简介:Service是Android四大组件中与Activity最相似的组件,它们都代表可执行的程序,Service与Activity的区别在于:Service一直在后台运行,它没有用户界面,所以绝对不会到前台来。一旦Service被启动之后,它就与Activity一样,它完全具有自己的声明周期,关于程序中Activity和Service的选择标准是:如果某个程序组件需要在运行时向用户呈现某种界面或者该程序需要和用户进行交互,那么就使用Activity;否则就考虑使用Service
目录:
一、定义一个继承Service类的子类
package com.contentprovide.liuliu.myservice;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
public class MyService extends Service {
public MyService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
}
// 重写oncread和ondestroy两个方法
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
System.out.println("Service被启动");
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
System.out.println("Service被摧毁");
}
}
二、在主布局文件activity_main.xml中定义两个按钮,一个用于启动Service,一个用于摧毁Service
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.contentprovide.liuliu.myservice.MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnstart"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="启动setvice"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnstop"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="停止service"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
/>
</LinearLayout>
三、使用Java代码实现Service的启动和摧毁(方法和Activity之间的跳转类似)
package com.contentprovide.liuliu.myservice;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button btnstart,btnstop;
Intent intent ;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btnstart = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnstart);
btnstop = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnstop);
//把需要跳转的Service类名放进Intent对象中
intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,MyService.class);
btnstart.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
//启动Service
startService(intent);
}
});
btnstop.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// 摧毁Service
stopService(intent);
}
});
}
}
最终实现效果:点击按钮,控制台输出效果
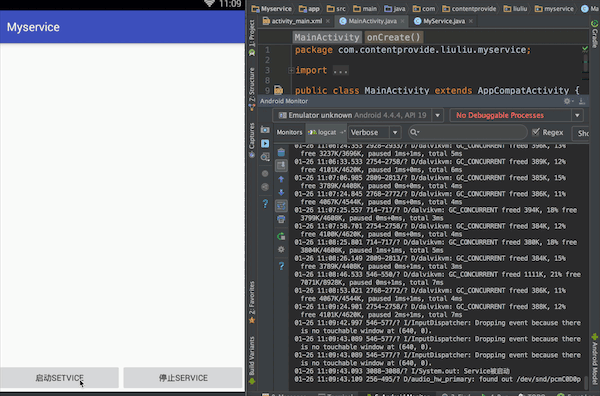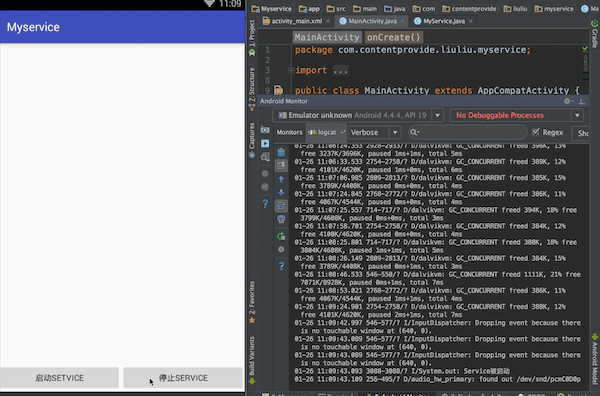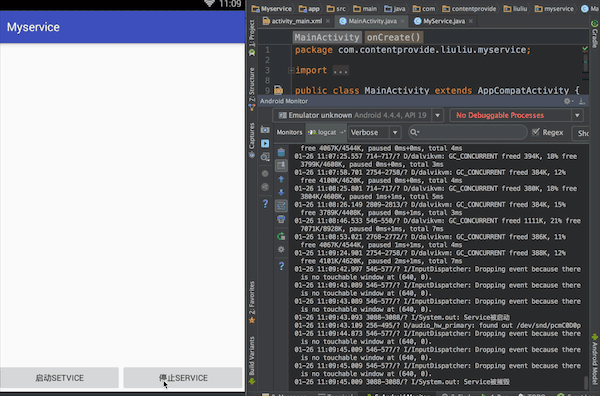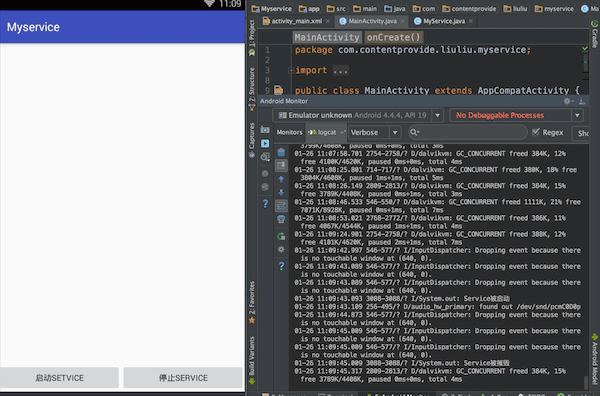
一、activity_main.xml布局文件,增加一个输入框,用于输入内容并向Service
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.contentprovide.liuliu.myservice.MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edit"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnstart"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="启动setvice" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnstop"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="停止service" />
</LinearLayout>
二、Java代码启动Service并将从输入框中获得的数据向Service传递
package com.contentprovide.liuliu.myservice;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
EditText edit;
Button btnstart, btnstop;
Intent intent;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
edit = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edit);
btnstart = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnstart);
btnstop = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnstop);
//把需要跳转的Service类名放进Intent对象中
intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class);
btnstart.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// 获得输入框中的内容并放入Intent对象中进行数据传递
intent.putExtra("input", edit.getText().toString());
//启动Service
startService(intent);
}
});
btnstop.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// 摧毁Service
stopService(intent);
}
});
}
}
三、在Service中接收从Activity中传递过来的数据,使用System输出
package com.contentprovide.liuliu.myservice;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
public class MyService extends Service {
String input = "默认数据";
public MyService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// 获取从Activity中传递过来的值
input = intent.getStringExtra("input");
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
// System.out.println("Service被启动");
while (true) {
// 输出接收到的数据
System.out.println(input);
try {
sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
// 重写oncread和ondestroy两个方法
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
System.out.println("Service被启动");
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
System.out.println("Service被摧毁");
}
}
最终实现效果:在文本框中输入内容,点击启动Service按钮,在控制台会输出文本框中的内容
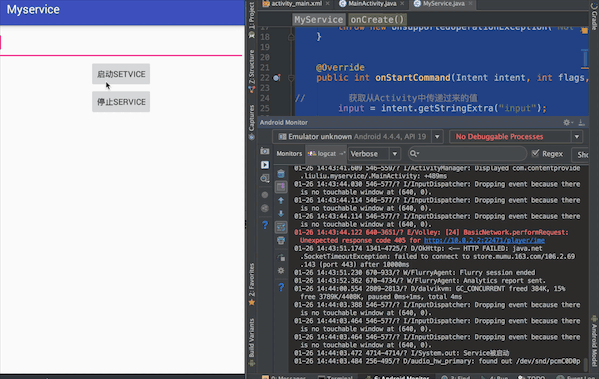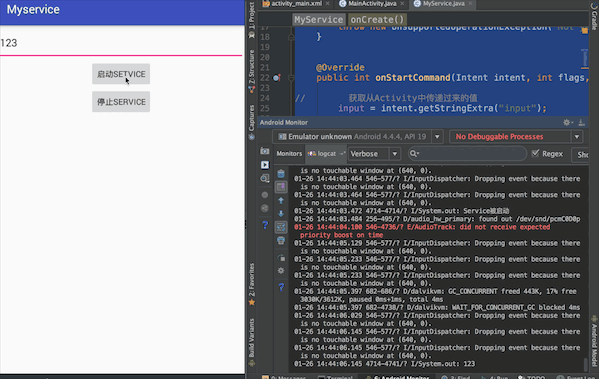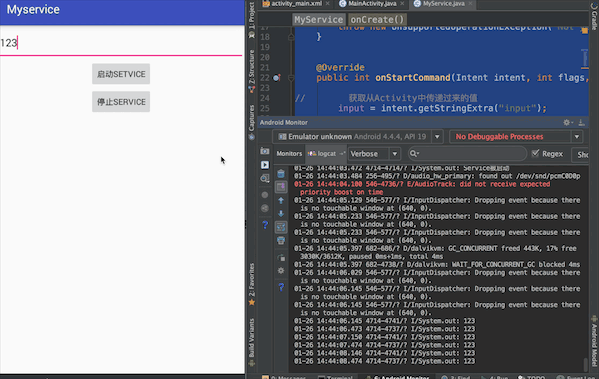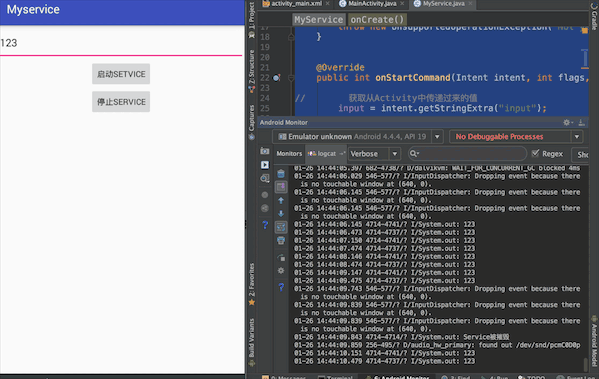
一、在activity_main.xml布局文件中添加两个按钮用于绑定和解除Service
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.contentprovide.liuliu.myservice.MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnstart"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="启动setvice" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnstop"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="停止service" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bind"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="绑定setvice" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/unbind"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="解除绑定service" />
</LinearLayout>
二、自定义一个类继承Binder类
package com.contentprovide.liuliu.myservice;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
public class MyService extends Service {
public MyService() {
}
// 自定义类继承Binder类
class MyBind extends Binder {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
//返回继承了Binder类的自定义类MyBind的对象
return new MyBind();
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
// 重写oncread和ondestroy两个方法
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
System.out.println("Service被启动");
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
System.out.println("Service被摧毁");
}
}
三、Java代码中实现Service的启动、停止、绑定、解除
package com.contentprovide.liuliu.myservice;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button btnstart, btnstop;
Button bind, unbind;
Intent intent;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btnstart = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnstart);
btnstop = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnstop);
bind = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bind);
unbind = (Button) findViewById(R.id.unbind);
//把需要跳转的Service类名放进Intent对象中
intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class);
btnstart.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
//启动Service
startService(intent);
}
});
btnstop.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// 摧毁Service
stopService(intent);
}
});
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 定义一个ServiceConnection对象
final ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
// 当Activity和Service绑定成功时回调该方法
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) {
System.out.println("service成功绑定");
}
// 当Activity和Service断开连接时回调该方法
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
System.out.println("service解除绑定");
}
};
bind.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// 将Activity和Service绑定,第一个参数是Intend对象,第二个参数是自定义的ServiceConnection对象,第三个是int类型参数
bindService(intent, serviceConnection, BIND_DEBUG_UNBIND);
}
});
unbind.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// 解除Service绑定
unbindService(serviceConnection);
}
});
}
}
实现效果:按顺序点击启动Service,绑定Service,停止Service,控制台依次输出:Service被启动、Service成功绑定、Service解除绑定、Service被摧毁。会发现这里虽然没有点击解除绑定Service,但是只要点击了停止Service就会先后输出Service解除绑定、Service被摧毁。这里涉及Service的声明周期
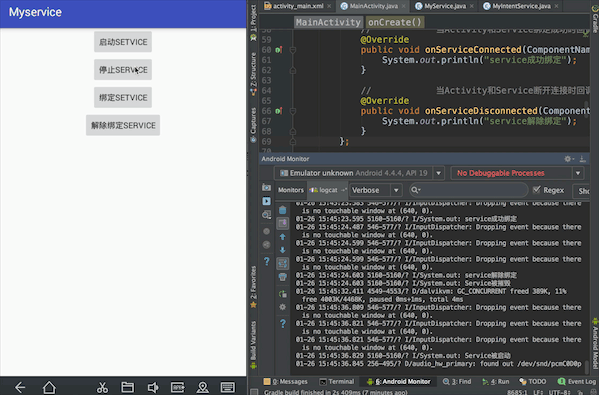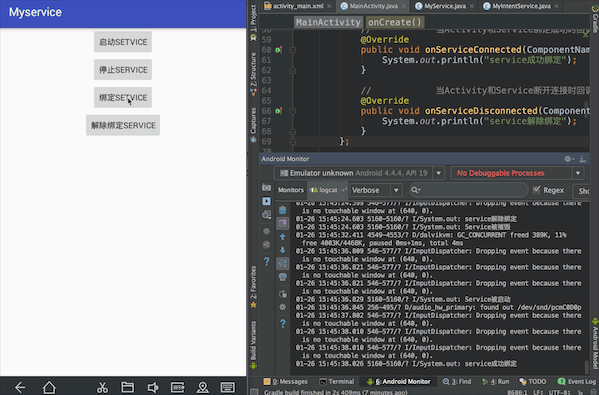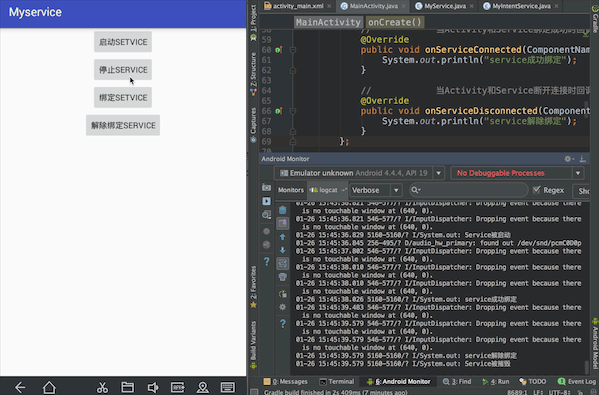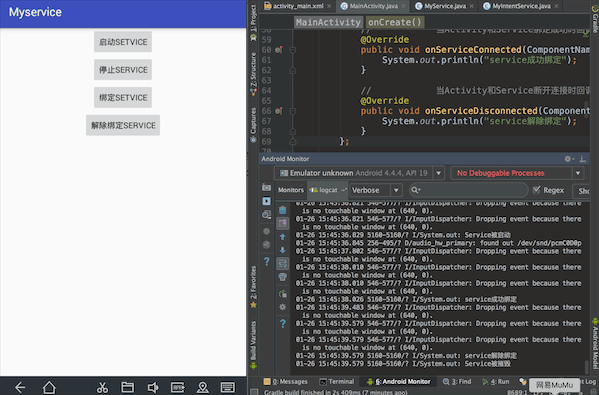
一、activity_main.xml中的布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.contentprovide.liuliu.myservice.MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edit"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tex"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="默认值" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnstart"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="启动setvice" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnstop"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="停止service" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bind"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="绑定setvice" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/unbind"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="解除绑定service" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/get_service"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="获取service数据" />
</LinearLayout>
二、自定义MyServicve类继承Service类
package com.contentprovide.liuliu.myservice;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
public class MyService extends Service {
String GetData = "";
int count = 0;
public MyService() {
}
// 自定义类继承Binder类
class MyBind extends Binder {
// 自定义方法,用于在Activity中调用传入参数给MyService中的相关变量
public void getData(String data) {
GetData = data;
}
//自定义方法,用于在Activity中调用获取在Service中的数据
public int getcount() {
return count;
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
//返回继承了Binder类的自定义类MyBind的对象
return new MyBind();
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
// 重写oncread和ondestroy两个方法
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
System.out.println("Service被启动");
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
while (true) {
count++;
System.out.println(GetData);
try {
sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
System.out.println("Service被摧毁");
}
}
三、在Java代码中传递数据给Service在控制台输出,并通过点击绑定Service按钮从Service中获取数据并且在界面中通过控件显示
package com.contentprovide.liuliu.myservice;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.Message;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
EditText edit;
TextView tex;
Button btnstart, btnstop;
Button bind, unbind;
Button get_service;
Intent intent;
MyService.MyBind mybind;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
edit = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edit);
tex = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tex);
btnstart = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnstart);
btnstop = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnstop);
bind = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bind);
unbind = (Button) findViewById(R.id.unbind);
get_service = (Button) findViewById(R.id.get_service);
//把需要跳转的Service类名放进Intent对象中
intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class);
btnstart.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
//启动Service
startService(intent);
}
});
btnstop.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// 摧毁Service
stopService(intent);
}
});
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 定义一个ServiceConnection对象
final ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
// 当Activity和Service绑定成功时回调该方法
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder iBinder) {
System.out.println("service成功绑定");
// 获取MyService中onBind方法返回的自定义Mybind对象
mybind = (MyService.MyBind) iBinder;
}
// 当Activity和Service断开连接时回调该方法
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName) {
System.out.println("service解除绑定");
}
};
bind.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// 将Activity和Service绑定,第一个参数是Intend对象,第二个参数是自定义的ServiceConnection对象,第三个是int类型参数
bindService(intent, serviceConnection, BIND_DEBUG_UNBIND);
if (mybind != null) {
mybind.getData(edit.getText().toString());
}
}
});
unbind.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// 解除Service绑定
unbindService(serviceConnection);
}
});
// 从Service中获取数据
get_service.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
int get_count;
Message msg = new Message();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
// 从service中获取数据,通过Handler对象调用sendMessage()方法将数据传递给handleMessage()方法,将得到的数据通过控件显示在界面中
if (mybind != null) {
get_count = mybind.getcount();//获得Service中相关的数据
bundle.putInt("get_count", get_count);
msg.setData(bundle);
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
});
}
Handler handler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(final Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
tex.setText(String.valueOf(msg.getData().getInt("get_count")));
}
};
}
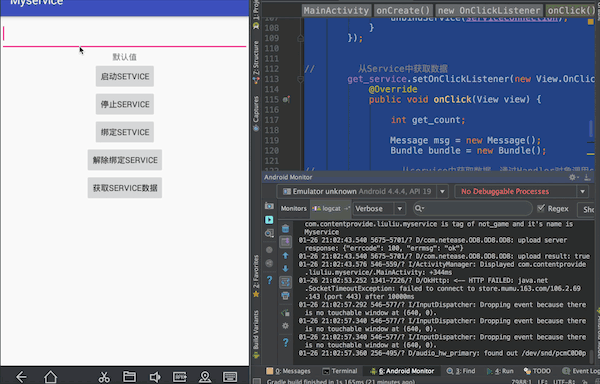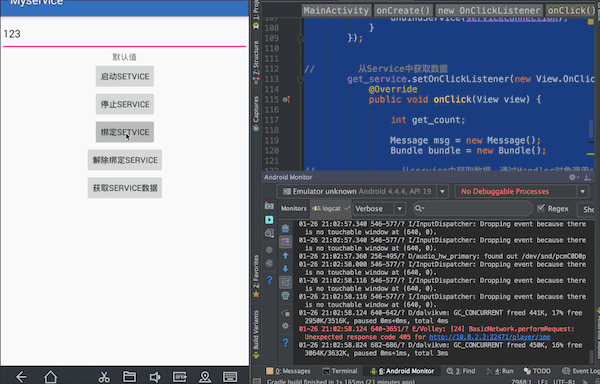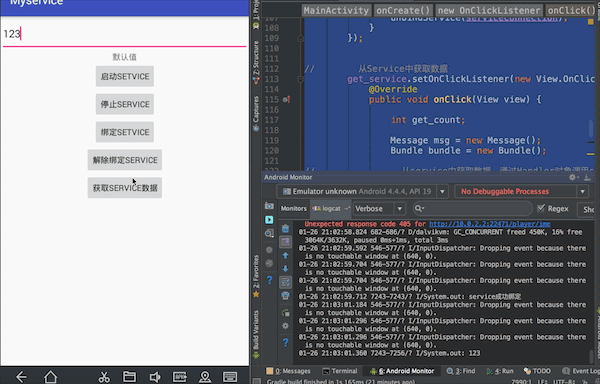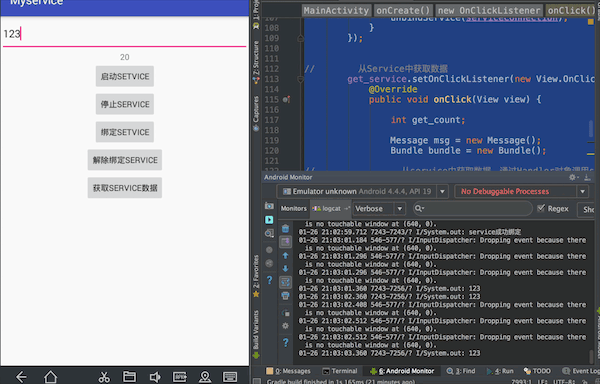
实现效果:点击绑定Service按钮将输入框中的内容传递给Service,在控制台输出;点击获取Service数据按钮从Service中获得相关数据,通过控件在界面显示。
-
android:exported:代表是否能被其他应用隐式调用,其默认值是由service中有无intent-filter决定的,如果有intent-filter,默认值为true,否则为false。为false的情况下,即使有intent-filter匹配,也无法打开,即无法被其他应用隐式调用。
-
android:name:对应Service类名
-
android:permission:是权限声明
-
android:process:是否需要在单独的进程中运行,当设置为android:process=”:remote”时,代表Service在单独的进程中运行。注意“:”很重要,它的意思是指要在当前进程名称前面附加上当前的包名,所以“remote”和”:remote”不是同一个意思,前者的进程名称为:remote,而后者的进程名称为:App-packageName:remote。
-
android:isolatedProcess :设置 true 意味着,服务会在一个特殊的进程下运行,这个进程与系统其他进程分开且没有自己的权限。与其通信的唯一途径是通过服务的API(bind and start)。
-
android:enabled:是否可以被系统实例化,默认为 true因为父标签 也有 enable 属性,所以必须两个都为默认值 true 的情况下服务才会被激活,否则不会激活。




 本文详细介绍了Android中Service组件的基本使用方法,包括启动、传递数据、绑定及解除绑定等操作,并展示了如何实现Service与Activity间的通信。
本文详细介绍了Android中Service组件的基本使用方法,包括启动、传递数据、绑定及解除绑定等操作,并展示了如何实现Service与Activity间的通信。
















 9987
9987

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








