mongoDB是非关系型数据库
database:数据库
collection:集合,类似于mysql中的table
document:文档,类似于mysql表中的一条数据
Mongoose:
是一个对象文档模型库,方便使用代码操作Mongodb数据库
介于mongoDB和代码逻辑之间,在代码实现中使用,更好的实现业务逻辑,从而和mongoDB做交互。
没有表链接,使用Population
操作步骤:
1、链接
//1、链接数据库,参数-数据库地址url,mongodb:ip:端口/数据库名称
mongoose.connect(mongodb:127.0.0.1:27017/dbName);
//2、设置回调
var db = mongoose.connection();
//2.1 设置链接失败的回调
db.on('error', console.error.bind(console, 'connection error:'));
//2.2 设置链接成功的回调
db.once('open', function() {
// we're connected!
});
//2.3 设置链接关闭的回调
db.on('close', ()=>{});
2、创建schema,在mongoose中,一切基于schema。得到了一个带有 String 类型 name 属性的 schema
var kittySchema = mongoose.Schema({
name: String
});3、创建model,model 是我们构造 document 的 Class,是Schema 编译来的构造函数,它们的实例就代表着可以从数据库保存和读取的 documents。 从数据库创建和读取 document 的所有操作都是通过 model 进行的
var Kitten = mongoose.model('Kitten', kittySchema);Schema
创建文档的结构对象,约束文档的属性和属性值的类型
const schema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: 'string',
size: 'string'
})model
模型对象:对模型操作的封装对象,model可以完成对文档的增删改查操作
var schema = new mongoose.Schema({ name: 'string', size: 'string' });
//创建模型对象
var Tank = mongoose.model('Tank', schema);documents
每一个document是model的实例,代表着 MongoDB 文档的一对一映射
//创建schema
var schema = new mongoose.Schema({ name: 'string', size: 'string' });
//创建model
var Tank = mongoose.model('Tank', schema);
//用model创建document
var small = new Thank({size:'small'})回调函数
所有的回调函数都使用 callback(error, result) 这种模式。如果查询时发生错误,error 参数即是错误文档, result 参数会是 null。如果查询成功,error 参数是 null,result 即是查询的结果。
查询结果的格式取决于做什么操作: findOne() 是单个文档(有可能是 null ),find() 是文档列表, count() 是文档数量,update() 是被修改的文档数量
操作
字段类型
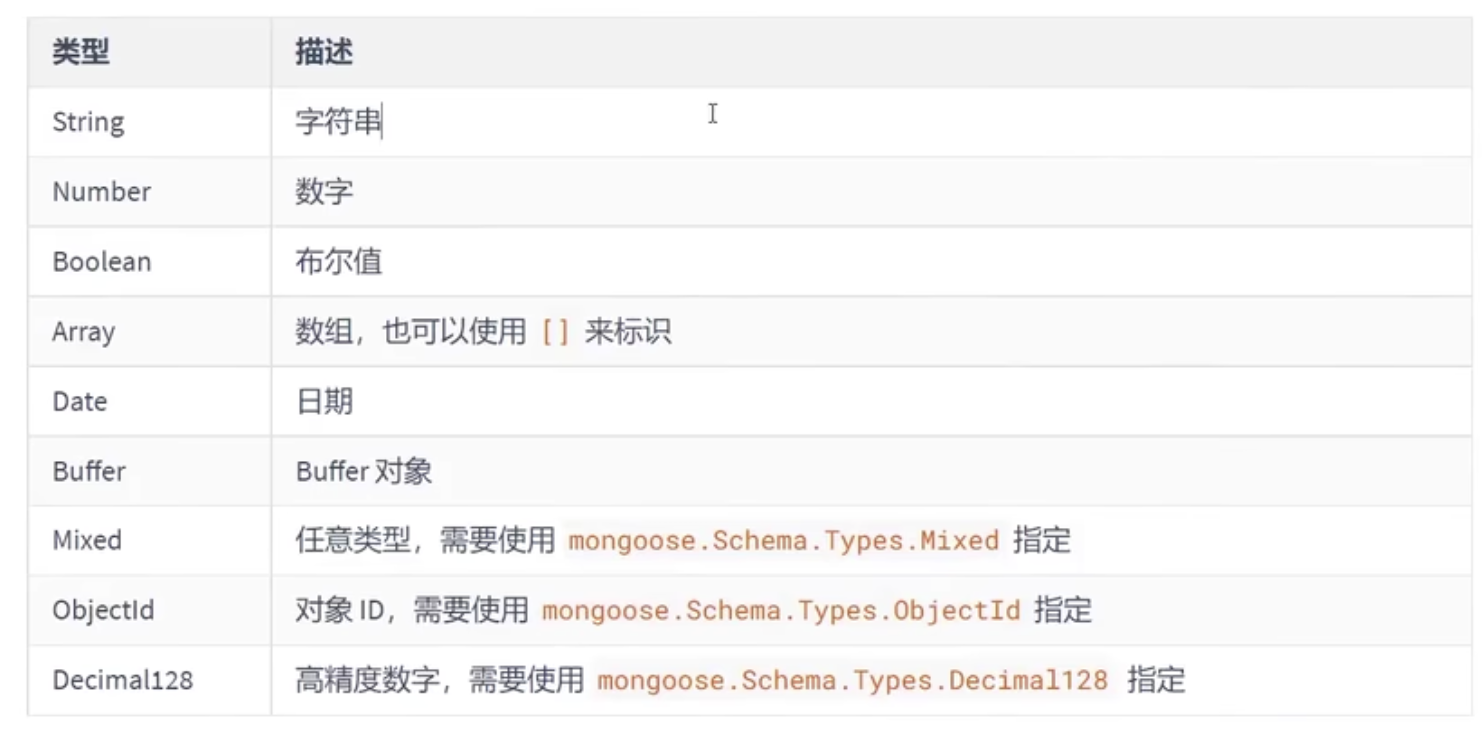
字段验证
对文档属性的值做校验
属性必填
const schema = new mongoose.Schema({
//name属性
name: {
type:string,属性类型
required:true //属性必填
},
size: 'string'
})设置属性默认值
const schema = new mongoose.Schema({
//name属性
name: {
type:string,属性类型
default:'这是一个默认值name' //设置默认值
},
size: 'string'
})枚举值
设置的值必须是枚举值中列举的选项
const schema = new mongoose.Schema({
//name属性
name: string,
size: string,
gender:{
type:string,
enum:['男','女']//设置的值必须是数组中的
}
})唯一值
unique需要重建集合才能有效果
const schema = new mongoose.Schema({
//name属性
name: {
type:string,//属性类型
default:'这是一个默认值name', //设置默认值
unique:true //设置其唯一性
},
size: 'string'
})1、新增
Tank.create({name:'西游记',size:'larger'},
//回调函数,err:错误信息,data:插入成功后的文档对象
(err,data)=>{});2、删除
依赖model,model 的 remove 方法可以删除所有匹配查询条件( conditions )的文档
//删除:param1-删除条件,param2-回调函数
Tank.remove({ size: 'large' }, function (err) {
if (err) return handleError(err);
// removed!
});3、更新
依赖Model
case1:用findById先查询到document,回调函数中更新:用=赋值size属性,再使用docuemnt.save
Tank.findById(id, function (err, tank) {
if (err) return handleError(err);
tank.size = 'large';
tank.save(function (err, updatedTank) {
if (err) return handleError(err);
res.send(updatedTank);
});
});case2:用findById先查询到document,回调函数中更新,使用.set()对size属性重新赋值,再使用document.save更新
Tank.findById(id, function (err, tank) {
if (err) return handleError(err);
tank.set({ size: 'large' });
tank.save(function (err, updatedTank) {
if (err) return handleError(err);
res.send(updatedTank);
});
});case3:只更新不获取,model.update(...)
Tank.update({ _id: id }, { $set: { size: 'large' }}, callback);case4:更新且获取数据,model.findAndUpdate
Tank.findByIdAndUpdate(id, { $set: { size: 'large' }}, { new: true }, function (err, tank) {
if (err) return handleError(err);
res.send(tank);
});4、查询
查询依赖model,支持 MongoDB 的高级查询语法。查询文档可以用 model 的 find, findById, findOne, 和 where 这些静态方法
Tank.find({ size: 'small' }).where('createdDate').gt(oneYearAgo).exec(callback);- 传入callback参数,操作会被立即执行,查询结果被传给回调函数(callback)
var Person = mongoose.model('Person', yourSchema);
// 查询每个 last name 是 'Ghost' 的 person, select `name` 和 `occupation` 字段
Person.findOne({ 'name.last': 'Ghost' }, 'name occupation', function (err, person) {
if (err) return handleError(err);
// Prints "Space Ghost is a talk show host".
console.log('%s %s is a %s.', person.name.first, person.name.last,
person.occupation);
});- 不传入callback参数,Query 的一个实例(一个 query 对象)被返回,这个 query 提供了构建查询器的特殊接口
// 查询每个 last name 是 'Ghost' 的 person,query是Query类型的变量
var query = Person.findOne({ 'name.last': 'Ghost' });
// select `name` 和 `occupation` 字段
query.select('name occupation');
// 然后执行查询
query.exec(function (err, person) {
if (err) return handleError(err);
// Prints "Space Ghost is a talk show host."
console.log('%s %s is a %s.', person.name.first, person.name.last,
person.occupation);
});- Query 能够用链式语法构建查询器,无需指定 JSON 对象,下面两个示例等效
// With a JSON doc
Person.
find({
occupation: /host/,
'name.last': 'Ghost',
age: { $gt: 17, $lt: 66 },
likes: { $in: ['vaporizing', 'talking'] }
}).
limit(10).
sort({ occupation: -1 }).
select({ name: 1, occupation: 1 }).
exec(callback);
// Using query builder
Person.
find({ occupation: /host/ }).
where('name.last').equals('Ghost').
where('age').gt(17).lt(66).
where('likes').in(['vaporizing', 'talking']).
limit(10).
sort('-occupation').
select('name occupation').
exec(callback);- 流式( stream )处理 MongoDB 的查询结果,需要调用 Query.cursor() 函数获得 QueryCursor 的一个实例
var cursor = Person.find({ occupation: /host/ }).cursor();
cursor.on('data', function(doc) {
// Called once for every document
});
cursor.on('close', function() {
// Called when done
});- 不支持联表查询,可以使用Population
5、条件控制
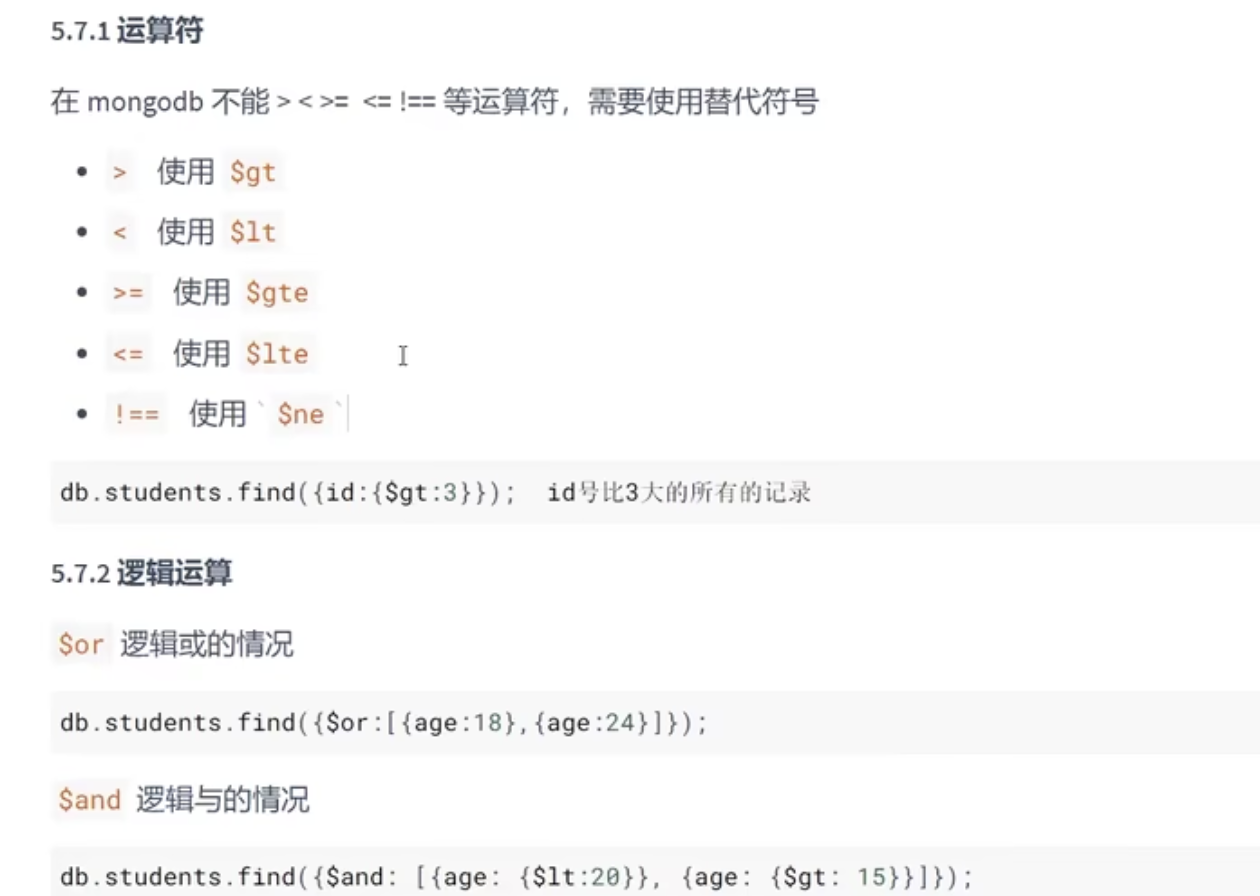
5.1 运算符

5.2 逻辑运算

5.3 正则匹配

6、个性化读取
6.1 字段筛选
只返回需要的字段

6.2 数据排序

6.3 数据截取
实现分页





 本文详细介绍了MongoDB的基本概念,如集合、文档和Mongoose的使用,以及如何通过Mongoose连接数据库、创建Schema、Model和进行增删改查操作,包括字段类型、验证、回调函数、查询语法和流式处理。同时提到了Population和个性化读取功能。
本文详细介绍了MongoDB的基本概念,如集合、文档和Mongoose的使用,以及如何通过Mongoose连接数据库、创建Schema、Model和进行增删改查操作,包括字段类型、验证、回调函数、查询语法和流式处理。同时提到了Population和个性化读取功能。
















 102
102

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








