java:异常处理
1 介绍
java语言的异常捕获结构由try、catch、finally3部分组成。其中,try语句存放的是可能发生异常的java语句;catch程序块用来激发被捕获的异常;finally是最后执行部分,无论try语句块代码如何退出,都将执行finally语句块。
tips:python的异常捕获(else是:如果没有异常执行这块代码,except可以一行语句添加多个可能发生的异常)

除数不能为0
无论成功失败,最终都会执行
2 语法
idea快捷输入try/catch语句:

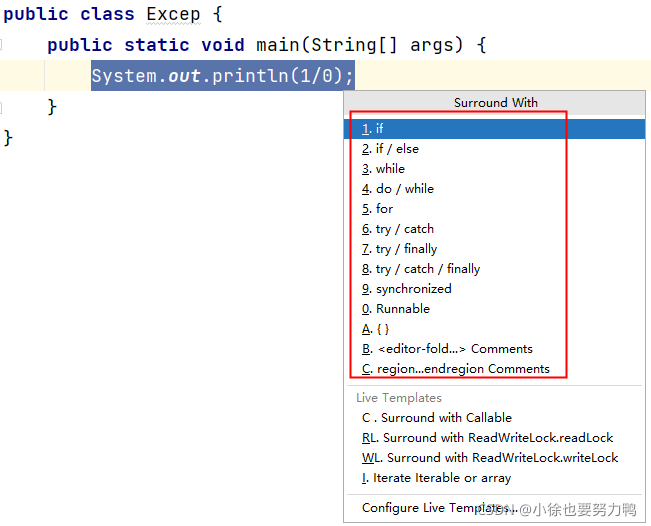
catch代码块中语句,常用的函数来获取异常有关的信息:
e.getMessage():用于输出错误性质;
toString():给出异常的类型和性质;
printStackTrace():指出异常的类型、性质、栈层次及出现在程序中的位置。
package com.base;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Excep {
public static void main(String[] args) {
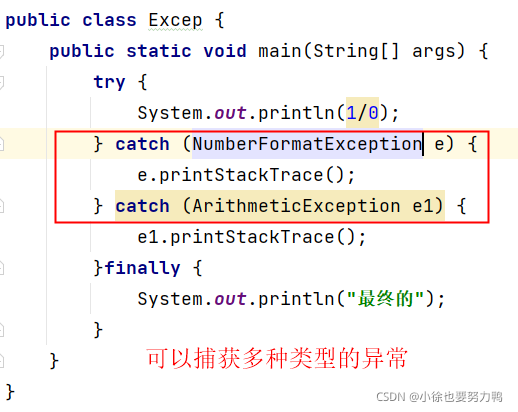
try {
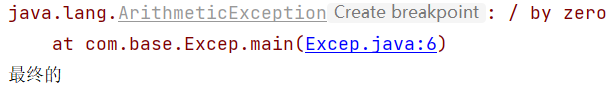
System.out.println(1/0);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ArithmeticException e1) {
System.out.println(e1.getMessage());
System.out.println("------");
System.out.println(e1.toString());
System.out.println("------");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(e1.getStackTrace()));
System.out.println("------");
e1.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("最终的");
}
}
}

3 finally语句块
完整的异常处理语句一定要包含finally语句,无论程序中有无异常发生,并且无论之间的try-catch是否顺利执行完毕,都会执行finally语句。
以下4种特殊情况,finally块不会被执行:
在finally语句块中发生了异常;
在前面的代码中使用了System.exit()退出程序;
程序所在的线程死亡;
关闭CPU。
4 自定义异常
继承Exception类即可自定义异常类,步骤如下:
(1)创建自定义异常类
(2)在方法中通过throw关键字抛出异常对象
(3)如果在当前抛出异常的方法中处理异常,可以使用try-catch语句块捕获并处理,否则在方法的声明处通过throws关键字指明要抛出给方法调用者的异常,继续进行下一步操作
(4)在出现异常方法的调用者中捕获并处理异常
自定义异常:
package com.base;
public class XXException extends Exception{
public XXException(String errMsg){
//父类构造方法
super(errMsg);
}
}
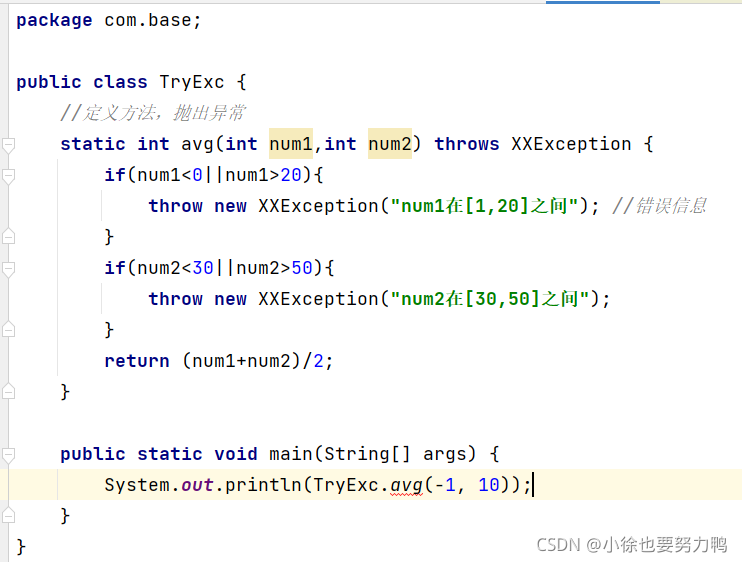
第一种方式:main方法增加throws 抛出该异常
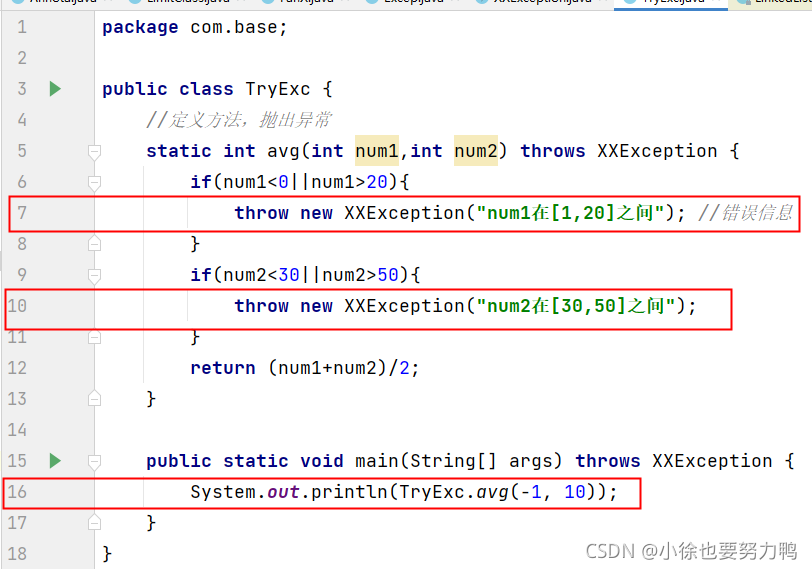
public class TryExc {
//定义方法,抛出异常
static int avg(int num1,int num2) throws XXException {
if(num1<0||num1>20){
throw new XXException("num1在[1,20]之间"); //错误信息
}
if(num2<30||num2>50){
throw new XXException("num2在[30,50]之间");
}
return (num1+num2)/2;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws XXException {
System.out.println(TryExc.avg(-1, 10));
}
}

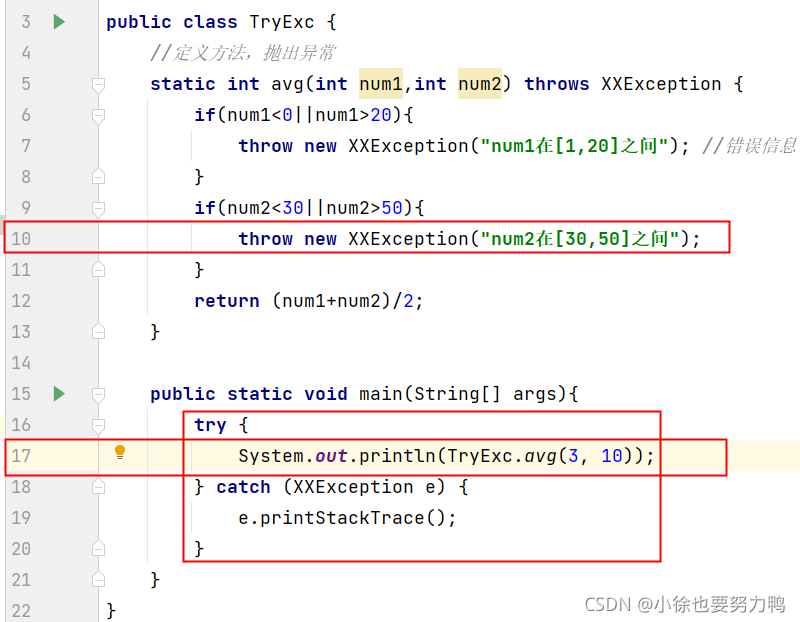
第二种方式:
System.out.println(TryExc.avg(-1, 10))后面ctrl+alt+T,增加try-catch语句:
5 在方法中抛出异常-throws、throw关键字
若某个方法可能会发生异常,但不想在当前方法中处理这个异常,则可以使用throws、throw关键字在方法中抛出异常
5.1 throws
throws关键字通常被应用在声明方法时,用来指定方法可能抛出的异常。多个异常可使用逗号分隔。
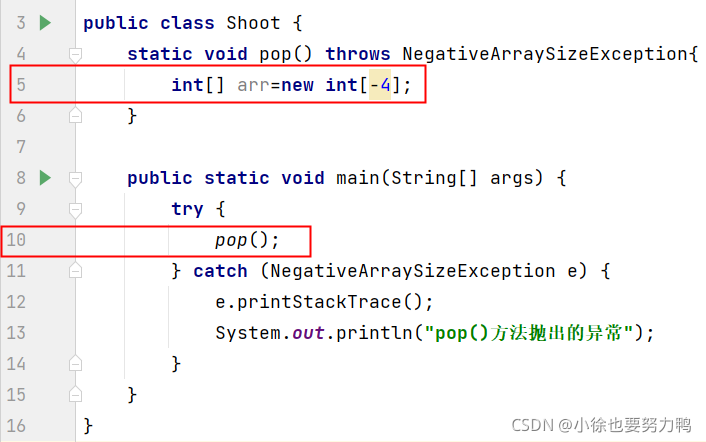
package com.base;
public class Shoot {
static void pop() throws NegativeArraySizeException{
int[] arr=new int[-4];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
pop();
} catch (NegativeArraySizeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("pop()方法抛出的异常");
}
}
}
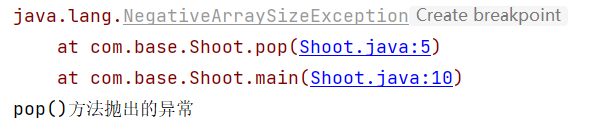
注意:使用throws关键字将异常抛给上一级后,如果不想处理该异常,可以继续向上抛出,但最终要有能够处理该异常的代码。
如果是Error、RuntimeException或他们的子类,可以不使用throws关键字来声明要抛出的异常,编译仍能顺利通过,但在运行时会被系统抛出。
5.2 throw关键字抛出异常
throw关键字通常用于方法体中,并且抛出一个异常对象。程序在执行到throw语句时立即终止,后面的语句都不执行。通过throw抛出异常后,如果想在上一级代码中来捕获并处理异常,则需要在抛出异常的方法中使用throws关键字在方法的声明中指明要抛出的异常;如果要捕捉throw抛出的异常,则必须使用try-catch语句块。
throw通常用来抛出用户自定义异常。
自定义异常类:
package com.base;
public class MyException extends Exception{ //创建自定义异常类
String msg;
public MyException(String ErrorMessage){
msg=ErrorMessage;
}
//注意,要调用自定义类的e.getMessage()打印信息,要重写Exception类的getMessage()方法
//否则自定义类的e.getMessage()返回的值是null
@Override
public String getMessage(){
return msg;
}
}
同级目录定义Captor类捕获异常:
package com.base;
public class Captor {
static int quotient(int x,int y)throws MyException{
if(y<0){
throw new MyException("除数不能是负数");
}
return x/y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int res=quotient(3,-1);
} catch (MyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("getMessage结果:"+e.getMessage());
}catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("除数,不可以为0.");
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("程序发生了其它的异常。");
}
}
}
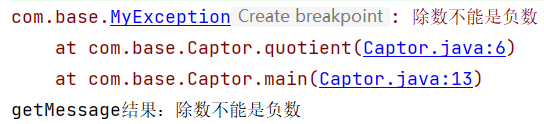
上面代码,如果调用quotient(3,0),程序跳转到catch (ArithmeticException e)代码块执行;如果还发生其他的异常,跳转到catch (Exception e)代码块执行。如果将catch (Exception e)写在其他的异常前面,其它的异常将永远得不到执行,因为Exception是所有异常类的父类。
6 运行时异常
RuntimeException异常是程序运行过程中产生的异常。java类库的每个包中都定义了异常类。所有这些类都是Throwable类的子类。Throwable类派生了两个子类,分别是Exception和Error类。Error类及其子类用来描述java运行系统中的内部错误以及资源耗尽的错误,这类错误比较严重。Exception类称为非致命性类,可以通过捕获处理使程序继续执行。Exception类又根据错误发生的原因分为RuntimeException异常和除RuntimeException之外的异常。
java中常见的RuntimeException异常,这些异常可以通过try-catch捕获:
NullPointerException:空指针异常
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:数组下标越界异常
ArithmeticException:算术异常
ArrayStoreException:数组中包含不兼容的值抛出的异常
IllegalArgumentException:非法参数异常
SecurityException:安全性异常
NegativeArraySizeException:数组长度为负异常
运行时异常例子:
MyRunException.java
package com.base1;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.ToStringBuilder;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.ToStringStyle;
public class MyRunException extends RuntimeException{
protected String errMsg;
protected ErrorEnum errorEnum;
public MyRunException(){super();}
public MyRunException(ErrorEnum e){
super(e.getDesc());
this.errorEnum=e;
}
public MyRunException(ErrorEnum e,String errMsg){
super(e.getDesc());
this.errorEnum=e;
this.errMsg=errMsg;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return ToStringBuilder.reflectionToString(this, ToStringStyle.SHORT_PREFIX_STYLE);
}
}
interface MyErrorLev {
//类似python的logging日志等级
String INFO="10";
String WARNING="20";
String ERROR="30";
String FATAL="40";
}
enum ErrorEnum{
NO_LOGIN_AUTH("101", "No_Login_Auth", "没有登录权限", MyErrorLev.ERROR),
ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT("201","Illegal_Argument","参数非法", MyErrorLev.WARNING);
private final String code;
private final String name;
private final String desc;
private final String level;
ErrorEnum(String code, String name, String desc, String level){
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
this.desc = desc;
this.level = level;
}
public String getLevel() {
return level;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
}
RunTiExc.java
package com.base1;
public class RunTiExc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
myAssert(false,ErrorEnum.NO_LOGIN_AUTH);
}
public static void myAssert(boolean b,ErrorEnum e1){
if(!b){
throw new MyRunException(e1);
}
}
}
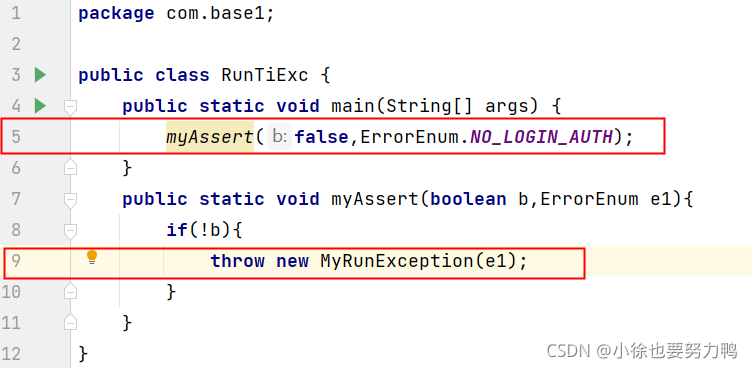
Exception in thread "main" MyRunException[errMsg=<null>,errorEnum=NO_LOGIN_AUTH,detailMessage=没有登录权限,cause=com.base1.MyRunException@330bedb4,stackTrace={},suppressedExceptions=[]]
at com.base1.RunTiExc.myAssert(RunTiExc.java:9)
at com.base1.RunTiExc.main(RunTiExc.java:5)























 382
382

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








