同栈一样,队列也是操作受限的线性表
两种存储结构:顺序存储结构和链式存储结构
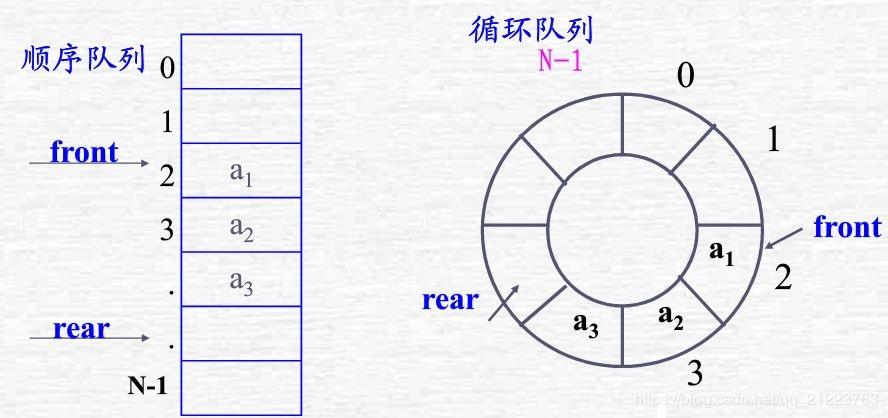
循环队列
用一个数组存储队列,按照“先进先出”的原则,一般设计成如右图的循环队列,注意"假溢出"的问题:rear始终加1,不能再入队了,但实际上出队前面还有空位置;变成循环队列之后,究竟如何判断队列为满?:队列大小为m时,有m-1个元素就认为是队满。
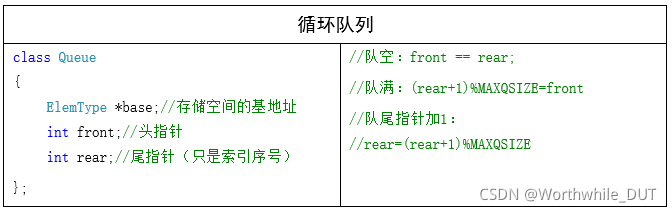
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAXSIZE = 10;
const int ERROR = 0;
const int OK = 1;
typedef int ElemType;
class Myqueue
{
public:
Myqueue();
int Queue_Length();
bool Queue_Push(ElemType record);//入队
bool Queue_Pop(); //出队
ElemType GetHead(); //获得队头元素
~Myqueue();
private:
ElemType* base;
int front;
int rear;
};
Myqueue::Myqueue()
{
this->base = new ElemType[MAXSIZE];
this->front = 0;
this->rear = 0;
}
int Myqueue::Queue_Length()//因为是循环队列
{
return (rear - front + MAXSIZE) % MAXSIZE;//循环的原因不要返回rear-front
}
bool Myqueue::Queue_Push(ElemType record)
{
if ((this->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == this->front)//作为循坏队列的队满的条件
return false;
base[this->rear] = record;
this->rear = (this->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;//不再rear++,而是采用循环的rear = (rear + 1) % MAXSIZE
return true;
}
bool Myqueue::Queue_Pop()
{
if (this->front == this->rear)
return false;
this->front = (this->front + 1 ) % MAXSIZE;
}
ElemType Myqueue::GetHead()
{
if (this->front == this->rear)
return false;
return base[this->front];
}
Myqueue::~Myqueue()
{
if (base)
{
delete[] this->base;
this->base = NULL;
}
this->front = 0;
this->rear = 0;
}
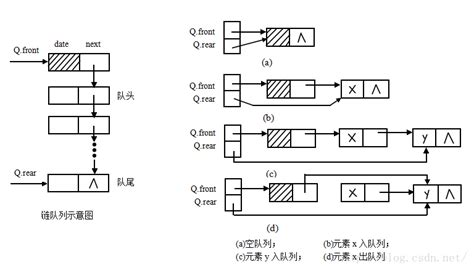
队列的链式存储
只有链式存储结构的表示,没有入队、出队等基本操作
class Node
{
ElemType data;
Node* next;
};
class LinkQueue
{
Node* front;//队头指针
Node* rear;//队尾指针
};
//入队不需要判断队满,出队需要判断队列是否为空,注意在链队出队操作时,
// 入队时,采用尾插法
//队列中的最后一个元素被删除时,队尾指针也丢失了,需要对队尾指针进行重新赋值(指向头节点)























 1142
1142

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








