1 Map<K ,V>集合:与Collection接口不同的是,每次存储的都是一对元素,也就是
K(key键)和V(value值)这一对,他们之间的关系称之为映射。
映射的规则:键是唯一的,值可以重复,但是一个键只能对应一个值。
2Map接口的常用实现类:
1HashMap<K,V>集合:底层是哈希表,查询快,无序的,多线程,不安全,可存储null
1.1 LinkedHashMap<K.V>:底层是哈希表+链表,保证迭代元素有序
2 Hashtable<K,V>:是一个线程安全的集合,单线程,速度较慢,不能存储空值空键
2.1 Properties:唯一和io流相结合的集合
3Map接口中的常用方法:
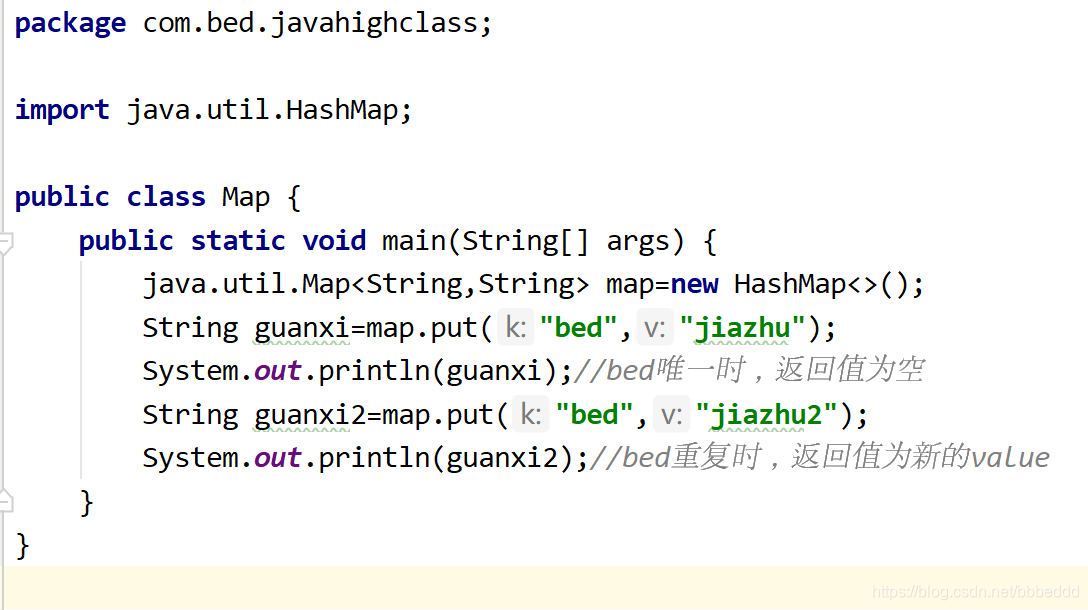
1public v put(K key,V value):把指定的键与值添加到Map集合中
注意:如果key只有一个 返回值V为null,如果key重复,会用新的value值替换旧的
value值并返回。
2 public V remove(Object key):把指定的键所对应的键值对从,Map集合中删除
3 public V get(Object key):key存在的话 返回对应的value值
4 boolean containsKey(Object Key):判断集合中是否包含指定的键
5 List<E> of (a,,b,c,d......):给集合一次性添加多个元素(List Set Map都可使用)。
使用前提:集合中存储元素个数已经确定,不再改变
使用注意事项:1该方法只适用于List Set Map接口,不适用接口的实现类
2 of方法的返回值也是一个不能改变的集合,不能再添加元素
3 Set和Map接口在使用of方法时,不能有重复元素
4Map集合的遍历:
第一种方法keySet:先将Map集合中的key通过keySet()方法,全部放入一个Set集合中,
然后遍历这个Set集合,最后通过map.get方法将对应的value也找出来。

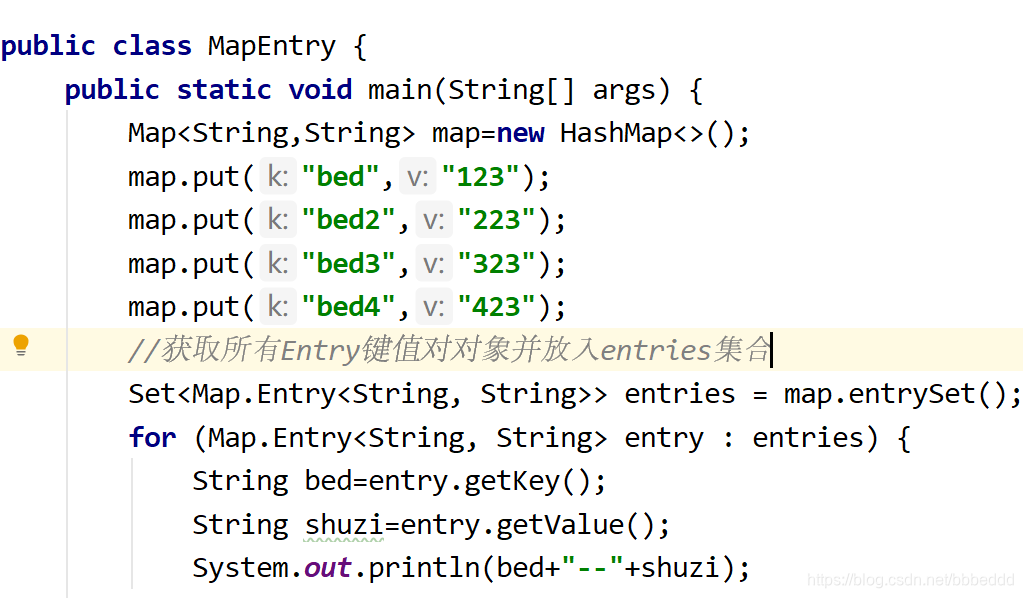
第二种方法:Set<Map.Entry<K,V>>:Entry就是k与value结合的证明。称为“键值对对象”
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>>将这个Entry证明存储到一个Set集合中,然后遍历Set集
合。然后再通过Entey对象中的两个方法Entry.getKey()和Entry.getValue
获取key和value
5HashMap存储自定义类型的键值:因为Map中的键不能重复,所以注意在自定义类作为键值
出现时,要重写hashCode和equals方法
案例1:计算输入的字符串中 每个字符的个数
package com.bed.javahighclass;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CharacterCount {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入");
String str=sc.next();
char[] strings=str.toCharArray();//将输入的字符串转换成字符组
HashMap<Character,Integer> map=new HashMap();//建立一个HashMap集合用来接收结果
for (char c : strings) {
if (map.containsKey(c)){
//如果map集合中已经有该字符c,那么让c对应的value值+1
Integer value=map.get(c);
value++;
map.put(c,value);
}else{//如果该字符是头一次出现
map.put(c,1);
}
}
System.out.println(map);
}
}
6程序的debug:让程序逐行执行,检查每行的运行结果。认识每个按钮的功能即可。
案例:斗地主发牌有序排列
package com.bed.javahighclass;
import java.sql.ClientInfoStatus;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
public class DouDiZhuIndex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, String> poker = new HashMap<>();//用来存放牌的主集合,前面是索引,后面是花色
ArrayList<Integer> pokerindex = new ArrayList<>();//单独拿出一个存放索引的集合
List<String> huase = List.of("♥", "♠", "♦", "♣");
List<String> numbers = List.of("2", "A", "K", "Q", "J", "10", "9", "8", "7", "6", "5", "4", "3");
//在总集合与索引中添加大王小王和对应的索引值
int index = 0;
poker.put(index, "大王");//大王index是0
pokerindex.add(index);
index++;
poker.put(index, "小王");//小王index是1
pokerindex.add(index);
//组装牌,装进poker总集合和索引集合中。此处按照16行的大小顺序进行组装
for (String number : numbers) {
for (String s : huase) {
index++;
pokerindex.add(index);
poker.put(index, s + number);//♥2index是3
}
}
System.out.println(pokerindex);
System.out.println(poker);
System.out.println("===========================");
Collections.shuffle(pokerindex);//洗牌
//发牌,准确的说是发牌的索引给每个玩家
ArrayList<Integer> player01 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> player02 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> player03 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> dipai = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <pokerindex.size(); i++) {
if (i >= 51) {
dipai.add(pokerindex.get(i));
} else if (i % 3 == 0) {
player01.add(pokerindex.get(i));
} else if (i % 3 == 1) {
player02.add(pokerindex.get(i));
} else if (i % 3 == 2) {
player03.add(pokerindex.get(i));
}
}
//将玩家手中的牌进行排序
Collections.sort(player01);
Collections.sort(player02);
Collections.sort(player03);
Collections.sort(dipai);
//调用pokershow方法
pokershow(poker,player01);
pokershow(poker,player02);
pokershow(poker,player03);
pokershow(poker,dipai);
}
//定义一个方法,将牌的总集合与玩家索引传进去,给每个玩家发牌并显示出来
public static void pokershow(HashMap<Integer, String> poker,ArrayList<Integer> List){
for (Integer key : List) {
String s = poker.get(key);//索引值对应的键值
System.out.print(s+" ");
}
System.out.println("");
}
}




 本文介绍了Java中的Map集合,包括其映射规则和常用实现类如HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap等。详细讲解了Map接口的方法,如put、remove、get等,并提到了Map集合的遍历方式。此外,还讨论了自定义类型作为键值时重写hashCode和equals方法的重要性,以及提供了一个计算字符串中字符个数的案例。
本文介绍了Java中的Map集合,包括其映射规则和常用实现类如HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap等。详细讲解了Map接口的方法,如put、remove、get等,并提到了Map集合的遍历方式。此外,还讨论了自定义类型作为键值时重写hashCode和equals方法的重要性,以及提供了一个计算字符串中字符个数的案例。
















 937
937

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








