我们从一个小的业务场景开始。
当一个springboot项目集成好Quartz框架之后,其前端界面如下:
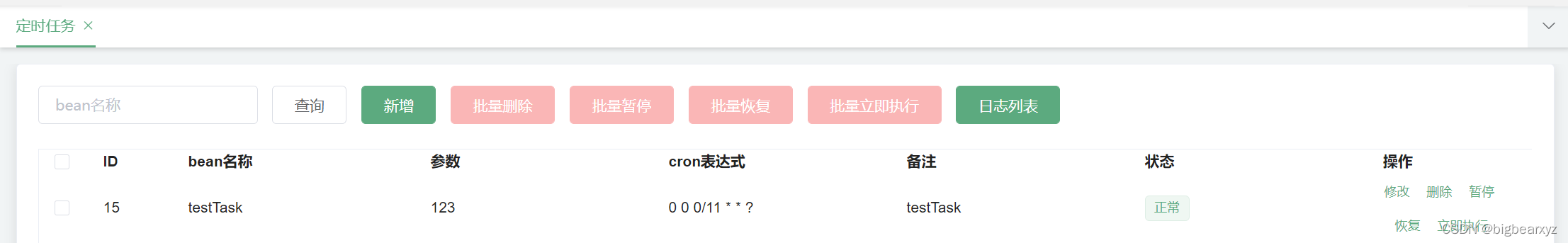
此时我们点击最右边的立即执行按钮,后台是如何执行的呢?
和我们平常的同步执行方法不同,这个方法其实是异步执行的。其核心原理就是,先把需要执行的任务信息持久化到数据库,再通过Quartz自带的后台线程查询数据库,获取需要执行的定时任务。
下面我们从源码开始分析:
点击上图的立即执行按钮之后,后台并不是直接调用testTask方法来执行任务,而是利用Quartz框架的Scheduler接口中的triggerJob方法来执行任务,具体代码如下:
/**
* 立即执行任务
*/
public static void run(Scheduler scheduler, ScheduleJobEntity scheduleJob) {
try {
//参数
JobDataMap dataMap = new JobDataMap();
dataMap.put(ScheduleJobEntity.JOB_PARAM_KEY, scheduleJob);
scheduler.triggerJob(getJobKey(scheduleJob.getJobId()), dataMap);
} catch (SchedulerException e) {
throw new GlobalException("立即执行定时任务失败", e);
}
}
public void triggerJob(JobKey jobKey, JobDataMap data) throws SchedulerException {
this.sched.triggerJob(jobKey, data);
}
我们进一步查看实现方法:
public void triggerJob(JobKey jobKey, JobDataMap data) throws SchedulerException {
this.validateState();
OperableTrigger trig = (OperableTrigger)TriggerBuilder.newTrigger().withIdentity(this.newTriggerId(), "DEFAULT").forJob(jobKey).build();
trig.computeFirstFireTime((Calendar)null);
if (data != null) {
trig.setJobDataMap(data);
}
boolean collision = true;
while(collision) {
try {
//1.持久化需要执行的job信息到数据库
this.resources.getJobStore().storeTrigger(trig, false);
collision = false;
} catch (ObjectAlreadyExistsException var6) {
trig.setKey(new TriggerKey(this.newTriggerId(), "DEFAULT"));
}
}
//2.通知Quartz的后台线程,执行定时任务
this.notifySchedulerThread(trig.getNextFireTime().getTime());
this.notifySchedulerListenersSchduled(trig);
}
此方法的核心便在于代码内注释的1、2两点注释,第一步持久化信息到数据库,之后再唤醒后台线程,执行前台传入的任务。
通过代码追踪,我们可以看到其详细的执行过程:
public void storeTrigger(final OperableTrigger newTrigger, final boolean replaceExisting) throws JobPersistenceException {
this.executeInLock(!this.isLockOnInsert() && !replaceExisting ? null : "TRIGGER_ACCESS", new JobStoreSupport.VoidTransactionCallback() {
public void executeVoid(Connection conn) throws JobPersistenceException {
JobStoreSupport.this.storeTrigger(conn, newTrigger, (JobDetail)null, replaceExisting, "WAITING", false, false);
}
});
}
protected void storeTrigger(Connection conn, OperableTrigger newTrigger, JobDetail job, boolean replaceExisting, String state, boolean forceState, boolean recovering) throws JobPersistenceException {
boolean existingTrigger = this.triggerExists(conn, newTrigger.getKey());
if (existingTrigger && !replaceExisting) {
throw new ObjectAlreadyExistsException(newTrigger);
} else {
try {
if (!forceState) {
boolean shouldBepaused = this.getDelegate().isTriggerGroupPaused(conn, newTrigger.getKey().getGroup());
if (!shouldBepaused) {
shouldBepaused = this.getDelegate().isTriggerGroupPaused(conn, "_$_ALL_GROUPS_PAUSED_$_");
if (shouldBepaused) {
this.getDelegate().insertPausedTriggerGroup(conn, newTrigger.getKey().getGroup());
}
}
if (shouldBepaused && (state.equals("WAITING") || state.equals("ACQUIRED"))) {
state = "PAUSED";
}
}
if (job == null) {
job = this.retrieveJob(conn, newTrigger.getJobKey());
}
if (job == null) {
throw new JobPersistenceException("The job (" + newTrigger.getJobKey() + ") referenced by the trigger does not exist.");
} else {
if (job.isConcurrentExectionDisallowed() && !recovering) {
state = this.checkBlockedState(conn, job.getKey(), state);
}
if (existingTrigger) {
//通过JDBC更新定时任务触发信息
this.getDelegate().updateTrigger(conn, newTrigger, state, job);
} else {
//通过JDBC插入定时任务触发信息
this.getDelegate().insertTrigger(conn, newTrigger, state, job);
}
}
} catch (Exception var10) {
throw new JobPersistenceException("Couldn't store trigger '" + newTrigger.getKey() + "' for '" + newTrigger.getJobKey() + "' job:" + var10.getMessage(), var10);
}
}
}
查看框架源码,很重要的一点便是抓住关键信息,这样才不会被源码绕晕,storeTrigger的关键信息便是其中的updateTrigger(conn, newTrigger, state, job)和insertTrigger(conn, newTrigger, state, job),这2个方法都是把触发信息通过JDBC写入到数据库。
依然可以通过代码追踪来验证,以updateTrigger为例,可见是标准的JDBC查询:
public int updateTrigger(Connection conn, OperableTrigger trigger, String state, JobDetail jobDetail) throws SQLException, IOException {
boolean updateJobData = trigger.getJobDataMap().isDirty();
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
if (updateJobData) {
baos = this.serializeJobData(trigger.getJobDataMap());
}
PreparedStatement ps = null;
boolean var8 = false;
int insertResult;
try {
if (updateJobData) {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(this.rtp("UPDATE {0}TRIGGERS SET JOB_NAME = ?, JOB_GROUP = ?, DESCRIPTION = ?, NEXT_FIRE_TIME = ?, PREV_FIRE_TIME = ?, TRIGGER_STATE = ?, TRIGGER_TYPE = ?, START_TIME = ?, END_TIME = ?, CALENDAR_NAME = ?, MISFIRE_INSTR = ?, PRIORITY = ?, JOB_DATA = ? WHERE SCHED_NAME = {1} AND TRIGGER_NAME = ? AND TRIGGER_GROUP = ?"));
} else {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(this.rtp("UPDATE {0}TRIGGERS SET JOB_NAME = ?, JOB_GROUP = ?, DESCRIPTION = ?, NEXT_FIRE_TIME = ?, PREV_FIRE_TIME = ?, TRIGGER_STATE = ?, TRIGGER_TYPE = ?, START_TIME = ?, END_TIME = ?, CALENDAR_NAME = ?, MISFIRE_INSTR = ?, PRIORITY = ? WHERE SCHED_NAME = {1} AND TRIGGER_NAME = ? AND TRIGGER_GROUP = ?"));
}
ps.setString(1, trigger.getJobKey().getName());
ps.setString(2, trigger.getJobKey().getGroup());
ps.setString(3, trigger.getDescription());
long nextFireTime = -1L;
if (trigger.getNextFireTime() != null) {
nextFireTime = trigger.getNextFireTime().getTime();
}
ps.setBigDecimal(4, new BigDecimal(String.valueOf(nextFireTime)));
long prevFireTime = -1L;
if (trigger.getPreviousFireTime() != null) {
prevFireTime = trigger.getPreviousFireTime().getTime();
}
ps.setBigDecimal(5, new BigDecimal(String.valueOf(prevFireTime)));
ps.setString(6, state);
TriggerPersistenceDelegate tDel = this.findTriggerPersistenceDelegate(trigger);
String type = "BLOB";
if (tDel != null) {
type = tDel.getHandledTriggerTypeDiscriminator();
}
ps.setString(7, type);
ps.setBigDecimal(8, new BigDecimal(String.valueOf(trigger.getStartTime().getTime())));
long endTime = 0L;
if (trigger.getEndTime() != null) {
endTime = trigger.getEndTime().getTime();
}
ps.setBigDecimal(9, new BigDecimal(String.valueOf(endTime)));
ps.setString(10, trigger.getCalendarName());
ps.setInt(11, trigger.getMisfireInstruction());
ps.setInt(12, trigger.getPriority());
if (updateJobData) {
this.setBytes(ps, 13, baos);
ps.setString(14, trigger.getKey().getName());
ps.setString(15, trigger.getKey().getGroup());
} else {
ps.setString(13, trigger.getKey().getName());
ps.setString(14, trigger.getKey().getGroup());
}
insertResult = ps.executeUpdate();
if (tDel == null) {
this.updateBlobTrigger(conn, trigger);
} else {
tDel.updateExtendedTriggerProperties(conn, trigger, state, jobDetail);
}
} finally {
closeStatement(ps);
}
return insertResult;
}
下面我们看持久化数据库之后,Quartz框架有做了什么,回到上面的triggerJob(JobKey jobKey, JobDataMap data)方法中,此时注释第一步执行完成,下面执行注释第二步,唤醒后台线程操作,执行this.notifySchedulerThread(trig.getNextFireTime().getTime())方法,通过代码追踪,最后进入到了QuartzSchedulerThread类中的signalSchedulingChange方法:
public void signalSchedulingChange(long candidateNewNextFireTime) {
synchronized(this.sigLock) {
this.signaled = true;
this.signaledNextFireTime = candidateNewNextFireTime;
//唤醒所有阻塞线程
this.sigLock.notifyAll();
}
}
以此来唤醒阻塞线程。
那么QuartzSchedulerThread类又是来干嘛的呢?
QuartzSchedulerThread就是我们前面提到的后台线程,Quartz框架在系统初始化时,便开始以while循环的形式使得QuartzSchedulerThread类中的run()方法一直运行,持续的扫描Quartz框架在数据库中生成的指定表,以triggers的形式来获取需要被执行的定时任务,如果扫描到triggers不为空,则通过线程池的方式来执行定时任务,以防止资源的过多消耗。
其具体代码实现如下(重点在注释1、2、3点):
public void run() {
int acquiresFailed = 0;
label228:
while(!this.halted.get()) {
try {
synchronized(this.sigLock) {
for(; this.paused && !this.halted.get(); acquiresFailed = 0) {
try {
this.sigLock.wait(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException var24) {
}
}
if (this.halted.get()) {
break;
}
}
if (acquiresFailed > 1) {
try {
long delay = computeDelayForRepeatedErrors(this.qsRsrcs.getJobStore(), acquiresFailed);
Thread.sleep(delay);
} catch (Exception var23) {
}
}
int availThreadCount = this.qsRsrcs.getThreadPool().blockForAvailableThreads();
if (availThreadCount > 0) {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.clearSignaledSchedulingChange();
//1.通过triggers判断是否有任务需要执行
List triggers;
try {
triggers = this.qsRsrcs.getJobStore().acquireNextTriggers(now + this.idleWaitTime, Math.min(availThreadCount, this.qsRsrcs.getMaxBatchSize()), this.qsRsrcs.getBatchTimeWindow());
acquiresFailed = 0;
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.log.debug("batch acquisition of " + (triggers == null ? 0 : triggers.size()) + " triggers");
}
} catch (JobPersistenceException var26) {
if (acquiresFailed == 0) {
this.qs.notifySchedulerListenersError("An error occurred while scanning for the next triggers to fire.", var26);
}
if (acquiresFailed < 2147483647) {
++acquiresFailed;
}
continue;
} catch (RuntimeException var27) {
if (acquiresFailed == 0) {
this.getLog().error("quartzSchedulerThreadLoop: RuntimeException " + var27.getMessage(), var27);
}
if (acquiresFailed < 2147483647) {
++acquiresFailed;
}
continue;
}
if (triggers != null && !triggers.isEmpty()) {
now = System.currentTimeMillis();
long triggerTime = ((OperableTrigger)triggers.get(0)).getNextFireTime().getTime();
for(long timeUntilTrigger = triggerTime - now; timeUntilTrigger > 2L; timeUntilTrigger = triggerTime - now) {
synchronized(this.sigLock) {
if (this.halted.get()) {
break;
}
if (!this.isCandidateNewTimeEarlierWithinReason(triggerTime, false)) {
try {
now = System.currentTimeMillis();
timeUntilTrigger = triggerTime - now;
if (timeUntilTrigger >= 1L) {
this.sigLock.wait(timeUntilTrigger);
}
} catch (InterruptedException var22) {
}
}
}
if (this.releaseIfScheduleChangedSignificantly(triggers, triggerTime)) {
break;
}
now = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
if (!triggers.isEmpty()) {
List<TriggerFiredResult> bndles = new ArrayList();
boolean goAhead = true;
synchronized(this.sigLock) {
goAhead = !this.halted.get();
}
if (goAhead) {
try {
List<TriggerFiredResult> res = this.qsRsrcs.getJobStore().triggersFired(triggers);
if (res != null) {
bndles = res;
}
} catch (SchedulerException var25) {
this.qs.notifySchedulerListenersError("An error occurred while firing triggers '" + triggers + "'", var25);
int i = 0;
while(true) {
if (i >= triggers.size()) {
continue label228;
}
this.qsRsrcs.getJobStore().releaseAcquiredTrigger((OperableTrigger)triggers.get(i));
++i;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < ((List)bndles).size(); ++i) {
TriggerFiredResult result = (TriggerFiredResult)((List)bndles).get(i);
TriggerFiredBundle bndle = result.getTriggerFiredBundle();
Exception exception = result.getException();
if (exception instanceof RuntimeException) {
this.getLog().error("RuntimeException while firing trigger " + triggers.get(i), exception);
this.qsRsrcs.getJobStore().releaseAcquiredTrigger((OperableTrigger)triggers.get(i));
} else if (bndle == null) {
this.qsRsrcs.getJobStore().releaseAcquiredTrigger((OperableTrigger)triggers.get(i));
} else {
JobRunShell shell = null;
try {
//2.初始化定时任务
shell = this.qsRsrcs.getJobRunShellFactory().createJobRunShell(bndle);
shell.initialize(this.qs);
} catch (SchedulerException var28) {
this.qsRsrcs.getJobStore().triggeredJobComplete((OperableTrigger)triggers.get(i), bndle.getJobDetail(), CompletedExecutionInstruction.SET_ALL_JOB_TRIGGERS_ERROR);
continue;
}
//3.以线程池的方式执行定时任务
if (!this.qsRsrcs.getThreadPool().runInThread(shell)) {
this.getLog().error("ThreadPool.runInThread() return false!");
this.qsRsrcs.getJobStore().triggeredJobComplete((OperableTrigger)triggers.get(i), bndle.getJobDetail(), CompletedExecutionInstruction.SET_ALL_JOB_TRIGGERS_ERROR);
}
}
}
}
} else {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
long waitTime = now + this.getRandomizedIdleWaitTime();
long timeUntilContinue = waitTime - now;
synchronized(this.sigLock) {
try {
if (!this.halted.get() && !this.isScheduleChanged()) {
this.sigLock.wait(timeUntilContinue);
}
} catch (InterruptedException var19) {
}
}
}
}
} catch (RuntimeException var31) {
this.getLog().error("Runtime error occurred in main trigger firing loop.", var31);
}
}
this.qs = null;
this.qsRsrcs = null;
}
从代码可以看出,真正的定时任务其实还是通过线程池来执行的,也就是执行的是线程池里面放的对象shell,我们关注的重点应该JobRunShell这个对象上面,我们可以看到JobRunShell是一个实现了Runnable接口的类,把它的实例化对象放在线程池中就会执行它的run()方法。
也就是真正的执行定时任务,具体代码如下:
public void run() {
this.qs.addInternalSchedulerListener(this);
try {
OperableTrigger trigger = (OperableTrigger)this.jec.getTrigger();
JobDetail jobDetail = this.jec.getJobDetail();
CompletedExecutionInstruction instCode;
label157:
while(true) {
while(true) {
JobExecutionException jobExEx = null;
Job job = this.jec.getJobInstance();
try {
this.begin();
} catch (SchedulerException var28) {
this.qs.notifySchedulerListenersError("Error executing Job (" + this.jec.getJobDetail().getKey() + ": couldn't begin execution.", var28);
return;
}
try {
if (!this.notifyListenersBeginning(this.jec)) {
return;
}
} catch (JobRunShell.VetoedException var27) {
try {
CompletedExecutionInstruction instCode = trigger.executionComplete(this.jec, (JobExecutionException)null);
this.qs.notifyJobStoreJobVetoed(trigger, jobDetail, instCode);
if (this.jec.getTrigger().getNextFireTime() == null) {
this.qs.notifySchedulerListenersFinalized(this.jec.getTrigger());
}
this.complete(true);
} catch (SchedulerException var22) {
this.qs.notifySchedulerListenersError("Error during veto of Job (" + this.jec.getJobDetail().getKey() + ": couldn't finalize execution.", var22);
}
return;
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long endTime;
try {
this.log.debug("Calling execute on job " + jobDetail.getKey());
//执行定时任务
job.execute(this.jec);
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
} catch (JobExecutionException var25) {
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
jobExEx = var25;
this.getLog().info("Job " + jobDetail.getKey() + " threw a JobExecutionException: ", var25);
} catch (Throwable var26) {
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.getLog().error("Job " + jobDetail.getKey() + " threw an unhandled Exception: ", var26);
SchedulerException se = new SchedulerException("Job threw an unhandled exception.", var26);
this.qs.notifySchedulerListenersError("Job (" + this.jec.getJobDetail().getKey() + " threw an exception.", se);
jobExEx = new JobExecutionException(se, false);
}
this.jec.setJobRunTime(endTime - startTime);
if (!this.notifyJobListenersComplete(this.jec, jobExEx)) {
return;
}
instCode = CompletedExecutionInstruction.NOOP;
try {
instCode = trigger.executionComplete(this.jec, jobExEx);
} catch (Exception var24) {
SchedulerException se = new SchedulerException("Trigger threw an unhandled exception.", var24);
this.qs.notifySchedulerListenersError("Please report this error to the Quartz developers.", se);
}
if (!this.notifyTriggerListenersComplete(this.jec, instCode)) {
return;
}
if (instCode != CompletedExecutionInstruction.RE_EXECUTE_JOB) {
try {
this.complete(true);
break label157;
} catch (SchedulerException var29) {
this.qs.notifySchedulerListenersError("Error executing Job (" + this.jec.getJobDetail().getKey() + ": couldn't finalize execution.", var29);
}
} else {
this.jec.incrementRefireCount();
try {
this.complete(false);
} catch (SchedulerException var23) {
this.qs.notifySchedulerListenersError("Error executing Job (" + this.jec.getJobDetail().getKey() + ": couldn't finalize execution.", var23);
}
}
}
}
this.qs.notifyJobStoreJobComplete(trigger, jobDetail, instCode);
} finally {
this.qs.removeInternalSchedulerListener(this);
}
}
可以看到就是通过job.execute(this.jec)这个方法来执行定时任务的。
从execute方法进去,我们可以看到:
public abstract class QuartzJobBean implements Job {
public QuartzJobBean() {
}
public final void execute(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
MutablePropertyValues pvs = new MutablePropertyValues();
pvs.addPropertyValues(context.getScheduler().getContext());
pvs.addPropertyValues(context.getMergedJobDataMap());
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
} catch (SchedulerException var4) {
throw new JobExecutionException(var4);
}
//抽象方法,可以自定义实现job信息
this.executeInternal(context);
}
protected abstract void executeInternal(JobExecutionContext var1) throws JobExecutionException;
}
在抽象类QuartzJobBean中的抽象方法executeInternal(),我们可以在系统中自定义实现,以完成定时任务的某些自定义功能,比如发送日志存储:
public class ScheduleJob extends QuartzJobBean {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Override
protected void executeInternal(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException {
ScheduleJobEntity scheduleJob = (ScheduleJobEntity) context.getMergedJobDataMap()
.get(ScheduleJobEntity.JOB_PARAM_KEY);
//获取spring bean
ScheduleJobLogService scheduleJobLogService = (ScheduleJobLogService) SpringContextUtils.getBean("scheduleJobLogService");
//数据库保存执行记录
ScheduleJobLogEntity log = new ScheduleJobLogEntity();
log.setJobId(scheduleJob.getJobId());
log.setBeanName(scheduleJob.getBeanName());
log.setParams(scheduleJob.getParams());
log.setCreateTime(new Date());
//任务开始时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
扩展:
上文中我们提到了Quartz框架的后台线程和线程池,那么这2个对象是如何初始化的呢?
其原理是利用了StdSchedulerFactory的Spring生命周期中的后置处理器,初始化了后台线程和线程池。具体信息如下:
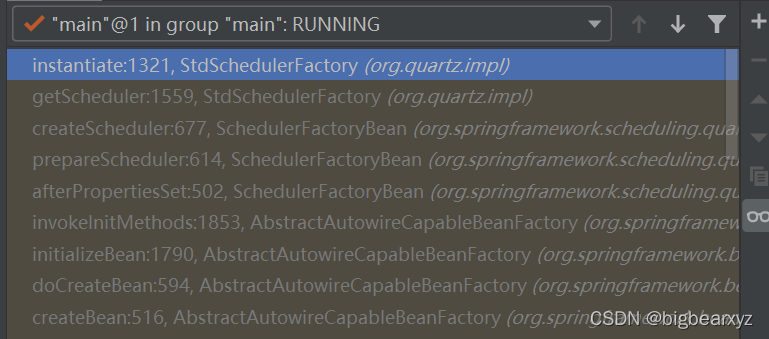
在StdSchedulerFactory执行initializeBean的过程中,通过调用StdSchedulerFactory类中的instantiate()方法,调用了下图中的tp.initialize()和qs = new QuartzScheduler(rsrcs, idleWaitTime, dbFailureRetry)两个方法,分别是线程池初始化和后台线程初始化:
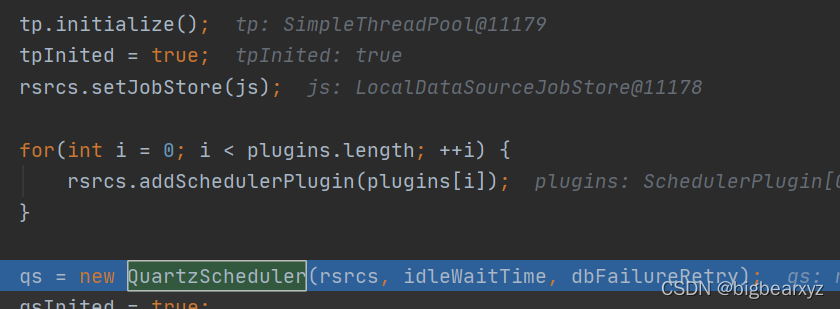
其具体代码如下,初始化线程池:
public void initialize() throws SchedulerConfigException {
if (this.workers == null || this.workers.size() <= 0) {
if (this.count <= 0) {
throw new SchedulerConfigException("Thread count must be > 0");
} else if (this.prio > 0 && this.prio <= 9) {
if (this.isThreadsInheritGroupOfInitializingThread()) {
this.threadGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
} else {
this.threadGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
ThreadGroup parent;
for(parent = this.threadGroup; !parent.getName().equals("main"); parent = this.threadGroup.getParent()) {
this.threadGroup = parent;
}
this.threadGroup = new ThreadGroup(parent, this.schedulerInstanceName + "-SimpleThreadPool");
if (this.isMakeThreadsDaemons()) {
this.threadGroup.setDaemon(true);
}
}
if (this.isThreadsInheritContextClassLoaderOfInitializingThread()) {
this.getLog().info("Job execution threads will use class loader of thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
Iterator workerThreads = this.createWorkerThreads(this.count).iterator();
while(workerThreads.hasNext()) {
//初始化线程池,保持运行
SimpleThreadPool.WorkerThread wt = (SimpleThreadPool.WorkerThread)workerThreads.next();
wt.start();
this.availWorkers.add(wt);
}
} else {
throw new SchedulerConfigException("Thread priority must be > 0 and <= 9");
}
}
}
初始化后台线程,也就是 new QuartzSchedulerThread(this, resources):
public QuartzScheduler(QuartzSchedulerResources resources, long idleWaitTime, @Deprecated long dbRetryInterval) throws SchedulerException {
this.resources = resources;
if (resources.getJobStore() instanceof JobListener) {
this.addInternalJobListener((JobListener)resources.getJobStore());
}
this.schedThread = new QuartzSchedulerThread(this, resources);
ThreadExecutor schedThreadExecutor = resources.getThreadExecutor();
schedThreadExecutor.execute(this.schedThread);
if (idleWaitTime > 0L) {
this.schedThread.setIdleWaitTime(idleWaitTime);
}
this.jobMgr = new ExecutingJobsManager();
this.addInternalJobListener(this.jobMgr);
this.errLogger = new ErrorLogger();
this.addInternalSchedulerListener(this.errLogger);
this.signaler = new SchedulerSignalerImpl(this, this.schedThread);
this.getLog().info("Quartz Scheduler v." + this.getVersion() + " created.");
}
结论:
可以看到Quartz框架的线程池的执行效率是存在问题的,比如初始化了20个线程,这20个线程是一直被占用的,会造成服务器资源的浪费。比较好的解决方案是现在常用的使用阻塞队列的形式来构造线程池,如果任务不多,只保留少数几个线程,如果有需要再对线程进行扩容。





 本文详细剖析了Quartz框架在SpringBoot项目中的应用,解释了点击“立即执行”按钮后,后台如何通过异步方式执行任务。核心原理包括将任务信息持久化到数据库,然后唤醒后台线程执行任务。文章深入源码,展示了任务调度的全过程,包括QuartzSchedulerThread的运行机制、线程池的初始化以及Job的执行流程。同时,指出了Quartz线程池可能存在的资源浪费问题,并提出了使用阻塞队列优化的建议。
本文详细剖析了Quartz框架在SpringBoot项目中的应用,解释了点击“立即执行”按钮后,后台如何通过异步方式执行任务。核心原理包括将任务信息持久化到数据库,然后唤醒后台线程执行任务。文章深入源码,展示了任务调度的全过程,包括QuartzSchedulerThread的运行机制、线程池的初始化以及Job的执行流程。同时,指出了Quartz线程池可能存在的资源浪费问题,并提出了使用阻塞队列优化的建议。
















 290
290

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








