1.算法思想
使用层序遍历+队列实现该功能。
孩子兄弟表示法能够有效的知道某个结点的所有孩子,因此使用层序遍历时:
获取队头结点,将该结点的所有孩子都入队。入队时判断是否为目标结点,如果是则返回该队头结点,否则将该队头结点处理完后继续处理该队头结点的兄弟结点,方法与前面一致。
2.定义结构体
使用二叉链表(孩子兄弟表示法)存储树的结构。
typedef struct BiNode {
char data;
struct BiNode *firstChild;
struct BiNode *rightSib;
} BiNode, *BiTree;
3.函数实现
- Q:用于存放结点的队列
- s,parent:工作指针和双亲结点
- front,rear,last:分别表示队头、队尾以及每层的最后一个结点指针
首先判断树是否为空或者要查找的是根结点,如果是则返回NULL。否则就将队头结点出队,然后将其全部孩子入队并判断是否为目标结点。如果是则返回该队头结点。当树中所有的结点都遍历完成还没找到目标结点的双亲结点时,返回NULL表示未找到。
BiNode* getParent(BiTree T, BiNode *p) {
BiNode *Q[MAXSIZE];//队列
BiNode *s = NULL,*parent = NULL;//s为工作结点,parent为双亲结点
int front=-1, rear=-1,last = 0;//队头队尾以及每层最后一个结点指针
if(!T) {//树为空
printf("该树为空!\n");
return NULL;
}
if(T->data == p->data) {//要找的是根结点
printf("根结点:%c没有双亲结点\n",T->data);
return NULL;
}
Q[++rear] = T;//根结点入队,并修改当前双亲结点为根结点
parent = T;
while(front < rear) {
s = Q[++front];
parent = s;//修改当前结点为双亲结点,开始将该结点的孩子入队
if(s->firstChild) {//该结点有孩子,入队
Q[++rear] = s->firstChild;
if(s->firstChild->data == p->data)//如果该孩子是目标结点,则返回parent
return parent;
s = s->firstChild;//否则将该结点第一个孩子的兄弟全部入队,每次入队都判断是否为目标结点
while(s->rightSib) {
Q[++rear] = s->rightSib;
s = s->rightSib;
if(s->data == p->data)
return parent;
}
}
if(front == last) {//遍历到该层最后一个结点,修改last
last = rear;
}
}
printf("该结点:%c没有双亲结点\n",p->data);
return NULL;//没有找到,返回NULL
}
4.测试结果
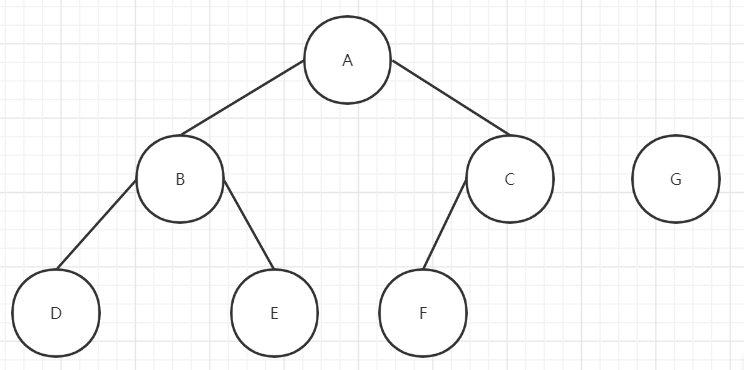
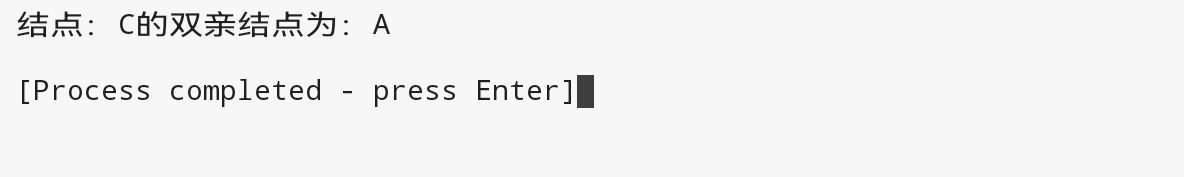
可能的几种结果如下:


5.完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MAXSIZE 50
typedef struct BiNode {
char data;
struct BiNode *firstChild;
struct BiNode *rightSib;
} BiNode, *BiTree;
BiNode* getParent(BiTree T, BiNode *p) {
BiNode *Q[MAXSIZE];//队列
BiNode *s = NULL,*parent = NULL;//s为工作结点,parent为双亲结点
int front=-1, rear=-1,last = 0;//队头队尾以及每层最后一个结点指针
if(!T) {//树为空
printf("该树为空!\n");
return NULL;
}
if(T->data == p->data) {//要找的是根结点
printf("根结点:%c没有双亲结点\n",T->data);
return NULL;
}
Q[++rear] = T;//根结点入队,并修改当前双亲结点为根结点
parent = T;
while(front < rear) {
s = Q[++front];
parent = s;//修改当前结点为双亲结点,开始将该结点的孩子入队
if(s->firstChild) {//该结点有孩子,入队
Q[++rear] = s->firstChild;
if(s->firstChild->data == p->data)//如果该孩子是目标结点,则返回parent
return parent;
s = s->firstChild;//否则将该结点第一个孩子的兄弟全部入队,每次入队都判断是否为目标结点
while(s->rightSib) {
Q[++rear] = s->rightSib;
s = s->rightSib;
if(s->data == p->data)
return parent;
}
}
if(front == last) {//遍历到该层最后一个结点,修改last
last = rear;
}
}
printf("该结点:%c没有双亲结点\n",p->data);
return NULL;//没有找到,返回NULL
}
int main() {
BiTree l1 = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));
BiNode *l2 = (BiNode *)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));
BiNode *l3 = (BiNode *)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));
BiNode *l4 = (BiNode *)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));
BiNode *l5 = (BiNode *)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));
BiNode *l6 = (BiNode *)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));
BiNode *l7 = (BiNode *)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));
l1->data = 'A';
l2->data = 'B';
l3->data = 'C';
l4->data = 'D';
l5->data = 'E';
l6->data = 'F';
l7->data = 'G';
l1->firstChild = l2;
l1->rightSib = NULL;
l2->firstChild = l4;
l2->rightSib = l3;
l3->firstChild = l6;
l3->rightSib = NULL;
l4->firstChild = NULL;
l4->rightSib = l5;
l5->firstChild = NULL;
l5->rightSib = NULL;
l6->firstChild = NULL;
l6->rightSib = NULL;
BiNode *p = l3;
BiNode *parent = getParent(l1,p);
if(parent)
printf("结点:%c的双亲结点为:%c\n",p->data,parent->data);
}





 该文介绍了一种使用层序遍历和队列的方法来寻找二叉树中特定节点的双亲节点。通过定义二叉链表结构体表示树的结构,然后实现一个函数,从根节点开始遍历,将节点及其子节点入队,直到找到目标节点或遍历结束。若未找到目标节点的双亲,则返回NULL。
该文介绍了一种使用层序遍历和队列的方法来寻找二叉树中特定节点的双亲节点。通过定义二叉链表结构体表示树的结构,然后实现一个函数,从根节点开始遍历,将节点及其子节点入队,直到找到目标节点或遍历结束。若未找到目标节点的双亲,则返回NULL。

















 636
636

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










