一、Android UI 构建基础
-
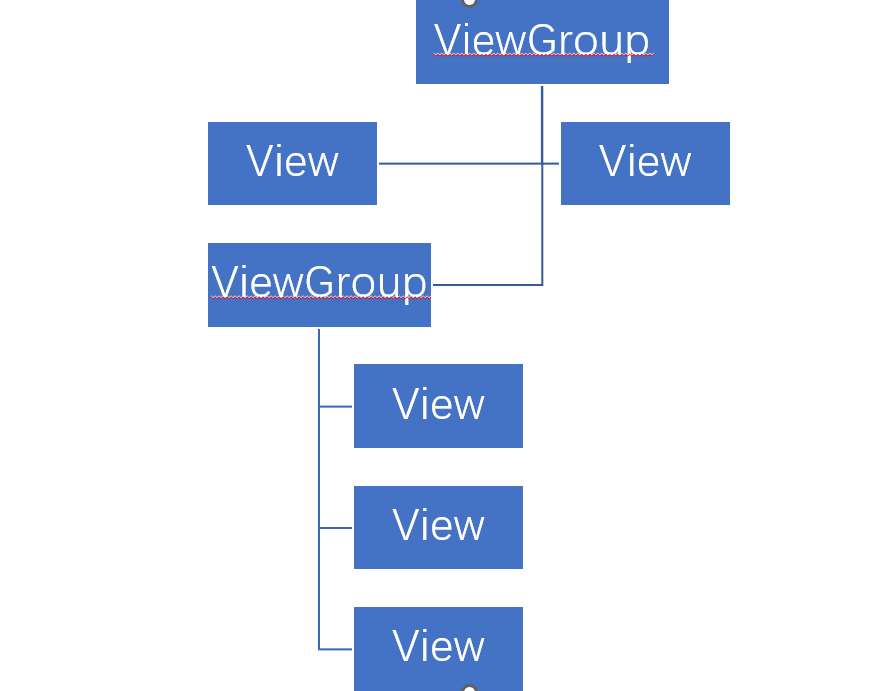
View 与 ViewGroup:所有 UI 元素都由它们构建。
-
ViewGroup 是容器,可包含
View或其它ViewGroup。 -
每个 Android 界面必须有一个
ViewGroup作为根容器。 -
二、布局编写方式
1、XML 布局(推荐)
-
优点:将布局代码与 Java 逻辑分离,结构清晰。
-
示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="使用XML布局文件控制UI界面"
android:textColor="#ff0000"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"/>
</RelativeLayout>
2.Java 代码编写布局
-
通过
new关键字创建View或ViewGroup,动态添加到布局中。
三、常用布局类型
| 布局类型 | 特点 |
|---|---|
| 线性布局(LinearLayout) | 水平或垂直排列控件 |
| 相对布局(RelativeLayout) | 通过相对定位排列控件 |
| 帧布局(FrameLayout) | 控件叠加显示 |
| 表格布局(TableLayout) |
以表格形式排列控件 |
四、布局通用属性
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
android:id | 设置布局标识 |
android:layout_width | 宽度(如 match_parent, wrap_content) |
android:layout_height | 高度 |
android:background | 背景(颜色或图片) |
android:layout_margin | 外边距(与周围元素或边界的距离) |
android:padding | 内边距(布局与内部控件的距离) |
五、LinearLayout 特有属性
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
android:orientation | 排列方向:vertical(垂直)或 horizontal(水平) |
android:layout_weight | 权重,用于分配剩余空间 |
六、对齐与位置属性
-
android:gravity:控制容器内部内容的对齐方式(如文本在按钮中的位置)。 -
android:layout_gravity:控制控件本身在父容器中的对齐方式。
七、案例:嵌套 LinearLayout
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1">
<!-- 四个文本组件 -->
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1">
<!-- 四个文本组件 -->
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>




















 251
251

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








