一、数学函数
1.1 基本运算
1.round(double a[,d]) 保留d位小数,默认保留整数
2.bround(double a[,d]) 保留d为小数,财务计数法(保留位的数字是单数时,后面是500则进一位,双数时不进位)
select bround(2.1651,2); =>2.17
select bround(2.1550,2); =>2.16
select bround(2.1650,2); =>2.16
select bround(2.1551,2); =>2.16
3.floor(double a) 向下取整
4.ceil(double a) 向上取整
5.abs(double a) 绝对值
6.positive(int/double a) 本身
7.negative(int/double a) 相反数
8.sign(double/int a) 判断正负函数
9.pi() 常量 Π
10.rand() 随机数0-1
11.exp(double) | e() 自然对数
1.2 对数运算
12.log(double base ,double a) log 以base为低的对数
13. ln(double a)
1.3 数学运算
14.pow(double a,double b) a^b
15.sqrt(double a) a^(1/2)
16.cbrl(double a) a^(1/3)
17.factorial(int a) 阶乘 a最大为20
18.pmod(a,b) 取余a%b
19.greatest(int a...b) 取最大值,只能列举
20.least(int a...b) 取最小值,只能列举
1.4 进制转化
21.bin(int a) 十进制转为二进制
22.hex(int a) || unhex(string a) 十进制转为十六进制
23.conv(int a,int from_pas,int to_pas) a从from_pas进制转为to_pas进制
1.3 三角函数
24.sin(double/decmal a)||cos() tan() 三角函数
25.asin() || acos() || atan() 反三角函数
26.degrees(double a) 弧度转角度
27.radains(double a) 角度转弧度
1.4 位运算
28.shiftleft(int a,int b) a按位左移b
29.shiftright(int a,int b) a按位右移b
30.shiftleftunsigned(int a,int b) (有符号)a按位左移b
二:时间函数
2.1 获取当前的函数
1.unix_timestamp([string date][,string format]) //获取当前时间 || 指定时间的 指定格式的时间戳
select unix_timestamp(); ==>1644806355
2.current_timestamp() //获取当前时间
select current_timestamp() ==2022-02-14 14:05:51.959
3.current_date() //获取当前日期
select current_date() ==>2022-02-14
2.2 时间<=>时间戳
4.from_unixtime(bigint timestamp,string format) // 按指定格式解析时间戳
select from_unixtime(1644819052,"yyyy-MM-dd hh-mm-ss:SS") ==>2022-02-14 06-10-52:00
5.to_date(string timestamp) //时间日期->日期
select to_date("2022-02-14 06-10-52:00") -->2022-02-14
6.date_format(string s,string format) //返回指定格式的时间日期
select date_format("2022-02-14 06-10-52:00","yyyy-MM-dd"); ==>2022-02-14
2.3 获取年、季、月、日、时、分、秒
7. year(string date)
8.month(string date)
9.day(string date)
10.hour(string date)
11.minute(string date)
12.second(string date)
13.weekday(string date) //星期几(中国时间方式)
14.dayofweek(string date) //星期几(美国时间方式)
15.last_day(string date) //当月最后一天
16.trunc(string date,string format) //返回当月、当年的的都一天
select trunc("2022-02-14 06-10-52:00","YYYY"); ==>2022-01-01
select trunc("2022-02-14 06-10-52:00","MM"); ==>2022-02-01
2.4 时间运算函数
17.add_months(strirng date ,int n) //增加月份 ,n为负数的时候为较少月份
18.date_add(string date,int n) //增加日期,n为负数的时候为减少天数
19.date_sub(string date,int n) //减少日期
20.datediff(string date1,string date2) //两个日期相差的天数
select datediff("2022-02-10","2022-01-11") ==>30
select datediff("2022-01-11","2022-02-10") ==>-30
22.months_between(string date1,string date2) // 两个日期相差的月份
23.next_day(string start_date,string day_of_week) //下一个星期几的日期
day_of_week为“Mon,Tue,Wed,Thu,Fri,Sat,Sun”
三、字符串函数
3.1 字符串处理
1.lower(string str) || case(string str) //将大写字母转化为小写字母
2.upper(string str) || rcase(string str) //将小写字母转化为大写字母
3.initcap(string str) //首字母大写
4.lpad(string str,int len,string pad) //左填充
5.rpad(string str,int len,string pad) //右填充
select lpad("ad",4,1); =>11ad
select rpad("ad",4,1); =>ad11
6.ltrim(string str) || rtrim(string str) || trim(string str) //左去空格、右去空格,左右去空格
7.repeat(string str,int n) //str 重复n次
8.reverse(string str) //字符串反转
9.length(string str) //字符串长度
10.translate(string str ,string str1,string str2) //str中str1全部替换成str2
11.lenvenshtein(string str1,string str2) //两个字符串字符之间的差异
select levenshein("abc12abcd","abab") =>5 =>差的是字符 c12 cd
12.space(int n) //重复n个空格
13.like //匹配 _ 匹配一个字符 % 匹配多个字符
14.rlike //正则匹配 # [ ] { } ? + * \d \w... 用 ^ $ 匹配开始和结束
select 'abcs13' like '_cs%'; =>false
select 'abcs13' like '%cs%'; =>true
select 'abcs13' rlike '[a-z].*!'; =>false
select 'abcs13' rlike '[a-z].*'; =>true
3.2 分割字符串
15.split(string str,string par) // str字符串 按 符号par进行分割
16.str_to_map(string str,string par1,string par2) // 将字符串分割成map的结合,par1是每次map的分割符,par2是每个key与value之间的分割符号
select str_to_map("1,a;2,b",';',','); =>{"1":"a","2":"b"}
16.in_file(string str,string file) //在文件中查找是否有字符串
17.instr(string str,string substr) //substr在str中是否存在
18.locate(string substr,string str[,int n]) //substr在str中是否存在(n表示从第几个字符开始查找)
19.find_in_set(string str,string liststr) //str在liststr中第一次出现的索引(liststr以","分割
select find_in_set("s1","a2,s3,s1,f3,s1"); =>3
3.3 正则查找替换
20. regex_extract(string str,string partten,int index) #正则匹配查找(返回正则匹配到的第几个字符)
21.regex_replace(string str,string partten,string substr) #正则匹配替换(将正则匹配到的字符串替换成substr字符串)
select regexp_extract("a1,a3!a2",'^[a-z0-9].*?,([0-9a-z].*?)!.*?',1) =>a3
select regexp_replace("a1,a3!a2",'\\d',"000"); =>a000,a000!a000
3.4 字符串拼接函数
22.concat(str1,str2....) #字符串拼接
23.concat_ws(string par,str1,str2,....) #有指定符号的字符串拼接
3.5 字符串截取
24.substr(string str,int start[,int len]) #从指定索引处截取字符串(可指定截取的长度)
25. substring_index(string str,string par,int indexs) #按指定符号par截取字符串,取前indexs个字符串
select substr("s1s2s3s4s5",2); =>1s2s3s4s5
select substring_index("a,b,c,d,e,f",",",3); =>a,b,c
3.6字符串处理-- 字符串=>数组
26.sentences(string str) #将str分割成多维数组,维度分割符(? ! 句子结束符号),元素之间的分隔符(,)
27.context_ngrams(Array<Array<string>>),Array<stirng>,int a) #统计二维数组中单词数量,输出json格式,eg:array('hello'.null) 表示 有(hello+任意字符串)的数量
28.ngrams(Array<Array<string>>,int start ,int num) #统计相同单词数量,输出从名次start(倒序)开始,取前num名
select sentences("hello word!hello java?scala ok.")
==> [["hello","word"],["hello","java"],["scala","ok"]]
select context_ngrams(array(array("hello","you","fjkf"),array("hello","hive","hello","you","are")),`array`('hello',null),2);
==>[{"ngram":["you"],"estfrequency":2.0},{"ngram":["hive"],"estfrequency":1.0}]
select ngrams(array(array("hello","you","fjkf"),array("hello","hive","hello","you","are")),1,2);
==>[{"ngram":["hello"],"estfrequency":3.0},{"ngram":["you"],"estfrequency":2.0}] |
3.7 url解析
29.parse_url(string urlstring,string part[,string key]) #解析url,
urlstring: 表示url字符串
part:表示需要解析的信息 ==> PROTOCOL(协议) || HOST(服务器地址,域)|| post(端口) ||PATH(路径) || query(查询)(选参数三key) || AUTHORITY(用户信息、网址和端口号) ||USERINFO(用户信息) || REF(引用、标识,通常用#号键) || FILE(文件)
select parse_url('https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/abcdef_12a?spm=1000.2115.3001.5343','PROTOCOL');
=>https
select parse_url('https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/abcdef_12a?spm=1000.2115.3001.5343','HOST');
=>blog.youkuaiyun.com
30.parse_url_tuple(string urlstring,str1,str2....) #表示解析url的多个信息,str1...表示需要解析的参数
select parse_url_tuple('https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/abcdef_12a?spm=1000.2115.3001.5343','HOST','AUTHORITY');
=>blog.youkuaiyun.com || blog.youkuaiyun.com
3.8 json 解析
31. get_json_object(string json,string par) #解析json中的某个值. (用$.属性)
32.json_tuple(string json,par1,par2...) #解析多个属性
select get_json_object('{"name":"Bob","age":10}','$.name'); =>Bob
select json_tuple('{"name":"Bob","age":10}','name','age'); =>Bob 10
四、加密
1. md5(string par) #非对称加密(不可逆)
2. base64(binary b) #对称加密(可逆)
3.unbase64(string par) #对称解密(可逆)
4. aes_encrypt(密码,密钥) #对称加密(可逆) ,密钥是16位,输出是乱码(二进制),需要用base64()转
5.aes_decrypt(密码(二进制乱码),密钥) #对称解密(可逆) 需要用unbase64()转为二进制乱码
select md5("abc"); ==>900150983cd24fb0d6963f7d28e17f7
select base64(cast('abc' as binary)); ==> YWJj
select unbase64("YWJj"); ==> abc
select base64(aes_encrypt("abc",'1234567890123456')); ==>Iig1Q00eW0x+EAlVOUTDNw==
select aes_decrypt(unbase64("Iig1Q00eW0x+EAlVOUTDNw=="),'1234567890123456'); ==>abc
五、聚合函数
5.1 基本函数
1. count()
2. sum()
3. max()
4. min()
5. avg()
5.2 方差函数
6. var_pop(col) || variance(col) #非空集合总体变量函数(指定列的方法)(((x1-x)^2+(x2-x)^....)/n)
7.var_smap(col) #非空集合样本变量函数(样本方差)((x1-x)^2+(x2-x)^....)/(n-1)
8.stddev_pop(col) #总体标准偏离函数(标准方差)
9.stddev_samp(col) #样本标准偏离函数(样本方差)
10.cover_pop(col) #协方差函数 E=(E(X*Y)-E(X)*E(Y))/n
11.cover_samp(col) #样本协方差函数 E=(E(X*Y)-E(X)*E(Y))/(n-1)
12.corr(col1,col2) #相关系数 p=∑(((xi-x平均)^2+(yi-y平均)^2))/((∑((xi-x平均)^2))^(1/2))*((∑((yi-y平均)^2))^(1/2))
5.3 中位数函数
13. percentile(col,p) #中位数函数,p(int || double)[0-1]表示在这个字段什么位置的函数 (逆序排序)==> 返回的是col中max和min 中某个位置的值(p表示百分比)
14.percentile(col,array(p1[,p2...])) #中位数函数,求多个位置的函数 (逆序排序)
15.percentile_approx(col,p[,B] ) #近似中位数,B表示内存消耗的近似精度,B越大,结果的精度越高,默认为10000 (逆序排序) p=(0-1)
16 ,percentile_approx(col,array(p1,p2...)[,B] ) #近似中位数,获取多个值 (逆序排序)
teach_id字段的值=(1,2,3)
select percentile(teach_id,1.0) from t_teach; ==>3.0
select percentile(teach_id,0.5) from t_teach; ==>1.0
select percentile(teach_id,0.3) from t_teach; ==>1.6
select percentile(teach_id,array(0.5,1)) from test.t_teach; ==>[2.0,3.0]
select percentile_approx(teach_id,0.5) from test.t_teach; ==>1.5
select percentile_approx(teach_id,array(0.2,0.4)) from test.t_teach
==>[1.0,1.2000000000000002]
5.4 集合
17. collect_list(col) #建立数组(不去重)
18. collent_set(col) #建立数组(去重)
19.colect_ws(',',collect_list(col)) #返回字符串
六、表生成函数
6.1 侧方图 lateral view
格式 select ... from tbname lateral view 函数(col) 别名 as 字段名
1. explode(array a || map m) #单列变多行
2. posexplode(array a ) #与explode相似,单列=>两列多行(index,元素)
3. inline (array<col>) #将结构体数组提取出来并插入到表中,一列=>多列
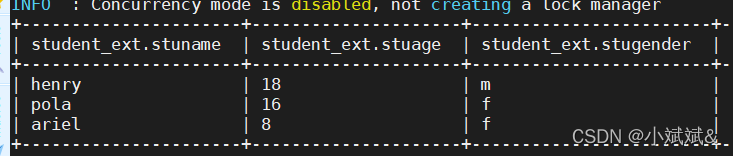
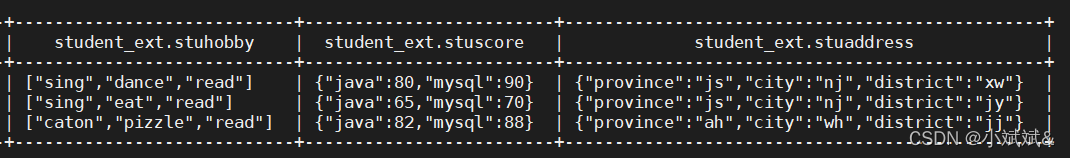
select stuname,hobby from student_ext lateral view explode(stuhobby) a as hobby;
==>侧方图相当于和原表的进行了join,连接条件是侧方图中未炸裂的字段
+----------+---------+
| stuname | hobby |
+----------+---------+
| henry | sing |
| henry | dance |
| henry | read |
| pola | sing |
| pola | eat |
| pola | read |
| ariel | caton |
| ariel | pizzle |
| ariel | read |
+----------+---------+
select stuname,index,hobby from student_ext lateral view posexplode(stuhobby) a as index,hobby;
+----------+--------+---------+
| stuname | index | hobby |
+----------+--------+---------+
| henry | 0 | sing |
| henry | 1 | dance |
| henry | 2 | read |
| pola | 0 | sing |
| pola | 1 | eat |
| pola | 2 | read |
| ariel | 0 | caton |
| ariel | 1 | pizzle |
| ariel | 2 | read |
+----------+--------+---------+
select stuname,province,city,district from student_ext lateral view inline(array(stuaddress)) a as province,city,district;
+----------+-----------+-------+-----------+
| stuname | province | city | district |
+----------+-----------+-------+-----------+
| henry | js | nj | xw |
| pola | js | nj | jy |
| ariel | ah | wh | jj |
+----------+-----------+-------+-----------+
4.stack(int n ,val1,val2...) #多列转多行 (缩短行,变为列)n表示将m行数据分为 n列,m/n行
5.group by+collect_list || collect_set #多行转单列
6.group by + case when #多行转多列
select tf.* from (select 0) t lateral view stack(3,10,20,30,40,50,60) tf;
+----------+----------+
| tf.col0 | tf.col1 |
+----------+----------+
| 10 | 20 |
| 30 | 40 |
| 50 | 60 |
+----------+----------+
t_score 原表数据
+-----------------+--------------------+----------------+
| t_score.stu_id | t_score.course_id | t_score.score |
+-----------------+--------------------+----------------+
| 1 | 1 | 80 |
| 1 | 2 | 90 |
| 1 | 3 | 99 |
| 2 | 1 | 70 |
| 2 | 2 | 60 |
| 2 | 3 | 80 |
| 3 | 1 | 80 |
| 3 | 2 | 80 |
| 3 | 3 | 80 |
| 4 | 1 | 50 |
| 4 | 2 | 30 |
| 4 | 3 | 20 |
| 5 | 1 | 76 |
| 5 | 2 | 87 |
| 6 | 1 | 31 |
| 6 | 3 | 34 |
| 7 | 2 | 89 |
| 7 | 3 | 98 |
+-----------------+--------------------+----------------+
select stu_id,collect_list(course_id) from t_score group by stu_id;
+---------+----------+
| stu_id | _c1 |
+---------+----------+
| 1 | [1,2,3] |
| 2 | [1,2,3] |
| 3 | [1,2,3] |
| 4 | [1,2,3] |
| 5 | [1,2] |
| 6 | [1,3] |
| 7 | [2,3] |
+---------+----------+
七、类型转换函数
1.baniry(string a) #转换为二进制
2.cast(a as type) #将a转换为tyoe进制下的数
八、集合函数
8.1 Map集合
1.size(Map<k,v> map) #集合长度
2.map_keys(Map<k,v> map) #获取map集合中的key
3.map_values(Map<k,v> map) #获取集合中的value的值
8.2 array数组
4.size(array a) #数组长度
5.array_contains(array a ,value v) # 查看数组中是否有某个元素
6.sort_array(array) #数组内元素排序
九、窗口函数
#控制粒度
func over(partition by filed1... order by feilda... rows between... and ...)
func over(distribute by filed1... sort by feilda... rows between ... and... || range between... and ...)
#partition by 表示从那一行进行分区处理(可选)
#order by 进行排序(可选)
#between .. and ... 表示从哪一行数据到哪一行数据(可选)
#rows表示窗口行数,range表示逻辑行数 ,unbounded preceding 第一行 unbounded following 最后一行,current row 当前行 n preceding 前几行 n following 后n行(可选)
9.1 function函数
1. first_value(col) #某分区排序内的第一个值
2. last_vlaue(col) #某分区排序内的最后一个值
3.lag(col,n,default) #统计往前的n行的col值,如果是null的话,则取默认值default
4.lead(col , n,default) #统计往后的n行的col值,如果是null的话,则取默认值default
5.ntile(n) #将数据切片,显示当前所在的片号,不能整分时,多出的部分放在第一切片
9.2 分析函数
1.row_number #排名函数,不会重复
2.rank() #排名函数,有并列名次,名次不连续1,2,2,4
3.dense_rank() #排名函数,有并列名次,名次连接1,2,2,3
4.cume_dist #分区内小于等于当前值人数/总行数 函数
5.percent_rank #当前行的rank值/分组内总行数





 这篇博客详细介绍了Hive中的各种函数,包括数学函数(如对数、三角函数、位运算)、时间函数(如获取当前时间、时间戳转换)、字符串函数(如字符串处理、分割、正则查找替换)以及加密、聚合等操作。此外,还涵盖了表生成、类型转换、集合和窗口函数的使用方法。
这篇博客详细介绍了Hive中的各种函数,包括数学函数(如对数、三角函数、位运算)、时间函数(如获取当前时间、时间戳转换)、字符串函数(如字符串处理、分割、正则查找替换)以及加密、聚合等操作。此外,还涵盖了表生成、类型转换、集合和窗口函数的使用方法。
















 927
927

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








