原文地址:http://www.mkyong.com/spring3/spring-aop-aspectj-annotation-example/
In this tutorial, we show you how to integrate AspectJ annotation with Spring AOP framework. In simple, Spring AOP + AspectJ allow you to intercept method easily.
Common AspectJ annotations :
- @Before – Run before the method execution
- @After – Run after the method returned a result
- @AfterReturning – Run after the method returned a result, intercept the returned result as well.
- @AfterThrowing – Run after the method throws an exception
- @Around – Run around the method execution, combine all three advices above.
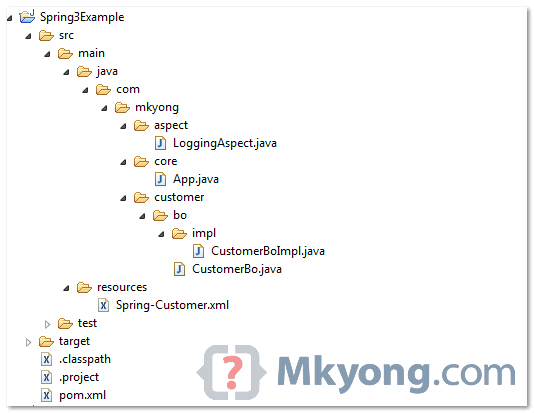
1. Directory Structure
See directory structure of this example.
2. Project Dependencies
To enable AspectJ, you need aspectjrt.jar, aspectjweaver.jar and spring-aop.jar. See following Maven
pom.xmlfile.AspectJ supported since Spring 2.0This example is using Spring 3, but the AspectJ features are supported since Spring 2.0.File : pom.xml
- <project ...>
- <properties>
- <spring.version>3.0.5.RELEASE</spring.version>
- </properties>
- <dependencies>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
- <version>${spring.version}</version>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
- <version>${spring.version}</version>
- </dependency>
- <!-- Spring AOP + AspectJ -->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
- <version>${spring.version}</version>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
- <artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
- <version>1.6.11</version>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
- <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
- <version>1.6.11</version>
- </dependency>
- </dependencies>
- </project>
3. Spring Beans
Normal bean, with few methods, later intercept it via AspectJ annotation.
- package com.mkyong.customer.bo;
- public interface CustomerBo {
- void addCustomer();
- String addCustomerReturnValue();
- void addCustomerThrowException() throws Exception;
- void addCustomerAround(String name);
- }
- package com.mkyong.customer.bo.impl;
- import com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo;
- public class CustomerBoImpl implements CustomerBo {
- public void addCustomer(){
- System.out.println("addCustomer() is running ");
- }
- public String addCustomerReturnValue(){
- System.out.println("addCustomerReturnValue() is running ");
- return "abc";
- }
- public void addCustomerThrowException() throws Exception {
- System.out.println("addCustomerThrowException() is running ");
- throw new Exception("Generic Error");
- }
- public void addCustomerAround(String name){
- System.out.println("addCustomerAround() is running, args : " + name);
- }
- }
4. Enable AspectJ
In Spring configuration file, put “
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />“, and define your Aspect (interceptor) and normal bean.File : Spring-Customer.xml
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd ">
- <aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
- <bean id="customerBo" class="com.mkyong.customer.bo.impl.CustomerBoImpl" />
- <!-- Aspect -->
- <bean id="logAspect" class="com.mkyong.aspect.LoggingAspect" />
- </beans>
4. AspectJ @Before
In below example, the
NotelogBefore()method will be executed before the execution of customerBo interface,addCustomer()method.
AspectJ “pointcuts” is used to declare which method is going to intercept, and you should refer to this Spring AOP pointcuts guide for full list of supported pointcuts expressions.
File : LoggingAspect.java
- package com.mkyong.aspect;
- import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
- @Aspect
- public class LoggingAspect {
- @Before("execution(* com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo.addCustomer(..))")
- public void logBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
- System.out.println("logBefore() is running!");
- System.out.println("hijacked : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
- System.out.println("******");
- }
- }
Run it(applicationContext.xml)
- public static void main(String args[]){
- ApplicationContext appContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
- CustomerBo customer = (CustomerBo) appContext.getBean("customerBo");
- customer.addCustomer();
- }
5. AspectJ @After
In below example, the
logAfter()method will be executed after the execution of customerBo interface,addCustomer()method.File : LoggingAspect.java
.- package com.mkyong.aspect;
- import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
- @Aspect
- public class LoggingAspect {
- @After("execution(* com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo.addCustomer(..))")
- public void logAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
- System.out.println("logAfter() is running!");
- System.out.println("hijacked : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
- System.out.println("******");
- }
- }
Run it
- CustomerBo customer = (CustomerBo) appContext.getBean("customerBo");
- customer.addCustomer();
6. AspectJ @AfterReturning
In below example, the
logAfterReturning()method will be executed after the execution of customerBo interface,addCustomerReturnValue()method. In addition, you can intercept the returned value with the “returning” attribute.To intercept returned value, the value of the “returning” attribute (result) need to be same with the method parameter (result).
File : LoggingAspect.java
- package com.mkyong.aspect;
- import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
- @Aspect
- public class LoggingAspect {
- @AfterReturning(
- pointcut = "execution(* com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo.addCustomerReturnValue(..))",
- returning= "result")
- public void logAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
- System.out.println("logAfterReturning() is running!");
- System.out.println("hijacked : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
- System.out.println("Method returned value is : " + result);
- System.out.println("******");
- }
- }
Run it
- CustomerBo customer = (CustomerBo) appContext.getBean("customerBo");
- customer.addCustomerReturnValue();
7. AspectJ @AfterReturning
In below example, the
logAfterThrowing()method will be executed if the customerBo interface,addCustomerThrowException()method is throwing an exception.File : LoggingAspect.java
- package com.mkyong.aspect;
- import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
- @Aspect
- public class LoggingAspect {
- @AfterThrowing(
- pointcut = "execution(* com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo.addCustomerThrowException(..))",
- throwing= "error")
- public void logAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable error) {
- System.out.println("logAfterThrowing() is running!");
- System.out.println("hijacked : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
- System.out.println("Exception : " + error);
- System.out.println("******");
- }
- }
Run it
- CustomerBo customer = (CustomerBo) appContext.getBean("customerBo");
- customer.addCustomerThrowException();
Output
- addCustomerThrowException() is running
- logAfterThrowing() is running!
- hijacked : addCustomerThrowException
- Exception : java.lang.Exception: Generic Error
- ******
- Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Exception: Generic Error
- //...
8. AspectJ @Around
In below example, the
File : LoggingAspect.javalogAround()method will be executed before the customerBo interface,addCustomerAround()method, and you have to define the “joinPoint.proceed();” to control when should the interceptor return the control to the originaladdCustomerAround()method.
- package com.mkyong.aspect;
- import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
- @Aspect
- public class LoggingAspect {
- @Around("execution(* com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo.addCustomerAround(..))")
- public void logAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
- System.out.println("logAround() is running!");
- System.out.println("hijacked method : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
- System.out.println("hijacked arguments : " + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
- System.out.println("Around before is running!");
- joinPoint.proceed(); //continue on the intercepted method
- System.out.println("Around after is running!");
- System.out.println("******");
- }
- }
Run it
- CustomerBo customer = (CustomerBo) appContext.getBean("customerBo");
- customer.addCustomerAround("mkyong");
Output
- logAround() is running!
- hijacked method : addCustomerAround
- hijacked arguments : [mkyong]
- Around before is running!
- addCustomerAround() is running, args : mkyong
- Around after is running!
- ******





 本文介绍如何在Spring框架中集成AspectJ注解实现方法拦截。通过具体示例展示了@Before、@After、@AfterReturning、@AfterThrowing及@Around等注解的使用方法。
本文介绍如何在Spring框架中集成AspectJ注解实现方法拦截。通过具体示例展示了@Before、@After、@AfterReturning、@AfterThrowing及@Around等注解的使用方法。
















 593
593

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








