原文地址:https://medium.com/@farshidabazari/improve-recyclerview-performance-ede5cec6c5bf
In my last project, I’ve been working on an application that has a vertical list which every item has a horizontal image list, just like Instagram. and I faced many problems with RecyclerView.
If you google it you can find some useful solutions to improve the performance but in my case (maybe on yours too) they couldn’t help me!
So I decided to share my problems and my solutions.
My Application Demo
What were my problems
- RecyclerView doesn’t scroll smoothly
- Some first items scrolled slowly
- Horizontal photo slider(like Instagram) doesn’t work very well
The First Problem
As I said my first problem was about RecyclerView’s smooth scroll.
I have a vertical RecyclerView that every item has a photo slider, some texts, a rating bar, a favorite image button, and a button.
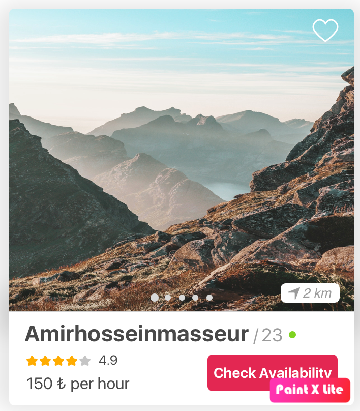
An item of RecyclerView
As you can see it’s not a complex view, except photo slider, On the other hands we can see this photo slider in Instagram and Airbnb application and they work perfectly without any lag.
The first thing that came to my mind was removing photo slider, I’ve just commented it to initialize from my adapter, but RecyclerView doesn’t scroll smoothly again.
So let’s go to solve the problem
1. The first thing is about RecyclerView initializing.
If it is possible to set the items height at the XML file, add this line to your RecyclerView Initializing method:
recyclerView.setHasFixedSize(true)
By this method, you told RecyclerView to don’t calculate items size every time they added and removed from RecyclerView.
2. Another method is ItemViewCacheSize
recyclerView.setItemViewCacheSize(20)
Set the number of offscreen views to retain before adding them to the potentially shared recycled view pool.
The offscreen view cache stays aware of changes in the attached adapter, allowing a LayoutManager to reuse those views unmodified without needing to return to the adapter to rebind them.
In other words, when you scroll the RecyclerView such that there’s a view that is just barely completely off-screen, the RecyclerView will keep it around so that you can scroll it back into view without having to re-execute onBindViewHolder()
3. setHasStableIds is our next method
adapter.setHasStableIds(true)
and in your adapter add this line:
override fun getItemId(position: Int): Long {
return position.toLong()
}
RecyclerView will attempt to synthesize visible structural change events for adapters that report that they have stable IDs when this method is used. This can help for the purposes of animation and visual object persistence but individual item views will still need to be rebound and relaid out.
These methods help you to improve your RecyclerView performance and maybe they could solve your all problems but in my case, my list scrolled with a bad lag especially on Samsung devices. so try to find other solutions besides these helpful methods.
After 2 days I found the problem, unfortunately, it was about ConstraintLayout.
I design my items layout with ConstraintLayout and because of many constrained tags it was heavy to inflate, so I change it to Linear and Relative layout and most of my problems solved.
Here you can see the performance of them:
RecyclerView with ConstraintLayout
RecyclerView without ConstraintLayout
It’s awesome, ConstraintLayout is an amazing layout to design, it’s easy to use and understanding, but in this case, I think it’s really awful. It’s very heavy to inflating and binding views.
Don’t use ConstraintLayout in RecyclerView
The Second Problem
The second problem is some first items scrolled slowly because onCreateViewHolder() called for the first 6 items.
So we can tell RecyclerView to load all first 6 items at the first initializing.
But How? PreCachingLayoutManager is the solution.
We can create a layout manager to load some offscreen (out of screen) items at the first time.
class PreCachingLayoutManager : LinearLayoutManager {
private val defaultExtraLayoutSpace = 600
private var extraLayoutSpace = -1
private var context: Context? = null
constructor(context: Context?) : super(context) {
this.context = context
}
constructor(context: Context, extraLayoutSpace: Int) : super(context) {
this.context = context
this.extraLayoutSpace = extraLayoutSpace
}
constructor(context: Context, orientation: Int, reverseLayout: Boolean) : super(
context,
orientation,
reverseLayout
) {
this.context = context
}
fun setExtraLayoutSpace(extraLayoutSpace: Int) {
this.extraLayoutSpace = extraLayoutSpace
}
override fun getExtraLayoutSpace(state: RecyclerView.State): Int {
return if (extraLayoutSpace > 0) {
extraLayoutSpace
} else defaultExtraLayoutSpace
}
}
This is the PreCachingLayoutManager that extended from LinearLayoutManager. As you can see there is a method named setExtraLayoutSpace with a parameter. this method returns the amount of extra space that should be laid out by LayoutManager, and the parameter is in the pixel, it means if you wanna preload items you can set it to [DeviceHeight*2] as extra layout space.
But be careful, extending the extra layout space is especially expensive. so after your, some first items loaded set it to the default value.
The Last Problem
Here we have a vertical RecyclerView with some Horizontal list in each item.
These Horizontal lists are PhotoSlider and if you search about how to implement PhotoSlider you find many libraries have been implemented by ViewPager.
But in this case that we have so many items, and also each item has many ViewPagers, so we faced with a bunch of Fragments to show just some pictures.
So I recommend using horizontal RecyclerView with LinearSnapHelper() to act like ViewPager instead of ViewPager for PhotoSlider.
We have some optimization here to
When the user swipes the side-wise the inner RecyclerView recycles the views and gives you a smooth scroll. But this is not the case when the user scrolls vertically. Each of the views of the inner RecyclerView is inflated again. This is because each of the nested RecyclerViews has a view pool of its own.
We can fix this by setting a single view pool for all the inner RecyclerViews.
photoSliderRecyclerView.setRecycledViewPool(RecyclerView.RecycledViewPool())
allows you to set a custom view pool to your recyclerView. The code looks like this
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
//Create viewHolder etc
holder.photoSliderRecyclerView.setRecycledViewPool(viewPool);
}
Thanks, Amir Hossein Ghasemi for pair programming.
Improve RecyclerView Performance
In my last project, I’ve been working on an application that has a vertical list which every item has a horizontal image list, just like Instagram. and I faced with many problems with RecyclerView.
If you google it you can find some useful solutions to improve the performance but in my case (maybe on yours too) they couldn’t help me!
So I decided to share my problems and my solutions.
My Application Demo
What were my problems
- RecyclerView doesn’t scroll smoothly
- Some first items scrolled slowly
- Horizontal photo slider(like Instagram) doesn’t work very well
The First Problem
As I said my first problem was about RecyclerView’s smooth scroll.
I have a vertical RecyclerView that every item has a photo slider, some texts, a rating bar, a favorite image button, and a button.

An item of RecyclerView
As you can see it’s not a complex view, except photo slider, On the other hands we can see this photo slider in Instagram and Airbnb application and they work perfectly without any lag.
The first thing that came to my mind was removing photo slider, I’ve just commented it to initialize from my adapter, but RecyclerView doesn’t scroll smoothly again.
So let’s go to solve the problem
1. The first thing is about RecyclerView initializing.
If it is possible to set the items height at the XML file, add this line to your RecyclerView Initializing method:
recyclerView.setHasFixedSize(true)
By this method, you told RecyclerView to don’t calculate items size every time they added and removed from RecyclerView.
2. Another method is ItemViewCacheSize
recyclerView.setItemViewCacheSize(20)
Set the number of offscreen views to retain before adding them to the potentially shared recycled view pool.
The offscreen view cache stays aware of changes in the attached adapter, allowing a LayoutManager to reuse those views unmodified without needing to return to the adapter to rebind them.
In other words, when you scroll the RecyclerView such that there’s a view that is just barely completely off-screen, the RecyclerView will keep it around so that you can scroll it back into view without having to re-execute onBindViewHolder()
3. setHasStableIds is our next method
adapter.setHasStableIds(true)
and in your adapter add this line:
override fun getItemId(position: Int): Long {
return position.toLong()
}
RecyclerView will attempt to synthesize visible structural change events for adapters that report that they have stable IDs when this method is used. This can help for the purposes of animation and visual object persistence but individual item views will still need to be rebound and relaid out.
These methods help you to improve your RecyclerView performance and maybe they could solve your all problems but in my case, my list scrolled with a bad lag especially on Samsung devices. so try to find other solutions besides these helpful methods.
After 2 days I found the problem, unfortunately, it was about ConstraintLayout.
I design my items layout with ConstraintLayout and because of many constrained tags it was heavy to inflate, so I change it to Linear and Relative layout and most of my problems solved.
Here you can see the performance of them:
RecyclerView with ConstraintLayout
RecyclerView without ConstraintLayout
It’s awesome, ConstraintLayout is an amazing layout to design, it’s easy to use and understanding, but in this case, I think it’s really awful. It’s very heavy to inflating and binding views.
Don’t use ConstraintLayout in RecyclerView
The Second Problem
The second problem is some first items scrolled slowly because onCreateViewHolder() called for the first 6 items.
So we can tell RecyclerView to load all first 6 items at the first initializing.
But How? PreCachingLayoutManager is the solution.
We can create a layout manager to load some offscreen (out of screen) items at the first time.
class PreCachingLayoutManager : LinearLayoutManager {
private val defaultExtraLayoutSpace = 600
private var extraLayoutSpace = -1
private var context: Context? = null
constructor(context: Context?) : super(context) {
this.context = context
}
constructor(context: Context, extraLayoutSpace: Int) : super(context) {
this.context = context
this.extraLayoutSpace = extraLayoutSpace
}
constructor(context: Context, orientation: Int, reverseLayout: Boolean) : super(
context,
orientation,
reverseLayout
) {
this.context = context
}
fun setExtraLayoutSpace(extraLayoutSpace: Int) {
this.extraLayoutSpace = extraLayoutSpace
}
override fun getExtraLayoutSpace(state: RecyclerView.State): Int {
return if (extraLayoutSpace > 0) {
extraLayoutSpace
} else defaultExtraLayoutSpace
}
}
This is the PreCachingLayoutManager that extended from LinearLayoutManager. As you can see there is a method named setExtraLayoutSpace with a parameter. this method returns the amount of extra space that should be laid out by LayoutManager, and the parameter is in the pixel, it means if you wanna preload items you can set it to [DeviceHeight*2] as extra layout space.
But be careful, extending the extra layout space is especially expensive. so after your, some first items loaded set it to the default value.
The Last Problem
Here we have a vertical RecyclerView with some Horizontal list in each item.
These Horizontal lists are PhotoSlider and if you search about how to implement PhotoSlider you find many libraries have been implemented by ViewPager.
But in this case that we have so many items, and also each item has many ViewPagers, so we faced with a bunch of Fragments to show just some pictures.
So I recommend using horizontal RecyclerView with LinearSnapHelper() to act like ViewPager instead of ViewPager for PhotoSlider.
We have some optimization here to
When the user swipes the side-wise the inner RecyclerView recycles the views and gives you a smooth scroll. But this is not the case when the user scrolls vertically. Each of the views of the inner RecyclerView is inflated again. This is because each of the nested RecyclerViews has a view pool of its own.
We can fix this by setting a single view pool for all the inner RecyclerViews.
photoSliderRecyclerView.setRecycledViewPool(RecyclerView.RecycledViewPool())
allows you to set a custom view pool to your recyclerView. The code looks like this
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
//Create viewHolder etc
holder.photoSliderRecyclerView.setRecycledViewPool(viewPool);
}
Thanks, Amir Hossein Ghasemi for pair programming.








 本文分享了在开发类似Instagram应用中遇到的RecyclerView性能问题及解决方案,包括使用setHasFixedSize、ItemViewCacheSize、setHasStableIds优化初始化,避免ConstraintLayout,预加载布局管理器,以及使用LinearSnapHelper和单一回收池提升滑动体验。
本文分享了在开发类似Instagram应用中遇到的RecyclerView性能问题及解决方案,包括使用setHasFixedSize、ItemViewCacheSize、setHasStableIds优化初始化,避免ConstraintLayout,预加载布局管理器,以及使用LinearSnapHelper和单一回收池提升滑动体验。
















 7502
7502

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








