概述
抽象类AbstractBeanFactoryAwareAdvisingPostProcessor及其父类AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor定义了这样一类BeanPostProcessor :
- 拥有一个
Advisor - 对每个
bean进行后置处理,如果该bean符合包裹自己所拥有的Advisor的条件,则将该Advisor包裹该bean。
这里将bean和Advisor包裹该bean的又分两种情况 :- 目标
bean是Advised,此时直接使用Advised接口定义的方法添加Advisor到目标bean; - 目标
bean不是Advised,此时为目标对象创建代理对象,并将Advisor添加到目标bean的代理对象上。
- 目标
以上主要逻辑基本实现在AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor 中,而AbstractBeanFactoryAwareAdvisingPostProcessor主要是在此基础上实现了BeanFactoryAware接口。并对AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor的方法prepareProxyFactory,isEligible做了覆盖实现。
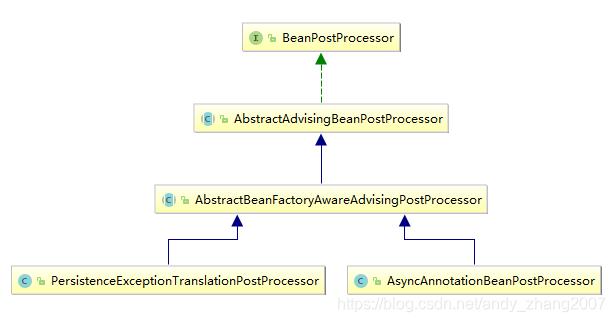
基于AbstractBeanFactoryAwareAdvisingPostProcessor,Spring框架内置了一些具体的实现,比如AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor。它们之间的继承关系如下图所示 :
源代码解析
源代码版本 : spring-aop-5.1.5.RELEASE
AbstractBeanFactoryAwareAdvisingPostProcessor
package org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public abstract class AbstractBeanFactoryAwareAdvisingPostProcessor
extends AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor
implements BeanFactoryAware {
@Nullable
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = (beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory ?
(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) beanFactory : null);
}
@Override
protected ProxyFactory prepareProxyFactory(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass(this.beanFactory, beanName, bean.getClass());
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = super.prepareProxyFactory(bean, beanName);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass() && this.beanFactory != null &&
AutoProxyUtils.shouldProxyTargetClass(this.beanFactory, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
return proxyFactory;
}
@Override
protected boolean isEligible(Object bean, String beanName) {
// 如果目标 bean 的 beanName 使 AutoProxyUtils.isOriginalInstance(beanName, bean.getClass())
// 方法返回 true,则当前 bean 也被认为是否不符合条件
// 这里需要注意一下 Spring 的一个小模式 : ORIGINAL_INSTANCE_SUFFIX
return (!AutoProxyUtils.isOriginalInstance(beanName, bean.getClass()) &&
super.isEligible(bean, beanName));
}
}
AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor
AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor的实现重点在以下方法 :
postProcessBeforeInitialization直接返回目标
bean,表示在bean前置处理阶段不做任何处理。postProcessAfterInitialization根据目标
bean类型判断目标bean是否需要被添加Advisor,需要的话向其添加Advisor。这里又分两种情况:- 目标
bean是Advised,此时直接使用Advised接口定义的方法添加Advisor到目标bean; - 目标
bean不是Advised,此时为目标对象创建代理对象,并将Advisor添加到目标bean的代理对象上。
- 目标
isEligible提供实现检测目标
bean是否符合被添加Advisor的条件。综合使用了缓存禁止和工具方法AopUtils#canApply(Advisor, Class)。
实现子类可以覆盖该方法。prepareProxyFactory准备目标
bean的代理工厂对象。
实现子类可以覆盖该方法。customizeProxyFactory定义一个空方法,实现子类可以覆盖实现该方法用于对目标对象的代理工厂对象做定制。
AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor 实现类
MethodValidationPostProcessorDefaultPointcutAdvisor含有验证器Pointcut和Advice逻辑- 使用方法可以参考 :
ValidationAutoConfiguration
AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessorAsyncAnnotationAdvisor
PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessorPersistenceExceptionTranslationAdvisor
AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor 源代码
package org.springframework.aop.framework;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import org.springframework.aop.Advisor;
import org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public abstract class AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor extends ProxyProcessorSupport
implements BeanPostProcessor {
// 当前 BeanPostProcessor 将要应用到符合条件的目标`bean`上的`Advisor`。
@Nullable
protected Advisor advisor;
// this.advisor 应用到已有 advisor 的最外面(离目标bean最远),还是最里面(离目标bean最近)。
// false 表示应用到已有 advisor 的最里面,离目标bean最近。
protected boolean beforeExistingAdvisors = false;
// 缓存机制,如果某个bean Class 符合被本 BeanPostProcessor 添加 Advisor 的条件,
// 则将其缓存下来,
// 本 BeanPostProcessor 处理每个 bean 时会先尝试使用该缓存,如果缓存中没有
// 会尝试使用 AopUtils#canApply(Advisor, Class) 进行检测
private final Map<Class<?>, Boolean> eligibleBeans = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
/**
* Set whether this post-processor's advisor is supposed to apply before
* existing advisors when encountering a pre-advised object.
* Default is "false", applying the advisor after existing advisors, i.e.
* as close as possible to the target method. Switch this to "true" in order
* for this post-processor's advisor to wrap existing advisors as well.
*
* Note: Check the concrete post-processor's javadoc whether it possibly
* changes this flag by default, depending on the nature of its advisor.
*/
public void setBeforeExistingAdvisors(boolean beforeExistingAdvisors) {
this.beforeExistingAdvisors = beforeExistingAdvisors;
}
// bean 初始化前置处理
// 该方法对目标bean不做任何处理,直接返回目标 bean
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
// bean 初始化后置处理
// 1. 如果属性 this.advisor 为 null 或者目标 bean 本身是一个 AopInfrastructureBean,
// 则不对赌目标 bean 做包装处理,而是直接返回目标 bean
// 2. 否则如果目标 bean 是 Advised 实例,未被冻结,并且符合当前 BeanPostProcessor
// 自定义的条件,则将 this.advisor 添加给它
// 3. 否则如果目标 bean 也不是 Advised 实例,但是符合当前 BeanPostProcessor
// 自定义的条件,则将为目标 bean 创建一个代理对象,将 this.advisor 添加给代理对象,
// 然后返回该代理对象用于代理目标 bean
// 4. 目标 bean 不符合当前 BeanPostProcessor 自定义的条件,则直接返回目标 bean 自身。
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (this.advisor == null || bean instanceof AopInfrastructureBean) {
// Ignore AOP infrastructure such as scoped proxies.
return bean;
}
if (bean instanceof Advised) {
// 目标 bean 已经实现了接口 Advised,所以直接使用 Advised
// 接口定义的能力添加 Advisor
Advised advised = (Advised) bean;
if (!advised.isFrozen() && isEligible(AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean))) {
// Add our local Advisor to the existing proxy's Advisor chain...
if (this.beforeExistingAdvisors) {
advised.addAdvisor(0, this.advisor);
}
else {
advised.addAdvisor(this.advisor);
}
return bean;
}
}
if (isEligible(bean, beanName)) {
// 目标 bean 符合当前 BeanPostProcessor 添加 Advisor 的条件
// 准备相应的代理创建工厂
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = prepareProxyFactory(bean, beanName);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(bean.getClass(), proxyFactory);
}
// 设置 this.advisor 到代理对象工厂
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisor);
// 调用代理工厂自定义方法进行自定义
// 当前类中 customizeProxyFactory 是一个空方法,
// 但实现子类可以覆盖实现提供自己的自定义逻辑
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
// 创建代理对象
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
// 目标 bean 不符合当前 BeanPostProcessor 添加 Advisor 的条件
// No proxy needed.
return bean;
}
/**
* Check whether the given bean is eligible for advising with this
* post-processor's Advisor.
* Delegates to #isEligible(Class) for target class checking.
* Can be overridden e.g. to specifically exclude certain beans by name.
*
* Note: Only called for regular bean instances but not for existing
* proxy instances which implement Advised and allow for adding
* the local Advisor to the existing proxy's Advisor chain.
* For the latter, #isEligible(Class) is being called directly,
* with the actual target class behind the existing proxy (as determined
* by AopUtils#getTargetClass(Object).
* @param bean the bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @see #isEligible(Class)
*/
protected boolean isEligible(Object bean, String beanName) {
return isEligible(bean.getClass());
}
/**
* Check whether the given class is eligible for advising with this
* post-processor's Advisor.
* Implements caching of canApply results per bean target class.
* @param targetClass the class to check against
* @see AopUtils#canApply(Advisor, Class)
*/
protected boolean isEligible(Class<?> targetClass) {
// 先尝试缓存
Boolean eligible = this.eligibleBeans.get(targetClass);
if (eligible != null) {
return eligible;
}
if (this.advisor == null) {
return false;
}
// 缓存没有命中,使用 AopUtils#getTargetClass(Object) 进行检测
eligible = AopUtils.canApply(this.advisor, targetClass);
this.eligibleBeans.put(targetClass, eligible);
return eligible;
}
/**
* Prepare a ProxyFactory for the given bean.
* Subclasses may customize the handling of the target instance and in
* particular the exposure of the target class. The default introspection
* of interfaces for non-target-class proxies and the configured advisor
* will be applied afterwards; #customizeProxyFactory allows for
* late customizations of those parts right before proxy creation.
* @param bean the bean instance to create a proxy for
* @param beanName the corresponding bean name
* @return the ProxyFactory, initialized with this processor's
* ProxyConfig settings and the specified bean
* @since 4.2.3
* @see #customizeProxyFactory
*/
protected ProxyFactory prepareProxyFactory(Object bean, String beanName) {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
proxyFactory.setTarget(bean);
return proxyFactory;
}
/**
* Subclasses may choose to implement this: for example,
* to change the interfaces exposed.
* The default implementation is empty.
* @param proxyFactory the ProxyFactory that is already configured with
* target, advisor and interfaces and will be used to create the proxy
* immediately after this method returns
* @since 4.2.3
* @see #prepareProxyFactory
*/
protected void customizeProxyFactory(ProxyFactory proxyFactory 的机会) {
// 提供给实现子类一个定制化 proxyFactory 的机会
}
}






















 508
508

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








