个强大的通用 Web应用平台。这样,Web 开发人员和系统工程师可以使用 Lua 脚本语言调动 Nginx 支持的各种 C 以及 Lua模块,快速构造出足以胜任 10K 乃至 1000K 以上单机并发连接的高性能 Web 应用系统。
-
OpenResty® 的目标是让你的Web服务直接跑在 Nginx 服务内部,充分利用 Nginx 的非阻塞 I/O 模型,不仅仅对HTTP 客户端请求,甚至于对远程后端诸如 MySQL、PostgreSQL、Memcached 以及 Redis等都进行一致的高性能响应。
二、缓存前移的实现
第一步:关闭nginx服务以及源码编译openresty(其OpenResty自身已经有nginx,所以需要把nginx关闭)
[root@hang1 sbin]# nginx -s stop

将openresty源码包上传给我们做实验的虚拟机

[root@hang1 memcache-2.2.5]# cd /mnt
[root@hang1 mnt]# ls
[root@hang1 mnt]# tar zxf openresty-1.13.6.1.tar.gz
[root@hang1 mnt]# cd openresty-1.13.6.1
[root@hang1 openresty-1.13.6.1]# ls
[root@hang1 openresty-1.13.6.1]# ./configure
[root@hang1 openresty-1.13.6.1]# gmake && gmake install


将上一篇博文最后用于测试的两个文件复制到指定目录下,用于后续的测试
[root@hang1 mnt]# cd memcache-2.2.5
[root@hang1 memcache-2.2.5]# cp memcache.php example.php /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/

第二步:修改openresty的配置文件
[root@hang1 memcache-2.2.5]# cd /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/
[root@hang1 conf]# ls
[root@hang1 conf]# vim nginx.conf
17 http {
18 upstream memcache{
19 server localhost:11211;
20 }
52 location /memc {
53 internal;
54 memc_connect_timeout 100ms;
55 memc_send_timeout 100ms;
56 memc_read_timeout 100ms;
57 set $memc_key $query_string;
58 set $memc_exptime 300;
59 memc_pass memcache;
60 }
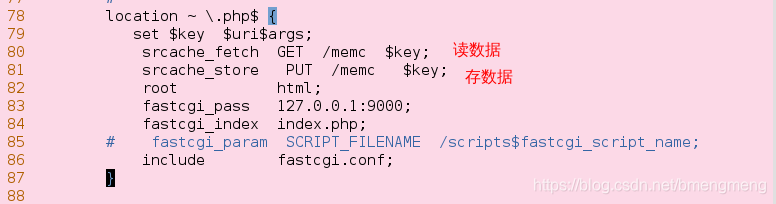
78 location ~ \.php$ {
79 set $key $uri$args;
80 srcache_fetch GET /memc $key;
81 srcache_store PUT /memc $key;
82 root html;
83 fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
84 fastcgi_index index.php;
85 # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
86 include fastcgi.conf;
87 }



-
配置文件详解
-
upstream属于handler,只是他不产生自己的内容,而是通过请求后端服务器得到内容,所以才称为upstream(上游)。请求并取得响应内容的整个过程已经被封装到nginx内部,所以upstream模块只需要开发若干回调函数,完成构造请求和解析响应等具体的工作。nginx将memcache缓存前移,客户端请求到来,先查看nginx缓存
-
所有请求都通过请求这个location来操作 memcache,memc-nginx-module存取memcache是基于http method语义的,
-
使用http的GET方法表示get、PUT方法表示set、这里我们将/memc设为internal表示只接受内部访问
-
不接收外部http请求,这是为了安全考虑,当然如果需要通过http协议开放外部访问,可以去掉internal然后使用deny和allow指令控制权限。比较重要的是memckey这个变量,它表示以什么作为key,这里我们直接使用Nginx内置的query_string来作为key,$memc_exptime表示缓存失效时间,以秒记。
-
这里统一设为300(5分钟),在实际应用中可以根据具体情况为不同的内容设置不同的过期时间。
-
为“~.php$”这个location配置了缓存,这表示所有以“.php”结尾的请求都会结果被缓存,当然这里只是示例需要,实际中一般不会这么配,而是为特定需要缓存的location配置缓存。
第三步:检测openresty配置文件是否有语法错误,并打开openstry
[root@hang1 conf]# /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
[root@hang1 conf]# /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx
少了一张启动服务的图,记得启动哦~

去浏览器访问:

这一步可做可不做:因为我没去浏览器访问,但是不影响什么
[root@hang1 conf]# pwd
/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf
[root@hang1 conf]# cd ../html/
[root@hang1 html]# ls
50x.html example.php index.html memcache.php
[root@hang1 html]# cp /usr/local/lnmp/nginx/html/memcache.php . #将之前的memcache文件复制到当前路径下
cp: overwrite `./memcache.php'? y
[root@hang1 html]#

第四步:压力测试


可以发现,相比上一篇博文中的一层缓存,再加一层缓存后,速度提高,且出错率都为0





 本文介绍了OpenResty,一个基于Nginx和Lua的高性能Web平台,用于构建高并发、高扩展性的动态Web应用。通过缓存前移,将缓存直接置于Nginx前端,提高了响应速度。文章详细阐述了如何关闭Nginx,编译OpenResty,以及如何配置OpenResty实现缓存前移,包括设置upstream、memcache缓存,并进行了压力测试验证效果。
本文介绍了OpenResty,一个基于Nginx和Lua的高性能Web平台,用于构建高并发、高扩展性的动态Web应用。通过缓存前移,将缓存直接置于Nginx前端,提高了响应速度。文章详细阐述了如何关闭Nginx,编译OpenResty,以及如何配置OpenResty实现缓存前移,包括设置upstream、memcache缓存,并进行了压力测试验证效果。
















 344
344

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








