
1.单列集合(List、Set)
1.1 存储元素可以重复: List(ArrayList、LinkedList)
特点:
- List集合类中元素有序(即添加和取出顺序一致),且可重复;
- List集合中的每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引(下标顺序索引),即支持索引;
- List容器中的元素都对应一个整数型的序号记其在容器中的位置,可以根据序号存取容器中的元素;
- List常用接口有 ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector。
List接口常用的方法:
void add (int index,Object ele) ;//在index位置插入ele元素;
boolean addAll (int index,Collection eles) ;//从index位置开始将eles集合中的所有元素添加进来;
Object get (int index) ;//获取指定index位置的元素;
int indexOf (Object obj) ;//返回obj在集合中首次出现的位置;
int lastIndexOf (Object obj) ;//返回obj在集合中末次出现的位置;
Object remove (int index) ;//移除指定index位置的元素,并返回此元素;
Object set (int index,Object ele) ;//设置指定index的位置的元素为ele,相当于是替换;
List subList (int fromIndex,int toIndex) ;//返回从fromIndex到toIndex位置的子集合;
常用使用方法示例:
//向上转型,用List来接收ArrayList
List list = new ArrayList();
//1. void add (int index,Object ele) :在index位置插入ele元素;
list.add("开心的你");
list.add(0,"帅气的我");//在0位置插入
System.out.println(list);//[帅气的我, 开心的你]
//2. boolean addAll (int index,Collection eles) :从index位置开始将eles集合中的所有元素添加进来;
List list1 = new ArrayList();
list1.add("Jack");list1.add("Tom");list1.add("Marry");
list.addAll(1,list1);
System.out.println(list);//[帅气的我, Jack, Tom, Marry, 开心的你]
//3. Object get (int index) :获取指定index位置的元素;
System.out.println(list.get(0));//帅气的我
//4. int indexOf (Object obj) :返回obj在集合中首次出现的位置;
System.out.println(list.indexOf("开心的你"));//4
//5. int lastIndexOf (Object obj) :返回obj在集合中末次出现的位置;
list.add("Jack");
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("Jack"));//5
//6. Object remove (int index) :移除指定index位置的元素,并返回此元素;
System.out.println(list.remove(5));//Jack
System.out.println(list);//[帅气的我, Jack, Tom, Marry, 开心的你]
//7. Object set (int index,Object ele) :设置指定index的位置的元素为ele,相当于是替换;
list.set(1,"!!!");
System.out.println(list);//[帅气的我, !!!, Tom, Marry, 开心的你]
//8. List subList (int fromIndex,int toIndex) :返回从fromIndex到toIndex位置的子集合;
//返回的子集合: [fromIndex,toIndex) 左闭右开
System.out.println(list.subList(2,4));//[Tom, Marry]
三种遍历方法:
import java.util.*;
public class ListFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//List的实现接口子类ArrayList LinkedList Vector
//List list = new ArrayList();
//List list = new LinkedList();
List list = new Vector();
list.add("熊大");
list.add("熊二");
list.add("光头强");
//迭代器iterator遍历
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
//增强for遍历
for (Object o:list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
//普通遍历
for (int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
ArrayList 使用注意事项:
- 允许存放任何元素,包括空元素null;
- ArrayList 是由数组来实现数据存储的;
- ArrayList基本等同于 Vector ,除了 ArrayList是线程不安全的,但执行效率高,在多线程的情况下不建议用ArrayList;
ArrayList 底层结构:
- ArrayList中维护了一个Object类型的数组,transient Object[ ] elementData; //transient 短暂的 表示该属性不会被序列化;
- 当创建ArrayList对象时,如果使用的是无参构造器,则初始elementData容量为0 ,第一次添加则扩容elementData为10,如需要再次扩容,则扩容elementData为1.5 倍;
- 如果使用的是指定大小的构造器,则初始扩容elementData容量为指定大小,如果需要再次扩容,则直接扩容为1.5倍。
Vector底层结构:
- Vector 底层也是一个对象数组,protected Object[ ] elementData;
- Vector 是线程同步的,即线程安全,Vector类的操作方法带有synchronized;
- 在开发中,需要线程同步安全时,考虑使用Vector。
LinkedList底层结构:
- LinkedList 实现了双向链表和双端队列的特点;
- 可以添加任意元素(元素可以重复),包括null;
- 线程不安全,没有实现同步;
- LinkedList底层维护了一个双向链表,LinkedList中维护了两个属性first和last分别指向 首节点 和 尾节点,每个节点(Node对象),里面又维护了prev、next、item三个属性,其中通过prev指向前一个,通过next指向后一个节点,最终完成双向链表,所以 LinkedList的元素的添加和删除不是通过数组完成的,相对来说效率较高。
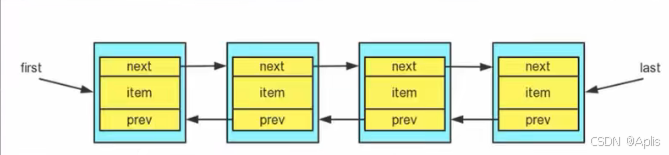
双向链表的模拟:
public class TestLinkedList01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//模拟一个简单的双向链表
Node jack = new Node("Jack");
Node tom = new Node("Tom");
Node marry = new Node("Marry");
//连接三个节点,形成双向链表
//jack -> tom -> marry
jack.next = tom;
tom.next = marry;
//jack <- tom <- marry
marry.pre = tom;
tom.pre = jack;
Node first = jack;//让first引用指向jack,就是双向链表的首节点
Node last = marry;//让last引用指向marry,就是双向链表的尾节点
//演示 从头到尾 遍历
System.out.println("--------- 从头到尾的遍历 --------");
while(true){
if(first == null){
break;
}
//输出first信息
System.out.println(first);
first = first.next;//输出完以后,first指向下一个
/*
Node name = Jack
Node name = Tom
Node name = Marry
进程已结束,退出代码0
*/
}
//从尾到头的遍历
System.out.println("--------- 从尾到头遍历 --------");
while(true){
if(last == null){
break;
}
//输出last信息
System.out.println(last);
last = last.pre;//输出完以后,first指向下一个
/*
Node name = Marry
Node name = Tom
Node name = Jack
*/
}
//演示链表的添加对象/数据
//在tom和marry之间插入一个对象
//1.先创建一个Node节点,name为smith
Node smith = new Node("Smith");
//2.把smith加入双向链表
smith.next = marry;
smith.pre = tom;
marry.pre = smith;
tom.next = smith;
//3.让first再次指向jack
first = jack;
//演示 从头到尾 遍历
System.out.println("--------- 插入smith后 从头到尾的遍历 --------");
while(true){
if(first == null){
break;
}
//输出first信息
System.out.println(first);
first = first.next;//输出完以后,first指向下一个
}/*
Node name = Jack
Node name = Tom
Node name = Smith
Node name = Marry
*/
}
}
//定义一个Node类,Node对象表示双向链表的一个节点
class Node{
public Object item;//真正存放数据的地方
public Node next;//指向下一个节点
public Node pre;//指向前一个节点
public Node(Object name){
this.item = name;
}
public String toString(){
return "Node name = "+item;
}
}
LinkedList使用:
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkListCRUD {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
//增
linkedList.add(1);//size=0添加一个新节点,首尾指针都指向这个新节点
linkedList.add(2);//last指向新节点,first还是指向第一个节点,next指向新节点
linkedList.add(3);
System.out.println("增后: "+linkedList);
//删
linkedList.remove();//默认删除第一个
System.out.println("删后: "+linkedList);//就是去掉指针
//改
linkedList.set(1,999);
System.out.println("改后: "+linkedList);
//查
//get(1) 得到双向链表的第二个对象
Object o = linkedList.get(1);
System.out.println(o);//999
//因为LinkedList是实现了List接口,所以遍历方式:
Iterator iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) { //快捷输入itit
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
//还有增强for 和普通for 遍历
}
}
1.2 set接口
- 无序(添加和取出的顺序不一致),没有索引;
- 不允许重复元素,所以最多包含一个null;
- JDK API 中Set的常用实现类有:HashSet 和 TreeSet。
set接口的遍历方式:
- 迭代器遍历;
- 增强for循环;
- 不能使用索引方式,因为无序;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class SetMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//以Set接口的实现类 HashSet 来演示
//Set接口的实现类对象(Set接口对象),不能存放重复元素
//Set接口对象存放和读取数据无序
//取出的顺序虽然不是添加的顺序,但是,是固定有序的
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add("John");
set.add("Lucy");
set.add("Jack");
set.add(null);
set.add(null);
System.out.println(set);//[null, John, Lucy, Jack] 执行多遍都是这个结果
set.remove(null);//等常用方法可以依照Colleciotn常用方法,是一致的
//遍历:迭代器
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Object o = iterator.next();
System.out.println(o);
}
//遍历:增强for (底层还是迭代器)
for(Object o:set){
System.out.println(o);
}
//不能索引遍历,且set接口对象没有get()方法
}
}
1.2.1 HashSet
- HashSet实现了Set接口;
- HashSet实际上是HashMap,可以从源码看出;
- HashSet 不保证元素是有序的,取决于hash后,再确定索引的结果;
- 不能有重复元素 / 对象。
import java.util.HashSet;
public class HashSet01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
//1.在执行add方法后,会返回一个boolean值
//2.如果添加成功,返回true,否则返回false
System.out.println(hashSet.add("john"));//true
System.out.println(hashSet.add("lucy"));//true
System.out.println(hashSet.add("john"));//false
System.out.println(hashSet.add("jack"));//true
System.out.println(hashSet.add("rose"));//true
hashSet.remove("john");//指定删除某对象
System.out.println("hashset = "+hashSet);//hashset = [rose, lucy, jack]
hashSet = new HashSet();
//HashSet不能添加相同的元素、数据
hashSet.add("lucy");//添加成功
hashSet.add("lucy");//加入不了
hashSet.add(new Dog("tom"));//OK
hashSet.add(new Dog("tom"));//也能加入
System.out.println("hashset = "+hashSet);//hashset = [Dog{name='tom'}, lucy, Dog{name='tom'}]
//经典面试题
hashSet.add(new String("ok"));//可以加入
hashSet.add(new String("ok"));//无法加入
System.out.println("hashset = "+hashSet);//hashset = [Dog{name='tom'}, ok, lucy, Dog{name='tom'}]
//看源码 add到底发生了什么 --》底层机制
}
}
class Dog{
private String name;
public Dog(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- HashSet 底层其实是HashMap,HashMap底层是(数组+链表+红黑树);
- 添加一个元素时,先得到 hash值-> 转成->索引值 ;
- 找到存储数据表 table ,看这个索引位置是否已经存放的所有元素;
- 如果没有,直接加入;
- 如果有,调用 equals 比较,如果相同,就放弃添加,如果不相同,则添加到最后;
- 在Java8中,如果一条链表的元素个数达到 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是8),并且table大小>=MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认是64),就会进行树化(红黑树);
1.2.2 LinkedHashSet
- LinkedHashSet 是 HashSet 的子类,继承HashSet,实现了Set接口;
- LinkedHashSet 底层是一个 LinkedHashMap,底层维护了一个 数组+双向链表;
- LinkedHashSet 根据元素的 hashCode 值来决定元素的存储位置,同时使用链表维护元素的次序,这使得元素看起来是以插入顺序保存的;
- LinkedHashSet 不允许添加重复元素;
2. 双列集合 (Map)
2.1 Map的特点
- Map 与 Collection 并列存在,用于保存具有映射关系的数据:Key - Value;
- Map 中的 Key 和 Value 可以是任何引用类型的数据,会封装到 HashMap$Node对象中;
- Map中的 Key 不允许重复,Map 中的 Value 可以重复;
- Map 的 Key 可以为 null,value 也可以为 null,但 key 为 null 只能有一个;
- 常用 String 类作为 Map 的 key,当然,其他类型也可以,但不常用;
- Key 和 Value 之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定的 Key 总能找到对应的 Value;
2.2 Map接口常用遍历接口方法:
- containsKey : 查找键是否存在;
- keySet : 获取所有的键;
- entrySet :获取所有关系;
- values : 获取所有的值;
import java.util.*;
public class MapFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("海绵宝宝","派大星");
map.put("熊大","熊二");
map.put("大头儿子","小头爸爸");
map.put("黑猫警长",null);
map.put(null,"奥特曼");
//第一种:先取出所有的Key,通过Key取出对应的value
Set keySet = map.keySet();
//(1)增强for
for(Object key : keySet){
System.out.println(key+" - "+map.get(key));
}
//(2)迭代器
Iterator iterator = keySet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object key = iterator.next();
System.out.println(key+" - "+map.get(key));
}
//第二种:把所有的value取出
Collection values = map.values();
//然后遍历Collection就行
//(1)增强for
for(Object value : values){
System.out.println(value);
}
//(2)迭代器
Iterator iterator1 = values.iterator();
while (iterator1.hasNext()) {
Object value = iterator1.next();
System.out.println(value);
}
//第三种:通过EntrySet来获取
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();
//(1)增强for
for(Object entry : entrySet){
//将entry转成map.Entry
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey()+" - "+m.getValue());
}
//(2)迭代器
Iterator iterator2 = entrySet.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator2.next();
//向下转型 Map.Entry
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) next;
System.out.println(m.getKey()+" - "+m.getValue());
}
}
}
 Java集合详解:List、Set与Map
Java集合详解:List、Set与Map





















 5614
5614












