目录
一、Map的概念和使用
1.什么是Map
Map不同于set,Map是一个接口,不能被实例化(如果需要实例化要实现TreeMap和HashMap)
Map类没有继承与Collection中,而是一个单独的键值对由<K,V>组成,并且K是唯一的不能被重复,如果添加的K重复,那么就会修改V中的值。但是map中的key不能被修改,如果需要修改请删除后重新加入
在Map中插入键值堆时,Key不能为空,value可以为空
Map中的Key和Value都可以被分离出来
2.对于Map遍历的使用
对于Map的遍历我们需要使用到Map.Entry<K,V>来进行遍历
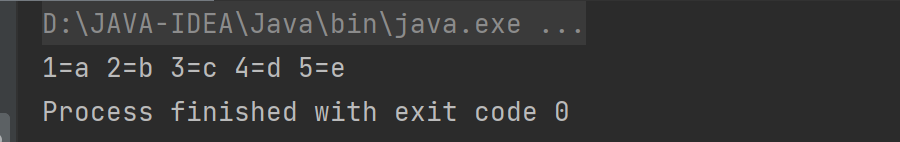
对于整体进行遍历:(entry)
for(Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry:map.entrySet()){
System.out.print(entry+" ");
}
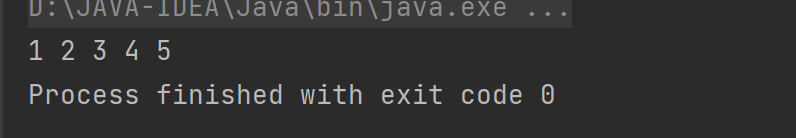
对于key进行遍历:(entry.getKey())
for(Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry:map.entrySet()){
System.out.print(entry.getKey()+" ");
}
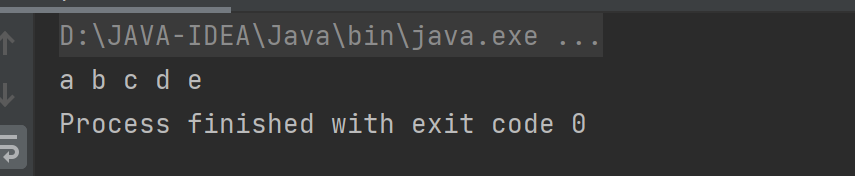
对于value进行遍历:(entry.getValue())
for(Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry:map.entrySet()){
System.out.print(entry.getValue()+" ");
}
3.Map常见方法的使用
| 方法 | 用法 |
| V get(Object key) | 返回key中对应的value |
| V getOrDefault(Object key,V defaultValue) | 返回key中对应的value,不存在返回defaultValue |
| V put(K key,V value) | 添加相应的键值对放入map中 |
| V remove(Object key) | 删除key以及相对应的映射关系 |
| Set<K> keySet() | 返回所有key的集合 |
| Collection<V> values() | 返回所有value的集合 |
| Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() | 返回所有的映射关系 |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | 判断是否包含key |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | 判断是否包含value |
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer,String> map=new HashMap<>();
//添加put
map.put(1,"a");
map.put(2,"b");
map.put(3,"c");
map.put(4,"d");
map.put(5,"e");
//get方法
System.out.println(map.get(1));//a
//getOrDefault方法
System.out.println(map.getOrDefault(1, "qwe"));//a
System.out.println(map.getOrDefault(10, "qwe"));//qwe
//remove删除
System.out.println(map.remove(1));//a
System.out.println(map.remove(10));//null
//keySet方法
Set<Integer> set=map.keySet();
//values方法(单独赋值)
Collection<String> list= map.values();
//判断包含关系
System.out.println(map.containsKey(1));//false
System.out.println(map.containsValue("a"));//flase
}注意:TreeMap和HashMap的区别。
| Map比较 | TreeMap | HashMap |
| 底层结构 | 红黑树 | 哈希桶 |
| 时间复杂度 | O(logN) | O(1) |
| 是否有序 | 关于Key有序 | 无序 |
| 线程安全 | 不安全 | 不安全 |
| 增删改查 | 需要进行元素的比较 | 通过哈希函数计算哈希地址在比较 |
| 比较与覆写 | Key必须可以比较 | 自定义需要重写equals方法和hashCode方法 |
| 应用场景 | 需要key有序 | 需要更高的时间性能 |
当哈希桶中的数组大于64,单链表大于8时,就会变成红黑树。
4、哈希表
4.1、哈希表的概念
相较于普通的顺序结构和平衡树的搜索效率,哈希表可以通过一一对应的关系,快速的查找到当前元素。
我们通过哈希函数实现:hash(key)=key%(数组长度)。
例如:我们插入一组数据(1,3,9,5,7)
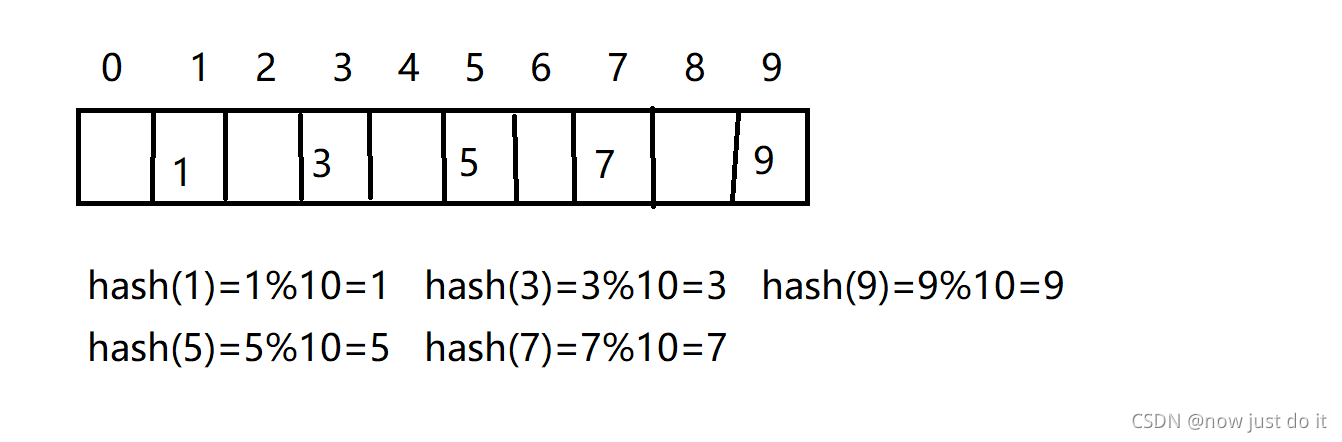
这样我们就快速的将数组插入到相应的位置,查找时通过哈希函数调用出来就行了,但是当哈希函数得到的两个值相同会怎么办?
4.2、哈希冲突
当使用不同关键字通过哈希函数计算出相同的哈希地址,这种现象我们称之为哈希冲突。
对于解决哈希冲突我们可以采用下图的方法:
对于避免哈希冲突:
设计哈希函数,我们采用可以采用的方法有:
1. 直接定制法
取关键字的某个线性函数为散列地址:Hash(Key)= A*Key + B 优点:简单、均匀 缺点:需要事先知道关键字的分布情况
2. 除留余数法
设散列表中允许的地址数为m,取一个不大于m,但最接近或者等于m的质数p作为除数,按照哈希函数:Hash(key) = key% p(p<=m),将关键码转换成哈希地址
3. 平方取中法
假设关键字为1234,对它平方就是1522756,抽取中间的3位227作为哈希地址; 再比如关键字为4321,对它平方就是18671041,抽取中间的3位671(或710)作为哈希地址 平方取中法比较适合:不知道关键字的分布,而位数又不是很大的情况
4. 折叠法
折叠法是将关键字从左到右分割成位数相等的几部分(最后一部分位数可以短些),然后将这几部分叠加求和,并按散列表表长,取后几位作为散列地址。折叠法适合事先不需要知道关键字的分布,适合关键字位数比较多的情况
5. 随机数法
选择一个随机函数,取关键字的随机函数值为它的哈希地址,即H(key) = random(key),其中random为随机数函数。
6. 数学分析法
设有n个d位数,每一位可能有r种不同的符号,这r种不同的符号在各位上出现的频率不一定相同,可能在某些位上分布比较均匀,每种符号出现的机会均等,在某些位上分布不均匀只有某几种符号经常出现。可根据散列表的大小,选择其中各种符号分布均匀的若干位作为散列地址。
哈希因子:
散列表的载荷因子为:a=填入表中的元素个数/散列表的长度。
当我们填入的个数大于载荷因子时,我们需要调节哈希表的大小,对数组进行扩容。
解决哈希冲突:
解决哈希冲突的方法有两种:闭散列和开散列
闭散列:
1、线性探测
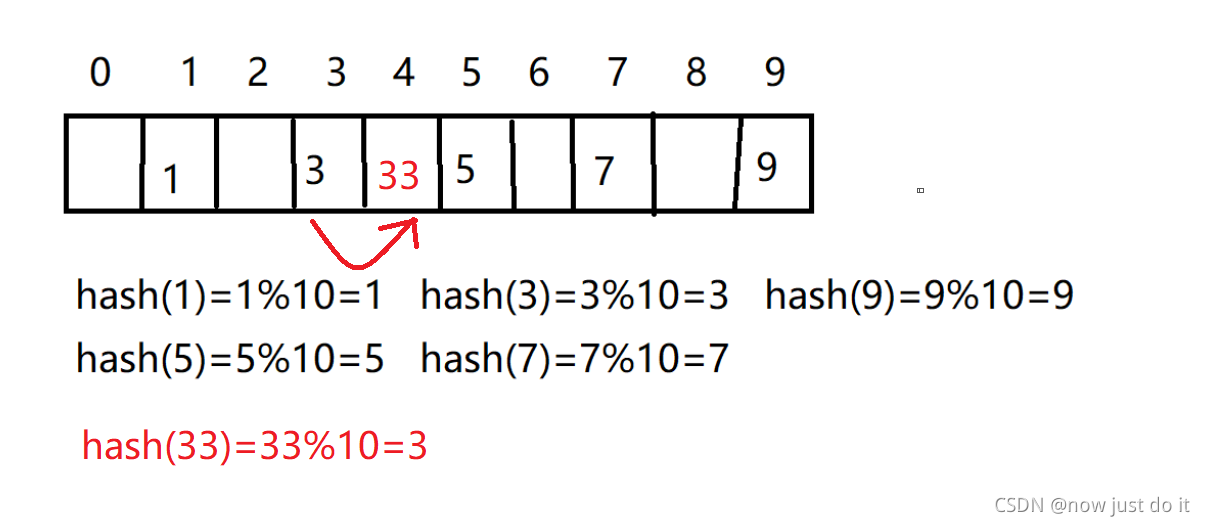
当使用哈希函数计算时,如果发生哈希冲突,那么我们就会向后位移找到第一个空位,将数据填入。
注意:不能随便的物理删除、否则找不到其他值的搜索。
2、二次探测
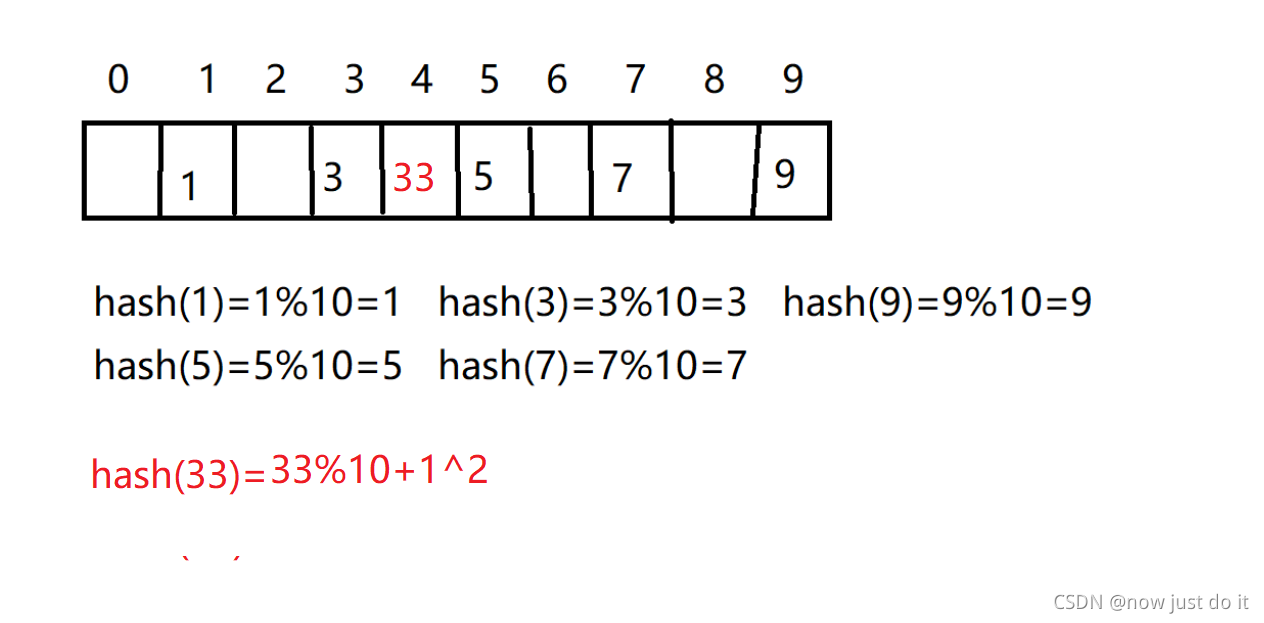
我们通过H=(H+I^2)%m和H=(H-1^2)%m来进行计算
注意:闭散列最大的缺陷是空间利用率比较低。
开散列:(哈希桶)
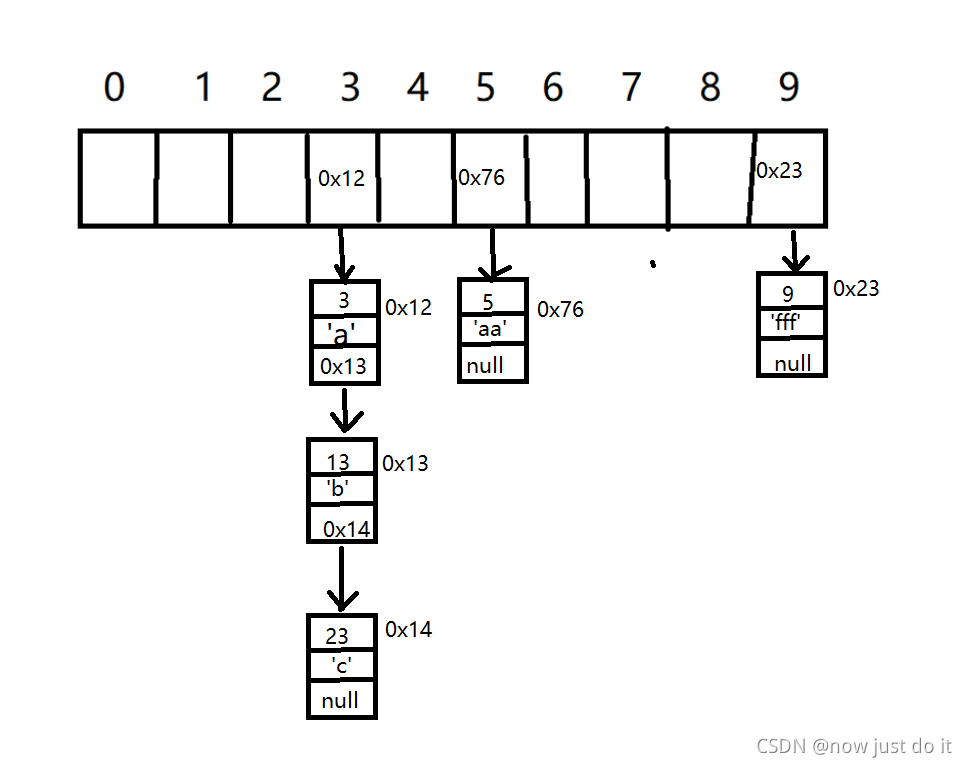
我们把每个桶中的元素用通过单链表链接起来。我们就通过这种方法进行插入,在jdk1.8之前我们使用的是头差法,在jdk1.8之后我们使用的是尾插法。
实现:
public class Test04 {
public static class Node{
public int key;
public int value;
Node next;
public Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
public Node[] array;
public int usedSize;
public Test04() {
this.array=new Node[10];
this.usedSize=0;
}
//添加方法
public void put(int key,int val){
int index=key%this.array.length;
Node cur=array[index];
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.key==key){
cur.value=val;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
Node node=new Node(key,val);
node.next=array[index];
array[index]=node;
if(loadFactor()>=0.75){
resize();
}
}
public void resize(){
Node[] newArray=new Node[this.array.length*2];
for(int i=0;i<this.array.length;i++){
Node temp=array[i];
while(temp!=null){
Node tempNext=temp.next;
int index=temp.key%newArray.length;
temp.next=newArray[index];
newArray[index]=temp;
temp=tempNext;
}
}
array=newArray;
}
public double loadFactor(){
return this.usedSize*1.0/this.array.length;
}
//获取方法
public int get(int key){
int index=key%this.array.length;
Node cur=array[index];
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.key==key){
return cur.value;
}
}
return -1;
}
}二、Set的概念和使用
1、什么是Set
Set是继承Collection中的一个接口,Set中储存了key
Set的底层是使用Map来实现的,Set可以对集合中的元素进行去重操作
Set中的元素不能被修改,只能被删除,同时不能插入null
2、Set常见方法的使用
| 方法 | 用法 |
| boolean add(E e) | 添加元素 |
| void clear() | 清空集合 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断o是否在集合中 |
| Iterator<E> iterator() | 返回迭代器 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除集合中的o |
| int size() | 返回集合中的个数 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 判断集合是否为空 |
| Object[] toArray() | 将集合中的元素转化为数组返回 |
| boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) | c中的元素是否在set中全部存在 |
| boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | 将c中的元素全部转换到set中 |
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
//添加
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(4);
set.add(5);
//判断存在
System.out.println(set.contains(1));//ture
//迭代器
Iterator<Integer> it=set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());//1 2 3 4 5
}
//个数
System.out.println(set.size());//5
//判断是否为空
System.out.println(set.isEmpty());//false
//转换成数组
Integer[] array= (Integer[])set.toArray();
}注意:TreeSet和HashSet的区别
| set底层结构 | TreeSet | HashSet |
| 底层结构 | 红黑树 | 哈希桶 |
| 时间复杂度 | O(logN) | O(1) |
| 是否有序 | 关于key有序 | 不一定有序 |
| 线程 | 不安全 | 不安全 |
| 增删改查区别 | 通过红黑树的特性来实现 | 计算key计算key然后进行插入和删除 |
| 比较与覆写 | Key必须可以比较 | 自定义需要重写equals方法和hashCode方法 |
| 应用场景 | 需要key有序 | 需要更高的时间性能 |
三、搜索树
3.1、搜索树的概念
搜索树又称二叉排序树:
若左子树不为空、左子树上所有的节点的值都小于根节点
若右子树不为空、右子树上所有的节点的值都大于根节点
它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
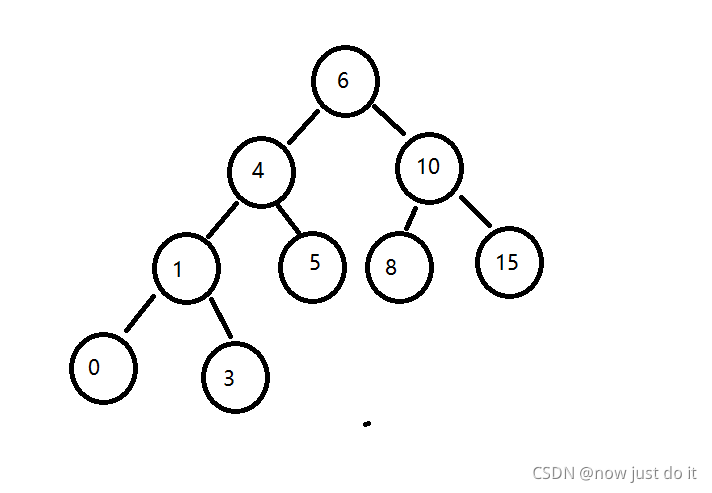
static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}3.2、查找
我们直接遍历搜索树就行了
public TreeNode search(int key) {
if(root==null) return null;
TreeNode cur=root;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val<key){
cur=cur.right;
}else if(cur.val>key){
cur=cur.left;
}else {
return cur;
}
}
return null;
}3.3插入
我们通过遍历之后找到相对应的位置然后进行插入就行了
public boolean insertTree(int val) {
if(root==null){
root=new TreeNode(val);
return true;
}
TreeNode cur=root;
TreeNode pre=null;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val<val){
pre=cur;
cur=cur.right;
}else{
pre=cur;
cur=cur.left;
}
}
if(pre.val<val){
pre.right=new TreeNode(val);
}else{
pre.left=new TreeNode(val);
}
return true;
}3.4删除
我们先对位置进行查找
1. cur.left == null
cur 是 root,则 root = cur.right
cur 不是 root,cur 是 parent.left,则 parent.left = cur.right
cur 不是 root,cur 是 parent.right,则 parent.right = cur.right
2. cur.right == null
cur 是 root,则 root = cur.left
cur 不是 root,cur 是 parent.left,则 parent.left = cur.left
cur 不是 root,cur 是 parent.right,则 parent.right = cur.left
3.cur.right!=null && cur.left!=null
我们找到cur的左边的最大值或者cur的右边的最小值
将它的值放入到cur位置上,在通过上述两种方法进行调换
public void remove(int key){
TreeNode cur=root;
TreeNode parent=null;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val<key){
parent=cur;
cur=cur.right;
}else if(cur.val==key){
removeNode(parent,cur);
}else{
parent=cur;
cur=cur.left;
}
}
}
public void removeNode(TreeNode parent,TreeNode cur){
if(cur.left==null){
if(cur==root){
root=cur.right;
}else if(parent.left==cur){
parent.left=cur.right;
}else{
parent.right=cur.right;
}
}else if(cur.right==null){
if(cur==root){
root=cur.left;
}else if(parent.left==cur){
parent.left=cur.left;
}else {
parent.right=cur.left;
}
}else{
TreeNode tempParent=cur;
TreeNode temp=cur.right;
while(cur.left!=null){
tempParent=temp;
temp=temp.left;
}
cur.val=temp.val;
if(tempParent.left==temp){
tempParent.left=temp.right;
}else{
tempParent.right=temp.right;
}
}
}




 本文详细介绍了Java集合框架中的Map、Set接口以及搜索树的相关概念和使用。Map是一个键值对接口,其内部实现如HashMap和TreeMap各有特点,包括哈希表的哈希冲突解决策略。Set接口基于Map实现,提供了元素去重功能,如HashSet和TreeSet的差异在于底层数据结构和排序特性。此外,文章还讲解了二叉搜索树(二叉排序树)的查找、插入和删除操作。
本文详细介绍了Java集合框架中的Map、Set接口以及搜索树的相关概念和使用。Map是一个键值对接口,其内部实现如HashMap和TreeMap各有特点,包括哈希表的哈希冲突解决策略。Set接口基于Map实现,提供了元素去重功能,如HashSet和TreeSet的差异在于底层数据结构和排序特性。此外,文章还讲解了二叉搜索树(二叉排序树)的查找、插入和删除操作。

















 942
942

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










