MIMO stands for Multiple Input, Multiple Output, and it is a technology used in wireless communication systems, including WiFi, to improve performance and data transfer rates. MIMO involves the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitting (sender) and receiving (receiver) devices. The basic idea is to use multiple spatial channels simultaneously to enhance communication.
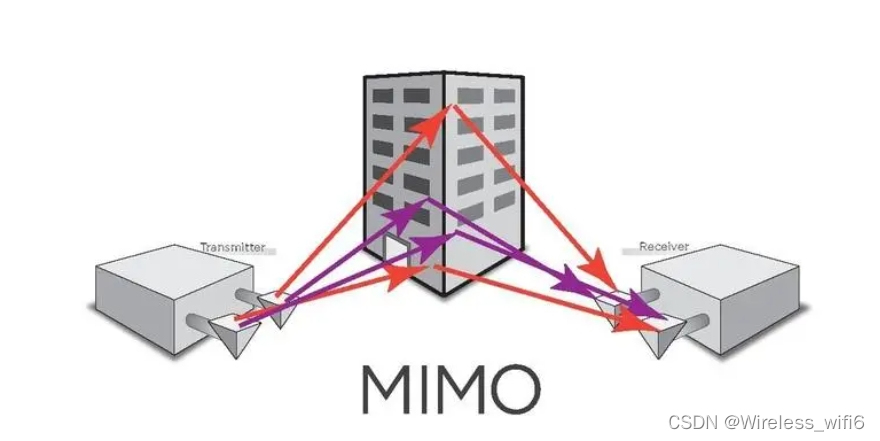
Here's a brief overview of how MIMO works in the context of WiFi:
1. **Multiple Antennas at Transmitter and Receiver:**
- The WiFi router or access point and the WiFi-enabled device (such as a laptop or smartphone) are equipped with multiple antennas.
2. **Spatial Multiplexing:**
- MIMO takes advantage of the spatial dimension by transmitting multiple data streams on the same channel simultaneously.
3. **Increased Data Throughput:**
- By using multiple antennas, MIMO increases the data throughput and improves the overall performance of the wireless communication link.
4. **Improved Signal Reliability:**
- MIMO can enhance the reliability of the wireless connection by using spatial diversity. Even if one signal path is affected by interference or obstacles, other paths may still provide a reliable connection.
5. **Beamforming:**
- Some MIMO systems implement beamforming, where the direction of the signals is adjusted to focus on the intended receiver. This can improve signal strength and coverage.
MIMO technology has become a standard feature in modern WiFi standards, such as 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6). It plays a crucial role in achieving higher data rates, better range, and improved overall performance in wireless networks.





 MIMO技术通过在发送器和接收器设备上使用多个天线,实现空间复用,提高数据传输速率和无线连接可靠性。现代WiFi标准如802.11n,802.11ac,和802.11ax(Wi-Fi6)广泛应用MIMO,以增强网络性能和信号覆盖。
MIMO技术通过在发送器和接收器设备上使用多个天线,实现空间复用,提高数据传输速率和无线连接可靠性。现代WiFi标准如802.11n,802.11ac,和802.11ax(Wi-Fi6)广泛应用MIMO,以增强网络性能和信号覆盖。
















 844
844

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








