文章目录
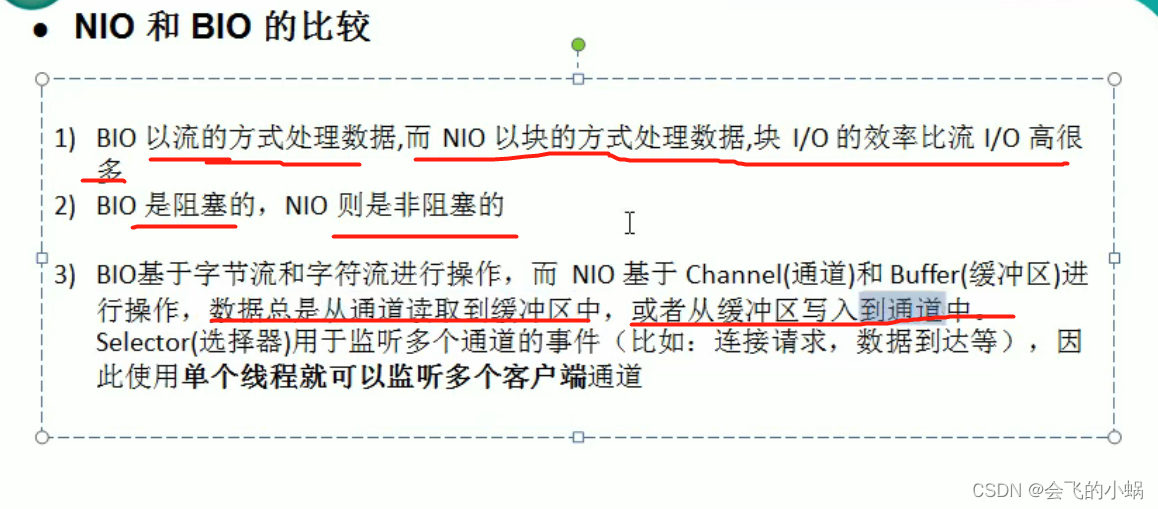
0、BIO与NIO的比较
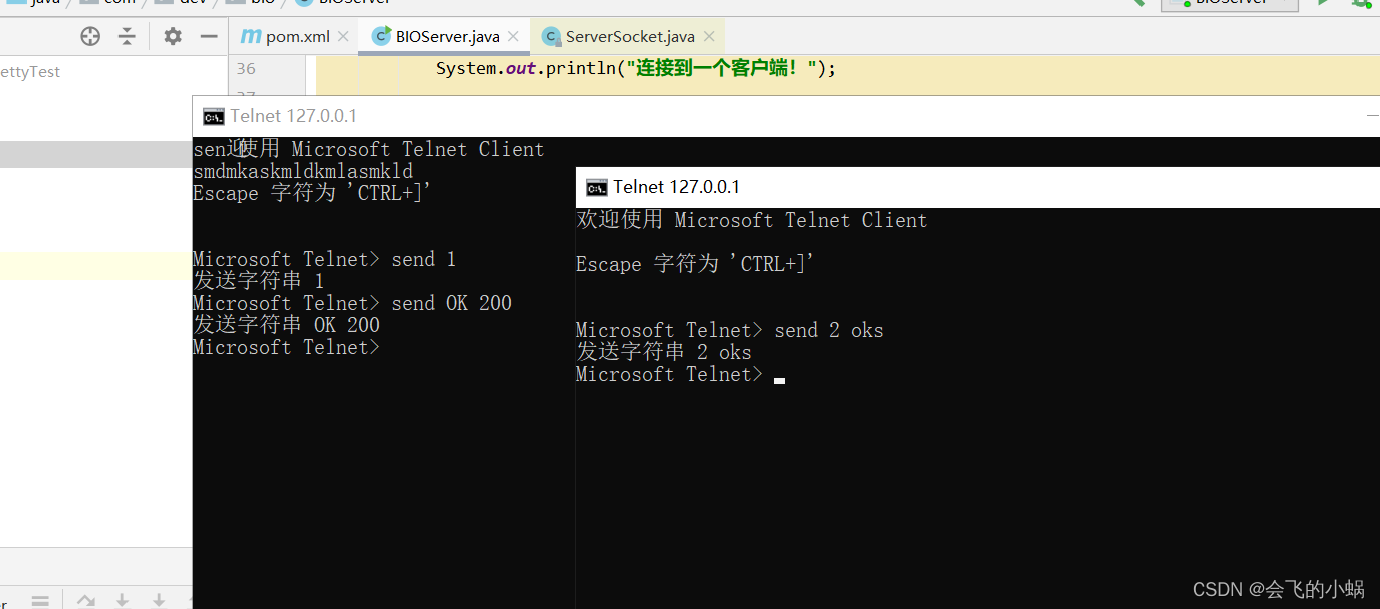
1、BIO实例
启动主函数后使用"cmd"窗口:
实验代码:
package com.dev.bio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* @author : lei.yu
* @date :2022/3/24 下午 4:54
* @description :
* @modyified By:
*/
public class BIOServer {
private final static int port=6666;//监听端口
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//线程池机制
//思路
//1. 创建一个线程池
//2. 如果有客户端连接,就创建一个线程,与之通讯(单独写一个方法)
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//线程池
//创建ServerSocket
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);//socket
//监听,等待客户端连接
System.out.println("服务启动!");
while (true){
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("等待连接");
//会阻塞在accept()
final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("连接到一个客户端!");
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
handler(socket);
}
}
);
}
}
//编写一个handler方法,和客户端通讯
public static void handler(Socket socket) {
try {
System.out.println("线程信息id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + "名字 = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
//通过socket获取输入流
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
//循环的读取客户端发送的数据
while (true) {
System.out.println("线程信息id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + "名字 = " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("read....");
int read = inputStream.read(bytes);
if (read != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, read));//输出客户端发送的数据
} else {
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("关闭和client的连接");
try {
socket.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
#连接
telnet 127.0.0.1 6666
#输入
"Ctrl+]"
#输入内容(send + 你想打印的内容)
send OK 200
2、NIO实例
buffer缓冲区实例
package com.dev.nio;
import java.nio.IntBuffer;
/**
* @author : lei.yu
* @date :2022/3/27 上午 8:34
* @description : NIO缓冲区 Buffer实例
* @modyified By:
*/
public class BufferServer {
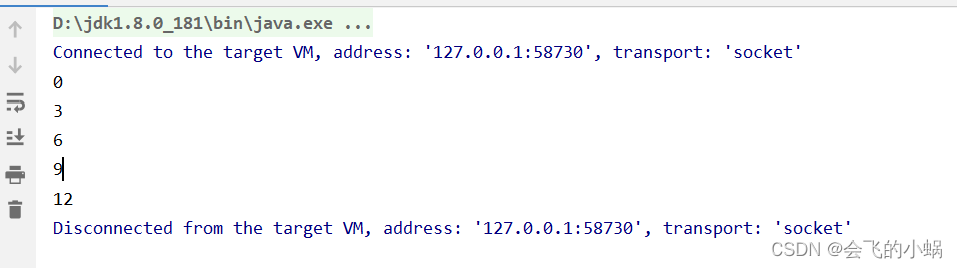
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个buffer ,大小为5
IntBuffer intBuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(5);
for (int i = 0; i < intBuffer.capacity(); i++) {
intBuffer.put(i*3);
}
//转换 存入为输出, 读写切换,这个是必须做的事
intBuffer.flip();
while (intBuffer.hasRemaining()){
// intBuffer.get(); 自己会维护一个索引,获取之后指针自动向下一个移动
System.out.println(intBuffer.get());
}
}
}
打印结果:
NIO三大核心原理总结

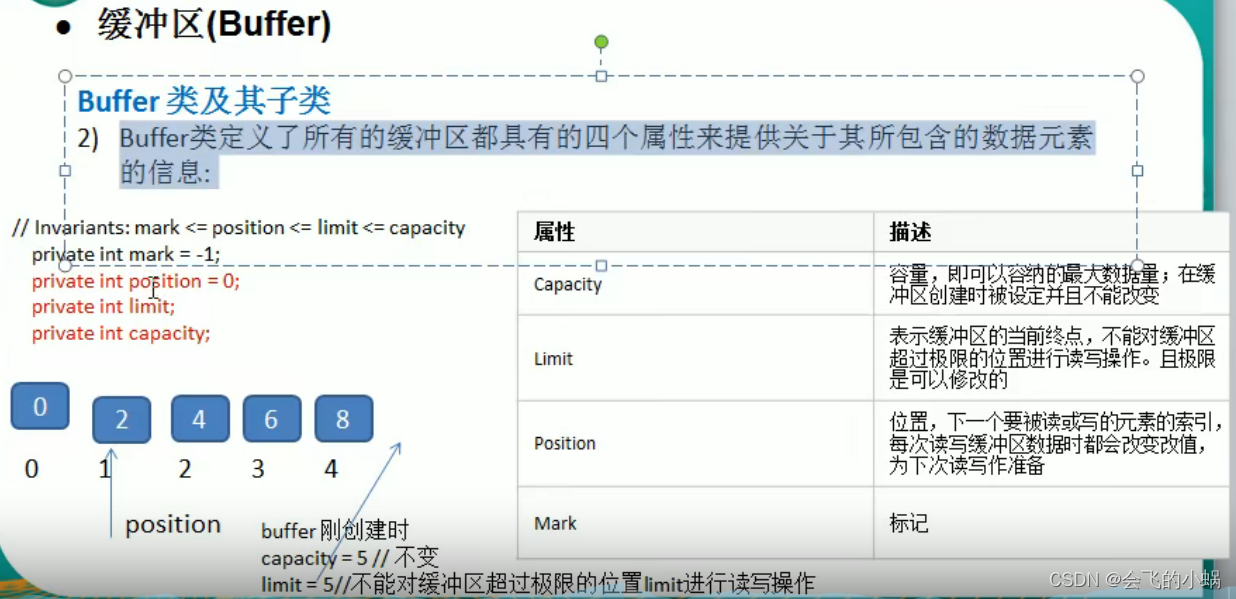
Buffer四大属性
Channel 结合 Buffer 的使用案例
写入流

输出流里面包含channel :
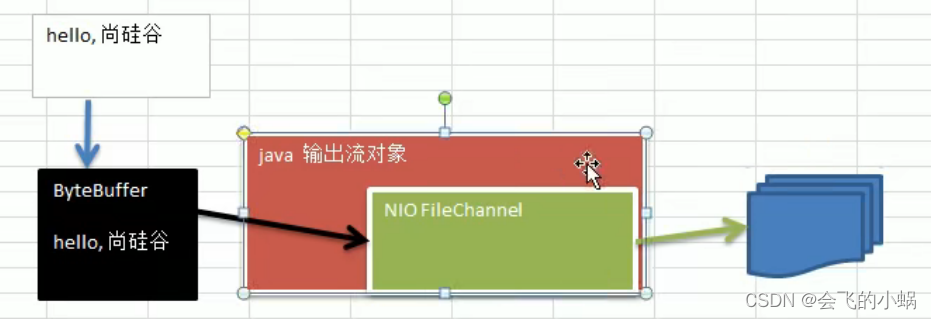
代码示例:
package com.dev.nio;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* @author :
* @date :2022/3/27 下午 1:30
* @description :
* @modyified By:
*/
public class ChannelBufferServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str="OK,海绵宝宝";
//创建一个输出流channel
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\file001.txt");
//创建一个通道
//通过 FileOutputStream 获取一个 filechannel,其实这个channel 的真是类型是 FilechannelImpl
FileChannel channel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//创建一个缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//将数据放入缓冲区
ByteBuffer put = byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
//切换输入流为输出流
byteBuffer.flip();
//将缓冲区数据写入到流中
channel.write(byteBuffer);
//关闭这个流
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
读取流
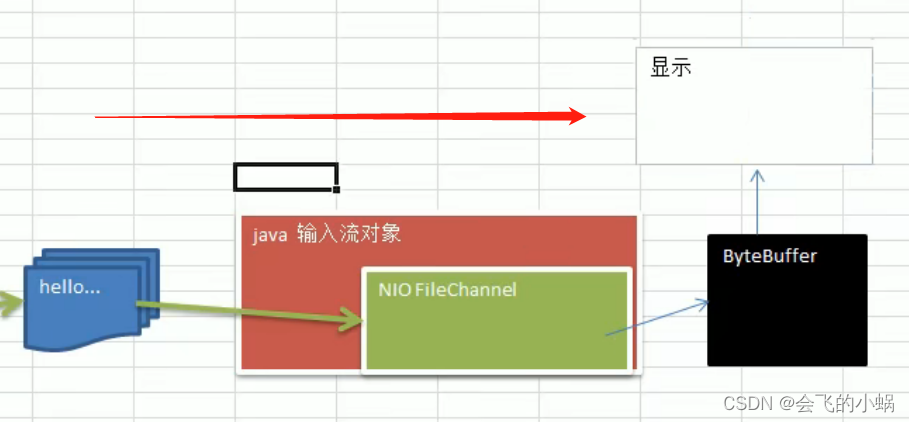
package com.dev.nio;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* @author :
* @date :2022/3/27 下午 2:26
* @description :
* @modyified By:
*/
public class channelBufferInputServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
File file = new File("d:\\file001.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
FileChannel channel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) file.length());
//读取缓冲区
channel.read(byteBuffer);
//将byteBuffer字节流转成字符串
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
使用一个buffer完成文件拷贝
完成目标:

实现原理图:
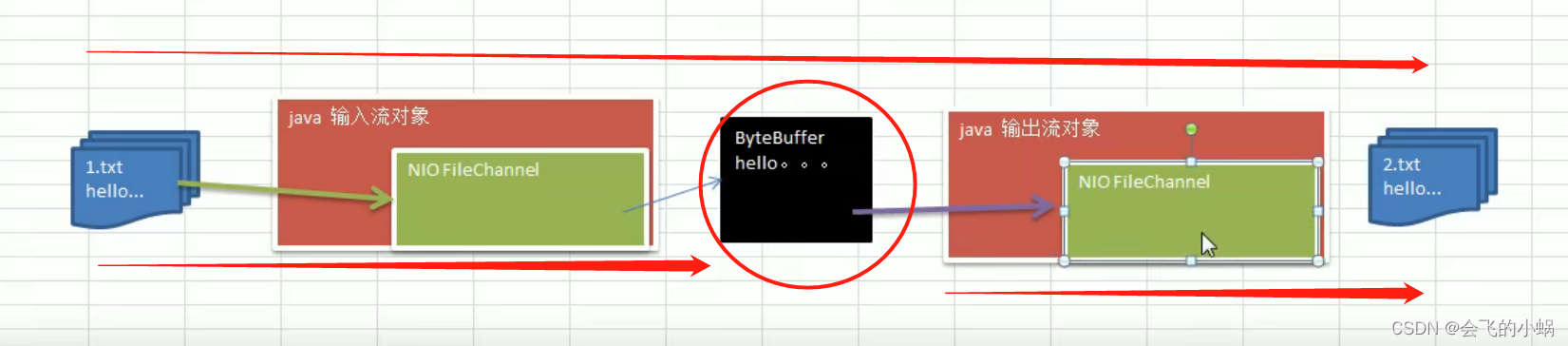
实验源码:
package com.dev.nio;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* @author :
* @date :2022/3/27 下午 6:08
* @description :
* @modyified By:
*/
public class BufferCopyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//创建一个
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\file001.txt");
FileChannel channel01 = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\file002.txt");
FileChannel channel02 = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//定义一个缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//遍历读取
while (true){
//1.必须清空,不然指针不能复位
byteBuffer.clear();
int read = channel01.read(byteBuffer);
if(read==-1){
break;
}
//2.切换通道[必须]
byteBuffer.flip();
channel02.write(byteBuffer);
}
}
}
使用 transferFrom 完成拷贝

实验源码:
package com.dev.nio;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* @author :lei.yu
* @date :2022/3/28 上午 8:01
* @description :
* @modyified By:
*/
public class NIOFileChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\file001.txt");
FileChannel channel01 = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\file002.txt");
FileChannel channel02 = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//拷贝
channel02.transferFrom(channel01,0,channel01.size());
//关闭通道
fileInputStream.close();
channel01.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
channel02.close();
}
}
MappedByteBuffer是一种效率低于零拷贝,但高于传统IO的IO操作。
特点:
可以让文件直接在内存(堆外)进行修改,操作系统不需要拷贝一次
实验源码:
package com.dev.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* @author :
* @date :2022/3/28 上午 8:52
* @description :
* @modyified By:
*/
public class MappedBetyBufferServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile rw = new RandomAccessFile("d:\\1.txt", "rw");
//获取通道
FileChannel channel = rw.getChannel();
/**
* 参数1:FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE 使用的读写模式
* 参数2:0 : 可以直接修改的起始位置
* 参数3:5:是映射到内存的大小(不是索引位置),即将1.txt 的多少个字节映射到内存
* 可以直接修改的范围就是 0-5,不包含 5
* 实际类型 DirectByteBuffer
*/
MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 5);
mappedByteBuffer.put(0,(byte)'H');
mappedByteBuffer.put(3,(byte)'9');
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException
* at java.nio.Buffer.checkIndex(Buffer.java:540)
* at java.nio.DirectByteBuffer.put(DirectByteBuffer.java:306)
* at com.dev.nio.MappedBetyBufferServer.main(MappedBetyBufferServer.java:30)
*/
mappedByteBuffer.put(5,(byte)'Y');//越界报错
rw.close();
System.out.println("修改成功~~~");
}
}
Selector 选择器
选择器基本简介:

选择器特点:
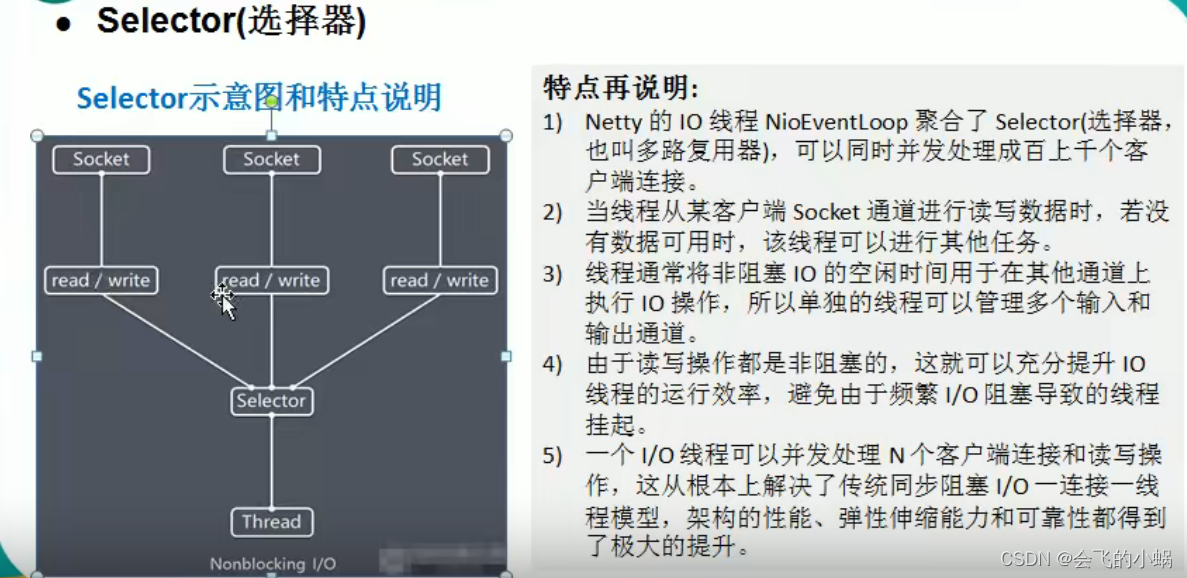
选择器的类方法:

选择器的注意事项:

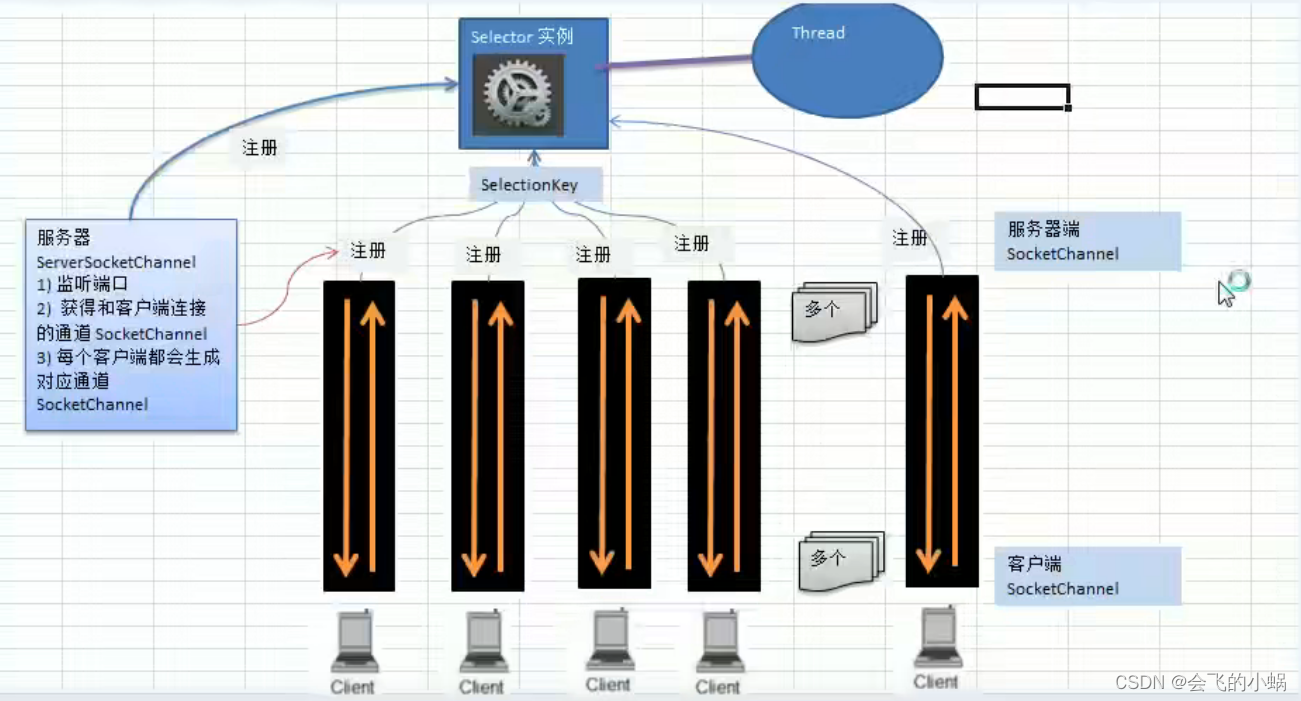
NIO重点分析图:

对图的说明:
- 1、当客户端连接时,会通过ServerSocketChannel 得到 SocketChannel。
- 2、将 SocketChannel 注册到 Selector 上,register ( Selector sel , int ops)。
- 3、注册后返回一个 SelectionKey , 会和该Selector 关联【集合】。
- 4、Selector 进行监听 select 方法,返回有事件发生的通道个数。
- 5、进一步得到各个 SelectionKey(有事件发生)
- 6、在通过SelectionKey 反相获取 SocketionKey ,方法 channel()
- 7、可以通过得到 channel , 完成业务处理
NIO 非阻塞网络编程快速入门
案例:
1、编写一个 NIO 入门案例,实现服务器端和客户端之间的数据简单通讯(非阻塞)
2、目的:理解 NIO 非阻塞网络编程机制
服务端源码 NIOServer :
package com.dev.nio.NIOTEST;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author :
* @date :2022/3/28 下午 1:43
* @description :
* @modyified By:
*/
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建ServerSocketChannel -> ServerSocket
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//得到一个Selector对象
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//绑定一个端口 :6666 ,在服务端进行监听
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(6666));
//设置为非阻塞【这一步很重要,不然会报错,默认为阻塞】
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//把serverSocketChannel 注册到 selector 关心事件 为 OP_ACCEPT
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
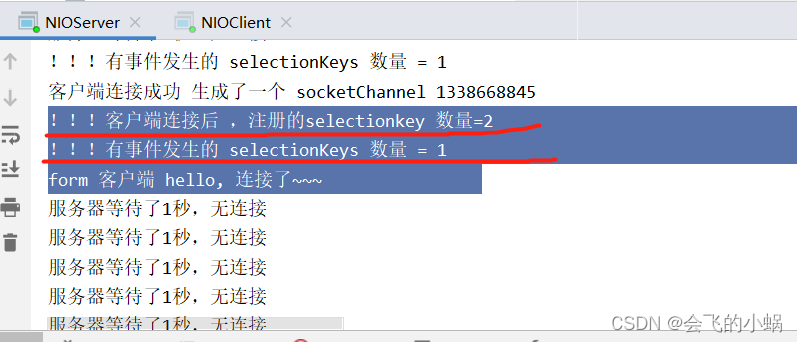
System.out.println("注册后的selectionkey 数量=" + selector.keys().size()); // 注册数
//循环等待客户端连接
while (true) {
//这里我们等待1秒,如果没有事件发生, 返回
if(selector.select(1000) == 0) { //没有事件发生
System.out.println("服务器等待了1秒,无连接");
continue;
}
//如果返回的>0, 就获取到相关的 selectionKey集合
//1.如果返回的>0, 表示已经获取到关注的事件
//2. selector.selectedKeys() 返回关注事件的集合
// 通过 selectionKeys 反向获取通道
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
System.out.println("!!!有事件发生的 selectionKeys 数量 = " + selectionKeys.size());
//遍历 Set<SelectionKey>, 使用迭代器遍历
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
//获取到SelectionKey
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
//根据key 对应的通道发生的事件做相应处理
if(key.isAcceptable()) { //如果是 OP_ACCEPT, 有新的客户端连接
//该该客户端生成一个 SocketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println("客户端连接成功 生成了一个 socketChannel " + socketChannel.hashCode());
//将 SocketChannel 设置为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将socketChannel 注册到selector, 关注事件为 OP_READ, 同时给socketChannel
//关联一个Buffer
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
System.out.println("!!!客户端连接后 ,注册的selectionkey 数量=" + selector.keys().size()); //2,3,4..
}
if(key.isReadable()) { //发生 OP_READ
//通过key 反向获取到对应channel
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
//获取到该channel关联的buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer)key.attachment();
channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("form 客户端 " + new String(buffer.array()));
}
//手动从集合中移动当前的selectionKey, 防止重复操作
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
对于带码的一些解释:
1、对操作系统有一定了解的同学,就会大概知道这里监听的是一个Accept通道。这个通道的
作用就是监听,实际建立连接了还会有一个通道。
2、简单说一下为什么。因为客户端发请求的时候,服务器这边是肯定要先有一个监听通道,
监听某个端口是否有客户端要建立链接,如果有客户端想要建立链接,那么会再创建一个和
客户端真正通信的通道。
3、如果有其它客户端还想要建立链接,这个Accept监听端口监听到了,就会再创建几个真正
的通信通道。
4、也就是Server的一个端口可以建立多个TCP连接,因为IP层协议通过
目标地址+端口+源地址+源端口四个信息识别一个上下文
客户端源码 NIOClient :
package com.dev.nio.NIOTEST;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
/**
* @author :
* @date :2022/3/28 下午 1:59
* @description :
* @modyified By:
*/
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//得到一个网络通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//设置非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//提供服务器端的ip 和 端口
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 6666);
//连接服务器
if (!socketChannel.connect(inetSocketAddress)) {
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
System.out.println("因为连接需要时间,客户端不会阻塞,可以做其它工作..");
}
}
//...如果连接成功,就发送数据
String str = "hello, 连接了~~~";
//Wraps a byte array into a buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
//发送数据,将 buffer 数据写入 channel
socketChannel.write(buffer);
System.in.read();
}
}
实验结果(推荐自己尝试):
SelectionKey,表示 Selector 和网络通道的注册关系
SelectionKey,表示 Selector 和网络通道的注册关系,共四种:
- int OP_ACCEPT:有新的网络连接可以 accept,值为 16
- int OP_CONNECT:代表连接已经建立,值为 8
- int OP_READ:代表读操作,值为 1
- int OP_WRITE:代表写操作,值为 4
源码中:
public static final int OP_READ = 1 << 0;
public static final int OP_WRITE = 1 << 2;
public static final int OP_CONNECT = 1 << 3;
public static final int OP_ACCEPT = 1 << 4;





 本文详细介绍了BIO和NIO的对比,包括BIO服务器和客户端实例,NIO的Buffer缓冲区操作,以及NIO的核心原理如Buffer属性、Channel与Buffer结合、MappedByteBuffer、Selector选择器等。通过实例展示了如何使用NIO进行文件操作和网络通信,并深入解析了SelectionKey在非阻塞网络编程中的角色。
本文详细介绍了BIO和NIO的对比,包括BIO服务器和客户端实例,NIO的Buffer缓冲区操作,以及NIO的核心原理如Buffer属性、Channel与Buffer结合、MappedByteBuffer、Selector选择器等。通过实例展示了如何使用NIO进行文件操作和网络通信,并深入解析了SelectionKey在非阻塞网络编程中的角色。

















 2291
2291

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










