1 Preface
1.1 Overview
HaploThread is a cross-platform desktop software designed for constructing and visualizing haplotype networks. Developed in C++ using the Qt framework, it integrates multithreaded algorithms including McAN and fastHaN (which contains MSN, MJN, TCS, etc.) and adopts a plugin-based architecture for modular extension. HaploThread provides an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI) that allows users to rapidly build and interactively explore haplotype networks from large-scale sequence datasets, supporting genetic variation and evolutionary relationship analysis.
The software runs fully offline, eliminating network dependence and ensuring data privacy. HaploThread delivers high computational performance for large datasets (millions of sequences), catering to population genetics, pathogen evolution tracking, and epidemiological research.
1.2 Background and Motivation
Existing desktop tools for haplotype network construction (e.g., TCS, Network, PopART, HapStar) mostly rely on single-threaded algorithms, which cannot efficiently handle large-scale sequence data, and often lack interactive visualization. Recently developed multithreaded algorithms such as McAN and fastHaN significantly improve computational efficiency but lack an integrated desktop platform that combines high-performance algorithms with a user-friendly GUI.
HaploThread aims to provide a powerful and easy-to-use platform featuring:
- Intuitive visualization — interactive network graphs displaying haplotype evolutionary relationships.
- High computational efficiency — multithreaded parallel algorithms for large-scale datasets.
- Ease of use — GUI-based workflow without command-line operations.
- Security and reliability — fully local execution ensures data privacy.
- Extensibility — plugin-based architecture supporting algorithm and feature expansion.
1.3 Target Users
HaploThread is designed for researchers, data analysts, and educators in population genetics, molecular epidemiology, phylogenetics, pathogen surveillance and origin tracing.
1.4 Feature Summary
- Integrated algorithms: McAN, MJN, MSN, TCS, etc.
- Versatile formats: supports VCF, PHYLIP, GraphML I/O.
- Interactive visualization: geospatial and temporal dynamic rendering.
- Cross-platform: binaries for Windows & macOS.
- Open & extensible: plugin architecture and GPL open-source license.
2 Installation and Configuration
Download: Download the package HaploThread-1.0.0-win-x64.zip from: https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/biocode/tool/BT007948 or
https://github.com/git-xubo/HaploThread
Extract: Unzip the package into a directory with English characters only.
Run: No installation is required. Simply double-click: ...\HaploThread-1.0.0-win-x64\HaploThread.exe to launch the program (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Home page of HaploThread.
3 Basic Usage Examples
3.1 Constructing a Haplotype Network
3.1.1 Entering the Construction Page
Click the haplotype construction icon ![]() on the home page (Figure 2) to enter the construction interface (Figure 3).
on the home page (Figure 2) to enter the construction interface (Figure 3).
Figure 2. “haplotype construction” highlighted on the home page.
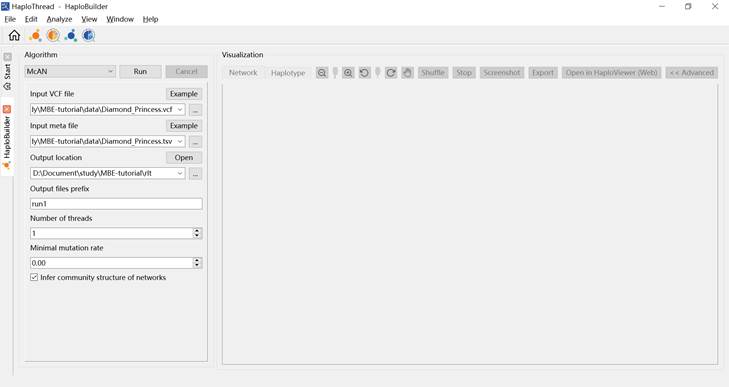
Figure 3. Haplotype construction interface.
3.1.2 Preparing Input Files
Download the example dataset Diamond_Princess_Data.zip from: https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/biocode/tool/BT007948
It includes:
- Diamond_Princess.vcf: genomic variants
- Diamond_Princess.tsv: metadata
3.1.3 Setting Parameters
Configure parameters under Algorithm, as shown in Figure 3 and Table 1.
Table 1. Parameter settings for haplotype network construction (McAN example)
| Parameter | Description |
| Algorithm | Keep default (McAN) |
| Input VCF file | Diamond_Princess.vcf |
| Input meta file | Diamond_Princess.tsv |
| Output location | Directory for result files |
| Output files prefix | Prefix for output files |
| Number of threads | Set based on available resources |
| Minimal mutation rate | Set to 0 (no mutation filtering) |
| Infer community structure | Recommended to enable |
3.1.4 Running the Construction
Click Run to start.
The constructed haplotype network appears on the right panel after completion (Figure 4).
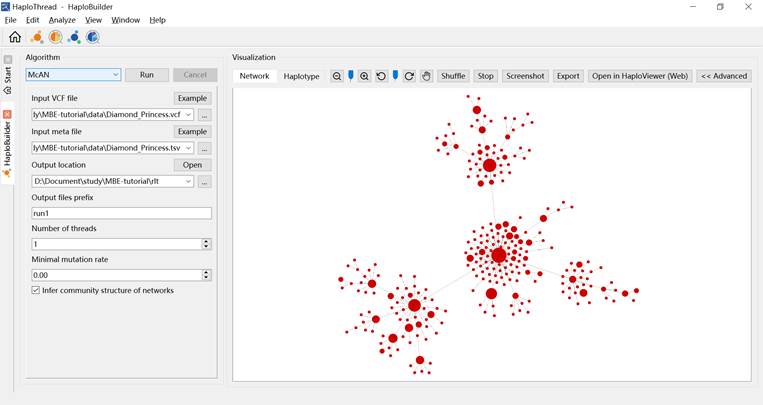
Figure 4. Example of construction results.
3.2 Visualization
After construction, visualization settings can be adjusted in the Properties panel.
3.2.1 Node Coloring
Under Visual, select a coloring scheme.
- By Country/Region — colors nodes by geographic origin (Figure 5). DP samples (from the Diamond Princess cruise ship) appear as a distinct lineage.
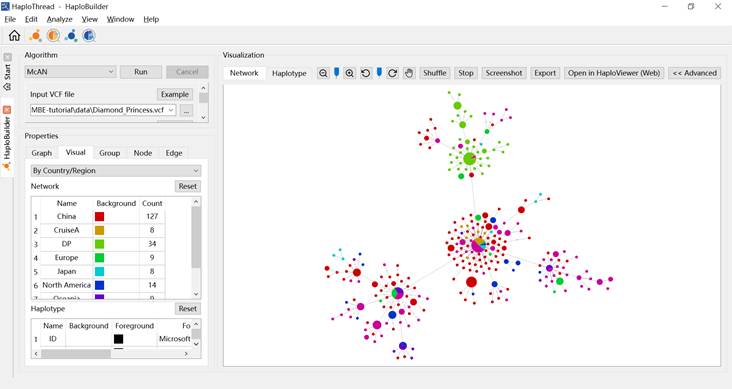
Figure 5. Coloring by geographic information.
- By Month / By Year — colors nodes by sampling date (Figures 6 and 7).
- By Group — colors nodes by detected clusters (Figure 8).
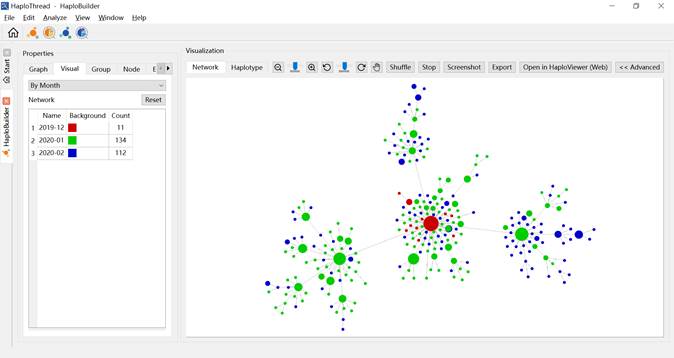
Figure 6. Haplotype network colored by month.
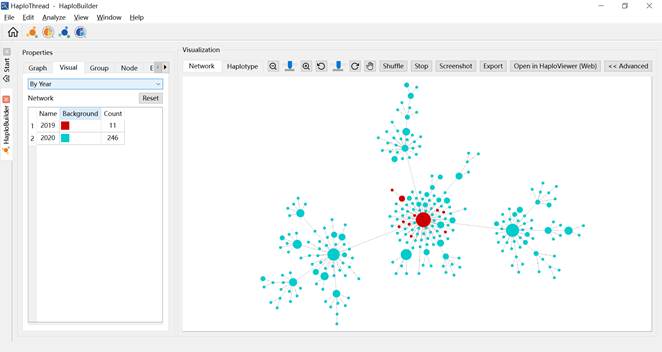
Figure 7. Haplotype network colored by year.
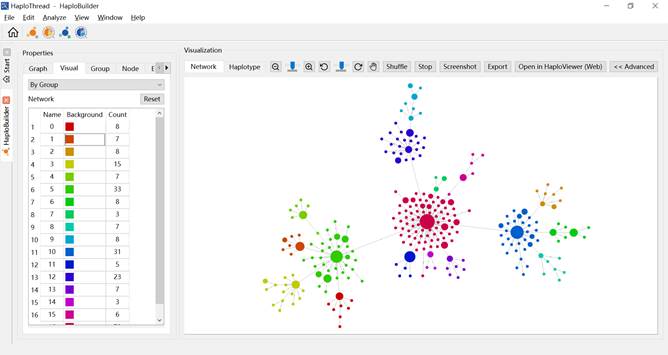
Figure 8. Haplotype network colored by cluster.
3.2.2 Hiding or Showing Nodes
In Graph, select Display by Day, then drag the slider to filter nodes by time (Figure 9).
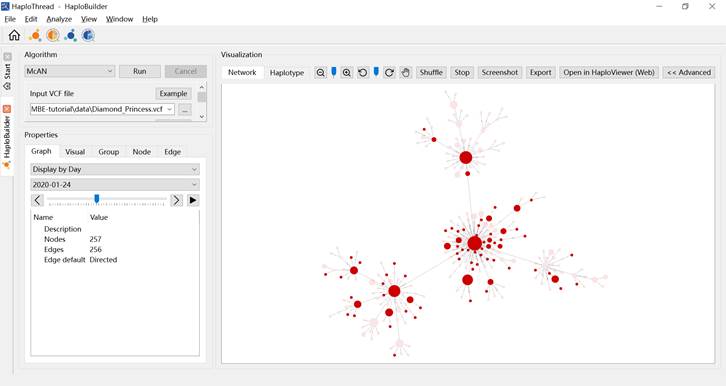
Figure 9. Haplotype network showing or hiding nodes based on time.
3.2.3 Manual Layout Adjustment
Click the pointer ![]() icon to switch to dragging mode and manually adjust node positions.
icon to switch to dragging mode and manually adjust node positions.
3.2.4 Displaying Haplotypes
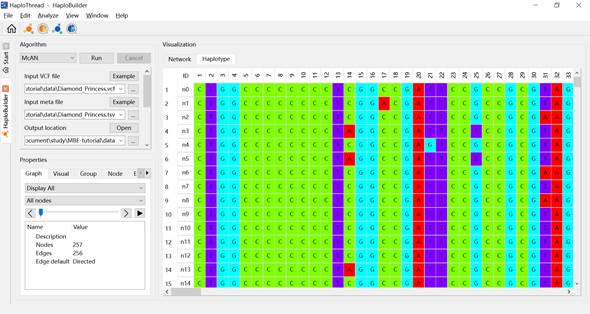
Figure 10. Displaying the bases of a haplotype.
3.3 Exporting the Haplotype Network
Click Export to save the network visualization. Supported formats:
- SVG
- PNG
- JPG
GraphML output is saved automatically under the output directory as: run1.haplonet.graphml (if the prefix is run1).
3.4 Visualizing a Pre-built Network
To visualize an existing GraphML haplotype network: Click Haplotype visualization ![]() on the home page (Figure 11). Go to File → Open… (Figure 12) and load a .graphml file. The same visualization features become available (Figure 13).
on the home page (Figure 11). Go to File → Open… (Figure 12) and load a .graphml file. The same visualization features become available (Figure 13).

Figure 11. The haplotype visualization icon is highlighted on the HaploThread homepage.
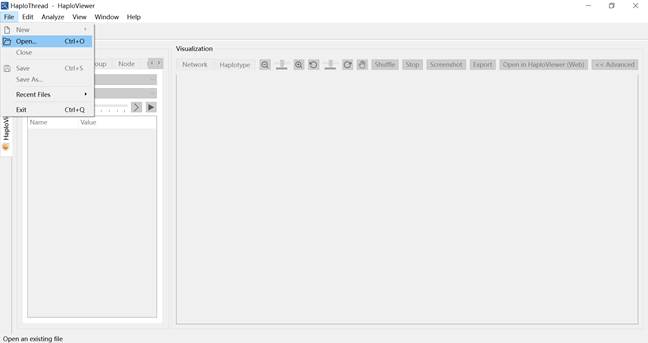
Figure 12. Opening a GraphML file in the visualization module.
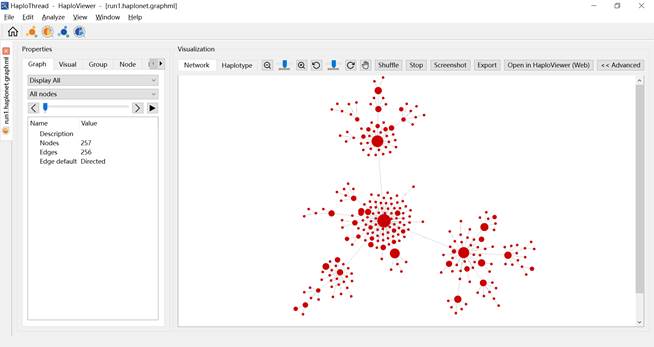
Figure 13. Software screenshot after opening a GraphML file in the visualization module.
4 FAQ
4.1 Missing VCRUNTIME140.dll / VCRUNTIME140_1.dll / MSVCP140.dll
Error message:
VCRUNTIME140.dll, VCRUNTIME140_1.dll, or MSVCP140.dll not found.
Cause: Missing Microsoft Visual C++ runtime libraries.
Solution:
Install the required Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable.
A download link is provided in the Dependencies section of this manual.
Restart HaploThread after installation.
5 How to Cite
If HaploThread is used in your research, please cite:
BibTex:
| @article {Xu2025.07.06.659816, author = {Xu, Bo and Li, Lun and Li, Cuiping and Wang, Anke and Fan, Zhuojing and Song, Shuhui}, title = {HaploThread: A Scalable Integrated Desktop Platform for Constructing and Visualizing Haplotype Networks for Large-sample Sequences}, elocation-id = {2025.07.06.659816}, year = {2025}, doi = {10.1101/2025.07.06.659816}, publisher = {Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}, URL = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2025/07/10/2025.07.06.659816}, eprint = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2025/07/10/2025.07.06.659816.full.pdf}, journal = {bioRxiv} } |
Plain text:
| Xu B, Li L, Li C, Wang A, Fan Z, Song S. (2025). HaploThread: A Scalable Integrated Desktop Platform for Constructing and Visualizing Haplotype Networks for Large-sample Sequences. bioRxiv, 2025.07.06.659816. doi:10.1101/2025.07.06.659816 Available at: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2025/07/10/2025.07.06.659816 |
You may also cite the software version:
| HaploThread v1.0.0, National Center for Bioinformation, Beijing Download: https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/biocode/tool/BT007948 |
6 References
- Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Röhl A. 1999. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 16:37-48.
- Chi L, Dong Y, Wang R, Yang S, Wu L, Xue Y, Chen H. 2025. HapNetworkView: a tool for haplotype network exploration and visualization. BMC Genomics 26:52.
- Chi L, Zhang X, Xue Y, Chen H. 2023. fastHaN: a fast and scalable program for constructing haplotype network for large-sample sequences. Mol Ecol Resour.
- Clement M, Posada D, Crandall KA. 2000. TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol Ecol 9:1657-1659.
- Excoffier L, Smouse PE. 1994. Using allele frequencies and geographic subdivision to reconstruct gene trees within a species: molecular variance parsimony. Genetics 136:343-359.
- Kumar S, Dudley J. 2007. Bioinformatics software for biologists in the genomics era. Bioinformatics 23:1713-1717.
- Leigh JW, Bryant D. 2015. popart: full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 6:1110-1116.
- Li L, Li C, Li N, Zou D, Zhao W, Luo H, Xue Y, Zhang Z, Bao Y, Song S. 2024. Machine Learning Early Detection of SARS-CoV-2 High-Risk Variants. Adv Sci (Weinh) 11:e2405058.
- Li L, Xu B, Tian D, Wang A, Zhu J, Li C, Li N, Zhao W, Shi L, Xue Y, et al. 2023. McAN: a novel computational algorithm and platform for constructing and visualizing haplotype networks. Brief Bioinform 24.
- Matschiner M. 2016. Fitchi: haplotype genealogy graphs based on the Fitch algorithm. Bioinformatics 32:1250-1252.
- Song S, Ma L, Zou D, Tian D, Li C, Zhu J, Chen M, Wang A, Ma Y, Li M, et al. 2020. The Global Landscape of SARS-CoV-2 Genomes, Variants, and Haplotypes in 2019nCoVR. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 18:749-759.
- Teacher AG, Griffiths DJ. 2011. HapStar: automated haplotype network layout and visualization. Mol Ecol Resour 11:151-153.
- Templeton AR, Crandall KA, Sing CF. 1992. A cladistic analysis of phenotypic associations with haplotypes inferred from restriction endonuclease mapping and DNA sequence data. III. Cladogram estimation. Genetics 132:619-633.
- Vences M, Patmanidis S, Schmidt J-C, Matschiner M, Miralles A, Renner SS. 2024. Hapsolutely: a user-friendly tool integrating haplotype phasing, network construction, and haploweb calculation. Bioinformatics Advances 4.
7 Contributor Statement
| Name | Contribution |
| Shuhui Song | Overall project supervision |
| Bo Xu | Architecture design, implementation, testing, documentation |
| Lun Li | Algorithm implementation, testing, documentation |
| Cuiping Li | Testing, documentation |
| Anke Wang | Visualization implementation |
| Zhuojing Fan | Logo & icon design |
8 Acknowledgements
This work was supported by:
- ANSO Collaborative Research Program (Grant No. ANSO-CR-KP-2022-09)
- National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32270718, 32170678)
We thank CNCB and NGDC for technical support, as well as all colleagues who provided valuable feedback during development and testing.




















 2142
2142

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








