C++内存越界导致的std::map异常
前段时间在定位一个程序崩溃的问题,虽然有dump文件,能够看到出问题的具体代码行数,问题都出在同一个map上。
dump1显示map下标插入数据时异常。

dump2显示调用map的clear函数异常。
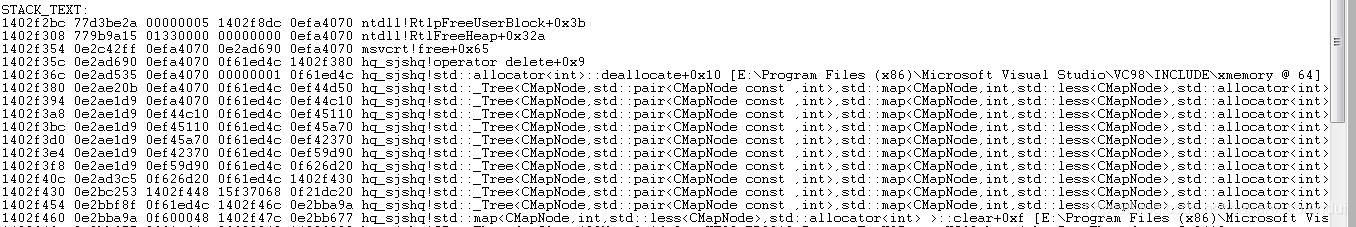
刚开始看到这两个dump,以为是多线程导致的访问冲突,看具体的代码发现对这个map的插入和删除操作是在同一个线程中的,所以排除这个可能,这时想到了另一种情况:程序中其他地方内存异常导致的程序崩溃,虽然表现在这个map对象处,但实际并不是由map引起的。因此对这个map对象所在类的所有成员变量进行一个个地排查,着重看char数组是否在调用strcpy或者memcpy时存在越界的情况,最终发现果真有一处数组越界,代码简单描述如下
char m_cXXLastUpdateTime[13];
char cLastUpdateTime[32];
memcpy(m_cXXLastUpdateTime, cLastUpdateTime, sizeof(cLastUpdateTime));
m_cXXLastUpdateTime是成员变量,它的大小只有13个字节,但是在调用memcpy赋值时,却拷贝了sizeof(cLastUpdateTime)=32个字节的大小,那么就会将m_cXXLastUpdateTime地址后面的19位全部覆盖,当在程序的其他地方使用到这个地址的变量时,就会出现Access violation,问题解决了。解决这个问题的过程是比较痛苦的,因为碰上这种程序中其他地方内存越界引起的内存破坏问题,通过分析dump文件并不能准确定位到具体原因,只能一行一行地分析代码,所以我们平常写代码对数组的赋值要格外小心。
下面以一个简单地例子来复现上述场景,例子代码如下:
#include <string>
class CheckDbf
{
public:
CheckDbf()
{
memset(szTime, 0, sizeof(szTime));
memset(szText, 0, sizeof(szText));
}
~CheckDbf()
{
}
public:
char szTime[13];
char szText[5];
};
int main()
{
char szBuf[32] = { 0 };
sprintf(szBuf, "20190613");
CheckDbf dbf;
sprintf(dbf.szText, "1234");
int nSize = sizeof(dbf);
memcpy(dbf.szTime, szBuf, sizeof(szBuf));
return 0;
}
调试该代码,查看dbf对象的成员变量内存:
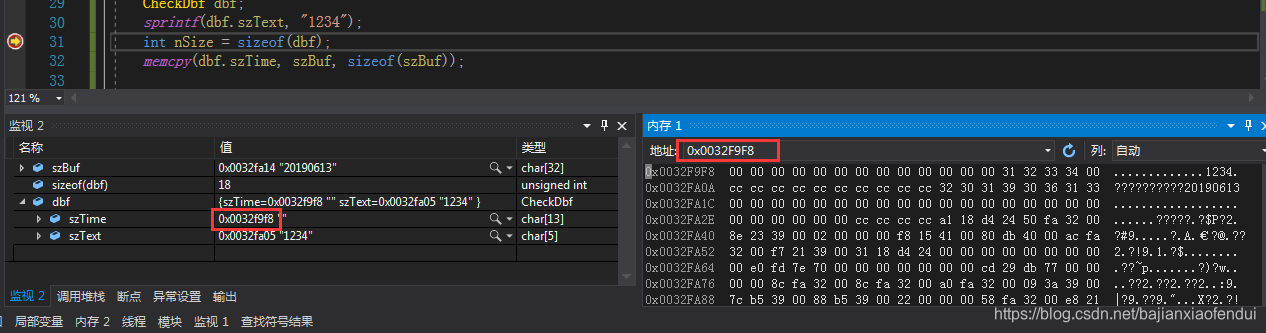 可以看到sizeof(dbf)=18,前面的13个字节为空是szTime的内容,后面的5个字节是szText的内容,ACSII码刚好是31 32 33 34 00,放开断点,走完memcpy函数,再看内存:
可以看到sizeof(dbf)=18,前面的13个字节为空是szTime的内容,后面的5个字节是szText的内容,ACSII码刚好是31 32 33 34 00,放开断点,走完memcpy函数,再看内存:
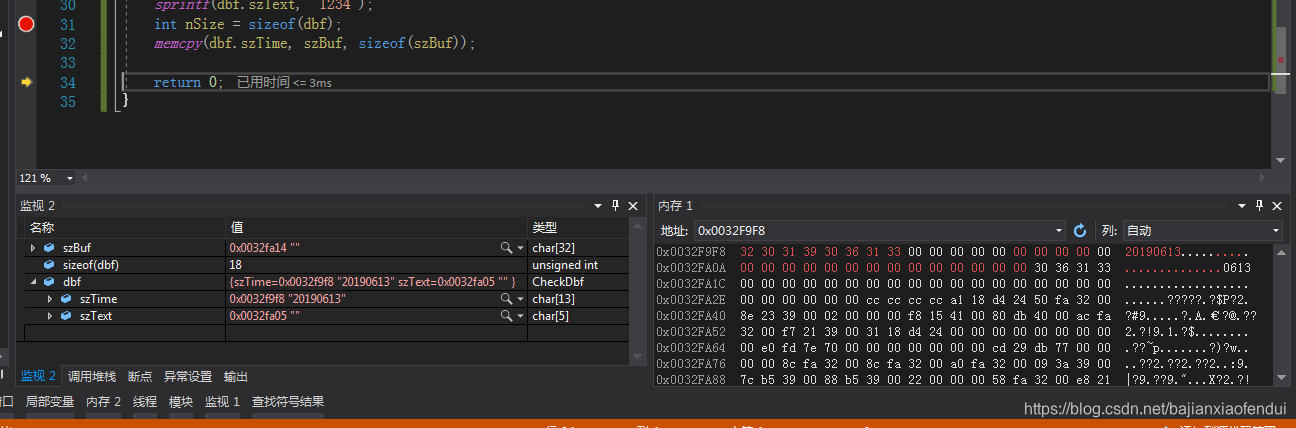
dbf对象的前面的13个字节和是szTime,并且是我们赋值的内容“20190613”,但是接下来的5个字节却全变了,因为被覆盖了,此时如果我们再访问szText并调用一些string函数,则会导致程序崩溃。将szText换成std::map成员变量也是一样的效果。
谨记:
1,memcpy时,拷贝的大小不要越界。
2,strcpy不要使用,改用strncpy,同样,拷贝的大小一定不要越界。





 本文深入分析了一起因C++中memcpy函数使用不当导致的内存越界问题,详细描述了如何通过代码审查定位并修复由内存破坏引发的std::map异常,强调了正确使用内存操作函数的重要性。
本文深入分析了一起因C++中memcpy函数使用不当导致的内存越界问题,详细描述了如何通过代码审查定位并修复由内存破坏引发的std::map异常,强调了正确使用内存操作函数的重要性。

















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










