Python中的字符串是非常常见且强大的数据类型之一.掌握其基本操作是每个Python开发者的必修课.下面我们将Python字符串的常用操作分为几个主要类别,帮助你更系统地了解和使用字符串.
1. 字符串定义和初始化
在Python中,字符串可以使用单引号(')、双引号(")或三引号(''' 或 """)来定义.
# 单引号和双引号
string1 = 'Hello'
string2 = "Python"
# 三引号用于多行字符串
multi_line_string = '''This is a
multi-line string'''
2. 字符串访问与切片
Python允许我们通过索引和切片访问字符串中的字符.字符串的索引从0开始,负数索引从后向前访问.
text = "Hello, Python!"
# 访问字符
print(text[0]) # 输出 'H'
print(text[-1]) # 输出 '!'
# 切片操作
print(text[0:5]) # 输出 'Hello'
print(text[:5]) # 输出 'Hello'
print(text[7:]) # 输出 'Python!'
3. 字符串拼接与重复
字符串拼接可以通过+操作符来完成,重复则使用*操作符.
text = "Hello"
# 拼接
new_text = text + ", Python!"
print(new_text) # 输出 'Hello, Python!'
# 重复
repeat_text = "Python! " * 3
print(repeat_text) # 输出 'Python! Python! Python! '
4. 字符串长度与判断
通过len()可以获得字符串的长度,startswith()和endswith()可以用来判断字符串的开始和结束部分.
text = "Hello, Python!"
# 获取字符串长度
print(len(text)) # 输出 15
# 判断字符串是否以某个字符开始或结束
print(text.startswith("Hello")) # 输出 True
print(text.endswith("Python!")) # 输出 True
5. 字符串查找与替换
通过find()、index()和replace()来查找和替换字符串中的内容.
text = "Hello, Python!"
# 查找子字符串
print(text.find("Python")) # 输出 7 (位置索引)
print(text.index("Python")) # 输出 7 (位置索引)
# 替换子字符串
new_text = text.replace("Python", "World")
print(new_text) # 输出 'Hello, World!'
6. 字符串大小写转换
Python提供了多种方法来转换字符串的大小写,lower()、upper()、title()等方法能够快速改变字符串的形式.
text = "hello, python!"
# 转换为小写
print(text.lower()) # 输出 'hello, python!'
# 转换为大写
print(text.upper()) # 输出 'HELLO, PYTHON!'
# 首字母大写
print(text.title()) # 输出 'Hello, Python!'
7. 去除空白字符
可以使用strip()、lstrip()、rstrip()去除字符串两端或一侧的空白字符.
text = " Hello, Python! "
# 去除两端空白
print(text.strip()) # 输出 'Hello, Python!'
# 去除左侧空白
print(text.lstrip()) # 输出 'Hello, Python! '
# 去除右侧空白
print(text.rstrip()) # 输出 ' Hello, Python!'
8. 字符串分割与连接
split()方法将字符串分割成多个部分,返回一个列表,而join()可以将列表中的元素连接成字符串.
text = "Hello, Python, World"
# 分割字符串
words = text.split(", ")
print(words) # 输出 ['Hello', 'Python', 'World']
# 连接列表元素
joined_text = " ".join(words)
print(joined_text) # 输出 'Hello Python World'
9. 字符串格式化
Python提供了三种常用的字符串格式化方式:f-string(推荐),str.format()和百分号格式化.
name = "Alice"
age = 25
# f-string(推荐方式)
formatted_text = f"My name is {name} and I am {age} years old."
print(formatted_text) # 输出 'My name is Alice and I am 25 years old.'
# str.format()
formatted_text = "My name is {} and I am {} years old.".format(name, age)
print(formatted_text) # 输出 'My name is Alice and I am 25 years old.'
10. 检查字符串内容
使用isalnum()、isalpha()、isdigit()等方法检查字符串的内容是否符合特定条件.
text = "Hello123"
# 判断是否为字母和数字组成
print(text.isalnum()) # 输出 True
# 判断是否全是字母
print(text.isalpha()) # 输出 False
# 判断是否全是数字
print(text.isdigit()) # 输出 False
11. 转义字符
在Python中,转义字符以反斜杠(\)开始,用于表示一些特殊字符,如换行符、制表符等.
text = "Hello\nPython!" # \n 表示换行
print(text)
text = "Hello\tPython!" # \t 表示制表符
print(text)
12. 多行字符串
使用三引号('''或""")可以定义多行字符串,适用于文档字符串或较长的文本.
multi_line_text = """This is a
multi-line string
in Python."""
print(multi_line_text)
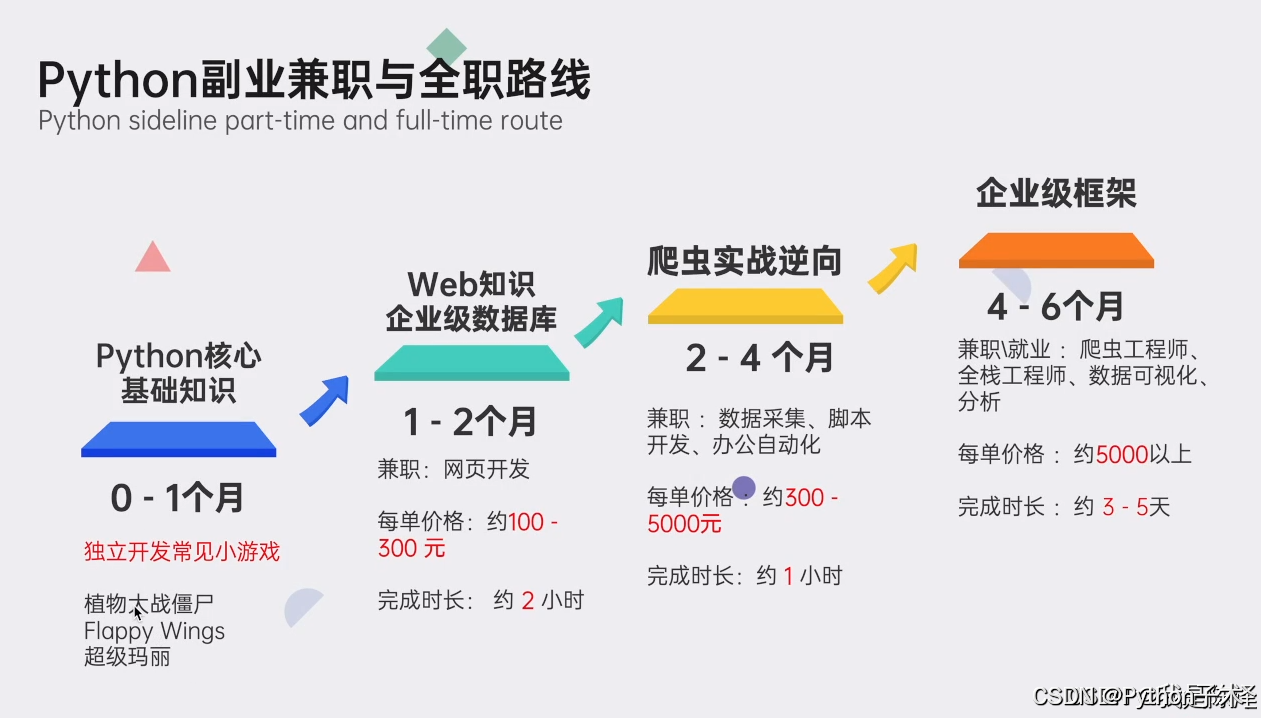
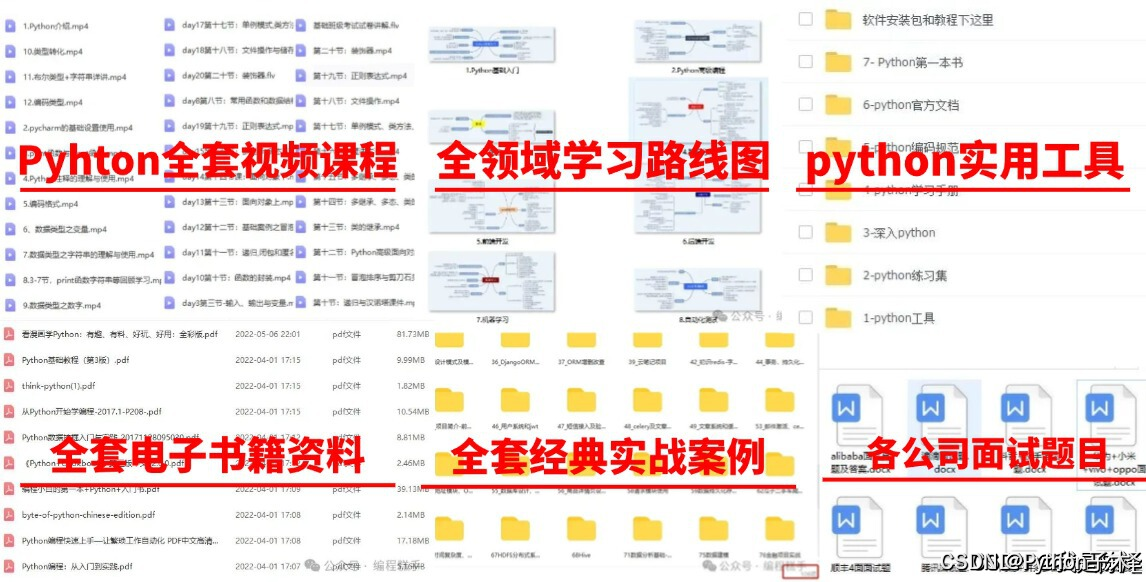
最后,我精心筹备了一份全面的Python学习大礼包,完全免费分享给每一位渴望成长、希望突破自我现状却略感迷茫的朋友。无论您是编程新手还是希望深化技能的开发者,都欢迎加入我们的学习之旅,共同交流进步!
🌟 学习大礼包包含内容:
Python全领域学习路线图:一目了然,指引您从基础到进阶,再到专业领域的每一步学习路径,明确各方向的核心知识点。
超百节Python精品视频课程:涵盖Python编程的必备基础知识、高效爬虫技术、以及深入的数据分析技能,让您技能全面升级。
实战案例集锦:精选超过100个实战项目案例,从理论到实践,让您在解决实际问题的过程中,深化理解,提升编程能力。
华为独家Python漫画教程:创新学习方式,以轻松幽默的漫画形式,让您随时随地,利用碎片时间也能高效学习Python。
互联网企业Python面试真题集:精选历年知名互联网企业面试真题,助您提前备战,面试准备更充分,职场晋升更顺利。
👉 立即领取方式:只需【点击这里】,即刻解锁您的Python学习新篇章!让我们携手并进,在编程的海洋里探索无限可能
 10分钟盘点Python基础字符串操作
10分钟盘点Python基础字符串操作
























 1189
1189

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








