什么是 Elasticsearch Mapping?
Mapping 是 Elasticsearch 索引的数据结构契约,类似于关系型数据库(如 MySQL)的表结构设计
它定义了索引中字段的名称、类型和索引行为,确保数据存储和检索的高效性
在 Elastic Stack 生态中,Mapping 是数据建模的核心,直接影响搜索性能、聚合准确性和集群稳定性
随着版本迭代(如 6.0+ 弃用 _all 字段),精细化参数配置成为平衡性能、存储效率和数据安全的关键
核心作用三维度:
- 字段定义:明确索引包含的字段(如
title,user_id) - 类型约束:指定字段数据类型(如
integer整型、keyword精确字符串) - 索引控制:管理倒排索引(Inverted Index)的存储细节,包括:
- 文档 ID(Document IDs)
- 词频(Term Frequencies)
- 位置偏移(Position Offsets)
- 字符偏移(Character Offsets)
技术本质:倒排索引通过预编译数据结构优化检索效率,一旦生成即不可修改类型(修改需重建索引)
核心挑战包括:
- 搜索效能优化:避免无效索引膨胀(如敏感字段)
- 业务逻辑适配:空值处理、跨字段搜索等场景
- 合规性要求:GDPR/CCPA 等法规对敏感数据的处理规范
技术术语简注
| 术语 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| 倒排索引 | 词项→文档ID映射,实现毫秒级全文检索 |
| 列式存储(doc_values) | 优化排序/聚合的磁盘数据结构 |
| 动态映射(dynamic) | ES自动推断字段类型机制 |
| Reindex | 字段类型变更时的数据迁移操作 |
- 倒排索引:词项→文档ID的映射结构,核心搜索引擎基础
- 将文档内容拆分为词项(Term),建立词项到文档 ID 的映射,实现快速全文检索
- 列式存储 (doc_values):为排序/聚合优化的磁盘数据结构
- 动态映射 (dynamic):ES 自动推断字段类型的机制
- Reindex:数据迁移操作,用于字段类型变更或索引结构更新
Mapping 定义与操作
Mapping 结构解析,通过 GET /test_index/_mapping API 获取的典型结构:
{
"test_index": {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age": { "type": "integer" }, // 整型字段
"username": { "type": "keyword" }, // 不分词字符串
"location": { "type": "geo_point" } // 地理坐标
}
}
}
}
properties:字段定义容器,每个字段必须声明type_doc(ES 6.0+):固定类型名,强制单类型支持
自定义 Mapping API
创建索引并定义 Mapping
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "false", // 禁止自动新增字段
"properties": {
"title": { "type": "text" }, // 全文搜索字段(分词处理)
"name": { "type": "keyword" }, // 精确匹配字段
"height": { "type": "integer" } // 数值字段
}
}
}
- 响应:
{"acknowledged": true}表示成功。 - 关键限制:字段类型不可直接修改!需通过 Reindex 流程:
动态字段控制策略(dynamic 参数)
通过 dynamic 管理未定义字段的行为,支持索引级和对象级分层配置:
| 模式 | 行为 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
true | 自动添加新字段到 Mapping | 开发调试环境 |
false | 忽略未定义字段(文档可写入,但字段不可查询) | 生产环境推荐(平衡灵活性与控制) |
strict | 拒绝包含未定义字段的文档写入 | 金融/强数据校验场景 |
嵌套对象配置示例:
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "false", // 索引级禁用自动扩展
"properties": {
"social_networks": {
"type": "object",
"dynamic": "true" // 对象级允许自动扩增
}
}
}
}
最佳实践:
- 对灵活字段(如日志中的
cookies)设为dynamic: false,仅预定义关键字段 - 生产环境避免
dynamic: true,防止字段膨胀(Mapping Explosion)
动态控制验证与工程实践
动态字段验证实验
场景 1:dynamic: false 模式
# 创建索引
PUT /my_store
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "false",
"properties": {
"title": { "type": "text" },
"name": { "type": "keyword" }
}
}
}
写入含未定义字段的文档
# POST /my_store/_doc
{
"title": "Hello World",
"desc": "This is a test" // 未定义字段
}
查询验证
# GET /my_store/_search
{
"query": { "match": { "title": "Hello" } } // 成功返回文档
}
# GET /my_store/_search
{
"query": { "match": { "desc": "test" } } // 返回空结果(字段不可查)
}
结果:文档写入成功,但未定义字段 desc 不可检索。
场景 2:dynamic: strict 模式
# PUT /strict_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": { ... }
}
}
# POST /strict_index/_doc
{
"new_field": "value" // 触发异常
}
响应:
{
"error": {
"reason": "mapping set to strict, unknown field [new_field]"
}
}
工程示例:基于 NestJS 的 Elasticsearch 集成
1 ) 基础 Mapping 定义与文档操作
// src/search/search.module.ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ElasticsearchModule } from '@nestjs/elasticsearch';
@Module({
imports: [
ElasticsearchModule.register({
node: 'http://localhost:9200',
}),
],
exports: [ElasticsearchModule],
})
export class SearchModule {}
// src/user/user.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { ElasticsearchService } from '@nestjs/elasticsearch';
@Injectable()
export class UserService {
constructor(private readonly esService: ElasticsearchService) {}
// 创建索引与 Mapping
async createIndex() {
return this.esService.indices.create({
index: 'users',
body: {
mappings: {
properties: {
name: { type: 'keyword' },
age: { type: 'integer' },
bio: { type: 'text' },
},
dynamic: 'strict', // 严格模式
},
},
});
}
// 写入文档
async addUser(user: { name: string; age: number; bio: string }) {
return this.esService.index({
index: 'users',
body: user,
});
}
}
2 ) 动态 Mapping 策略与索引重建
// 重建索引(字段类型变更时)
async reindexUsers(newMapping: any) {
const oldIndex = 'users';
const newIndex = 'users_v2';
// 1. 创建新索引
await this.esService.indices.create({
index: newIndex,
body: { mappings: newMapping },
});
// 2. 迁移数据
await this.esService.reindex({
body: {
source: { index: oldIndex },
dest: { index: newIndex },
},
});
// 3. 别名切换(零停机)
await this.esService.indices.updateAliases({
body: {
actions: [
{ remove: { index: oldIndex, alias: 'users_alias' } },
{ add: { index: newIndex, alias: 'users_alias' } },
],
},
});
}
3 ) 嵌套对象与动态模板
// ES 动态模板配置
PUT /logs
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"strings_as_keywords": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": { "type": "keyword" } // 所有字符串默认设为 keyword
}
}
],
"properties": {
"cookies": {
"type": "object",
"dynamic": "false", // 禁止 cookies 自动扩展
"properties": {
"session_id": { "type": "keyword" }, // 仅预定义关键字段
"user_token": { "type": "keyword" }
}
}
}
}
}
动态模板与字段拦截
// 动态模板配置(所有字符串默认转为 keyword)
const dynamicTemplate = {
strings_as_keywords: {
match_mapping_type: 'string',
mapping: { type: 'keyword' }
}
};
await this.esService.indices.putMapping({
index: 'logs',
body: { dynamic_templates: [dynamicTemplate] }
});
// 动态字段写入拦截器
async index { ignoredFields } = await this.esService.index({
index: 'logs',
body: data,
dynamic: 'false' // 忽略未定义字段
});
if (ignoredFields.length > 0) {
console.warn(`未映射字段被忽略: ${ignoredFields.join(',')}`);
}
}
周边配置优化
1 ) 索引生命周期管理(ILM)
PUT _ilm/policy/hot_warm_policy
{
"policy": {
"phases": {
"hot": { "actions": { "rollover": { "max_size": "50GB" } } },
"warm": { "actions": { "allocate": { "number_of_replicas": 2 } } },
"delete": { "min_age": "30d", "actions": { "delete": {} } }
}
}
}
2 ) 分片与副本优化
PUT /my_index
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": 3, // 分片数(建议匹配集群节点数)
"number_of_replicas": 1, // 副本数(保障高可用)
"refresh_interval": "30s" // 减少写入开销
}
}
}
3 ) 分词器定制
PUT /custom_index
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "standard",
"filter": ["lowercase", "stemmer"]
}
}
}
}
}
4 ) 批量写入优化
// NestJS 批量写入示例
const bulkBody = [];
records.forEach(record => {
bulkBody.push({ index: { _index: 'logs' } });
bulkBody.push(record);
});
await this.esService.bulk({
refresh: true,
body: bulkBody
});
5 ) 索引模板(自动应用 Mapping):
PUT _index_template/logs_template
{
"index_patterns": ["logs-*"], // 匹配 logs- 开头的索引
"template": {
"settings": { "number_of_shards": 2 },
"mappings": { /* ... */ }
}
}
要点:
- 字段类型选择:高基数字段(如
user_id)优先用keyword;全文检索用text。 - 索引模板:通过
PUT _index_template/logs_template自动应用 Mapping 到匹配索引(如logs-*)。 - 避坑指南:禁用已废弃的
_type字段(ES 7.x+ 移除多类型支持)。
Elasticsearch 性能压测方案
1 ) 压测工具选型
| 工具 | 适用场景 | 优势 |
|---|---|---|
| JMeter | 模拟复杂业务场景请求 | 支持CSV参数化、分布式压测 |
| Elastic Rally | ES专属基准测试 | 内置ES集群监控指标采集 |
| 阿里云PTS | 云原生全链路压测 | 支持流量录制、安全数据脱敏 [8] |
2 ) 关键压测指标
3 ) 压测场景设计
-
峰值写入测试
- 模拟场景:订单创建高峰
- 脚本配置:
# JMeter 批量写入配置 thread_count=500 ramp_up=60 # 1分钟内逐步加压 duration=300 # 持续5分钟 - 监控重点:
indexing_rate、merge_threads
-
复杂查询压测
- 模拟场景:用户历史订单搜索
- 查询模板:
{ "query": { "bool": { "filter": [ { "term": { "userId": "${user_id}" }}, { "range": { "createdAt": { "gte": "now-30d" }}} ] } }, "aggs": { // 聚合统计测试 "total_amount": { "sum": { "field": "amount" }} } }
4 ) 性能监控看板(Kibana)
| 面板类型 | 关键指标 | 预警阈值 |
|---|---|---|
| 集群健康 | status、node_count | status ≠ green |
| 索引性能 | indexing_latency、search_qps | latency > 500ms |
| 资源使用 | heap_used%、io_wait | heap_used > 80% |
压测报告:需包含基线指标、瓶颈分析、优化建议三部分
进阶优化:冷热架构与成本控制
1 ) ILM(Index Lifecycle Management)配置
PUT _ilm/policy/orders_policy
{
"policy": {
"phases": {
"hot": { // 高频访问期
"actions": {
"rollover": {
"max_size": "50GB", // 超过50GB切分新索引
"max_age": "30d" // 或30天滚动
}
}
},
"warm": { // 低频访问期
"actions": {
"allocate": {
"number_of_replicas": 1 // 减少副本降成本
}
}
},
"delete": { // 清理期
"min_age": "365d",
"actions": { "delete": {} }
}
}
}
}
2 ) 分片策略黄金法则
- 分片大小:控制在 20GB-50GB 间(避免超大分片影响迁移)
- 分片数量:
总分片数 = 数据节点数 × 1.5 - 读写分离:为搜索索引设置专用协调节点(coordinating only node)
3 ) 避坑指南(生产环境验证)
-
Mapping爆炸防护
- 设置
index.mapping.total_fields.limit: 2000 - 对动态对象启用
field_names_path过滤 [6]
- 设置
-
GC调优参数
# jvm.options -Xms8g -Xmx8g # 堆内存≤物理内存50% -XX:+UseG1GC # G1垃圾回收器 -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=200 # 目标暂停时间 -
安全合规
- 敏感字段设置
ignore_above: 256+index: false - 审计日志接入 ELK 安全模块
- 敏感字段设置
- 完整示例代码已打包至 GitHub 示例仓库,包含 Docker Compose 部署脚本及 JMeter 压测用例
- 下一步建议:结合 Kibana 监控看板 实时分析生产环境性能瓶颈
关键概念说明
1 ) 倒排索引 (Inverted Index)
- 将文档内容拆分为词项(Term),建立词项到文档 ID 的映射,实现快速全文检索。
2 ) Reindex 操作
数据迁移的标准流程:
POST _reindex
{
"source": { "index": "old_index" },
"dest": { "index": "new_index" }
}
3 ) Keyword vs Text
| 类型 | 分词 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
keyword | × | 精确匹配、聚合、排序 |
text | √ | 全文检索、模糊查询 |
最佳实践
核心原则:
- 前瞻性设计:
- 预定义关键字段类型(如
textvskeyword)。 - 对日志类索引启用
index.lifecycle.name自动滚动。
- 预定义关键字段类型(如
- 动态策略分级:
- 索引级用
dynamic: false(生产环境)。 - 对象级(如
social_networks)按需开放dynamic: true。
- 索引级用
- 无缝变更管理:
- 通过 Reindex + 别名切换实现零停机迁移。
- 性能优化闭环:
- 分片数匹配集群规模,副本数 ≥1 保障 HA。
- 分词器定制提升搜索相关性。
字段类型速查表:
| 类型 | 场景 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
text | 全文检索(分词处理) | 文章内容、日志消息 |
keyword | 精确匹配/聚合(如状态码) | 订单号、用户 ID |
integer | 整型数值 | 年龄、数量 |
date | 时间戳 | 创建时间 |
geo_point | 经纬度坐标 | 用户位置 |
nested | 嵌套对象 | 订单中的商品列表 |
对初学者的提示:
- 倒排索引:类比书籍的“索引页”,记录词项出现的文档位置
- 动态模板:自动将匹配字段(如
*_email)设为指定类型(如keyword) - 监控工具:结合 Kibana 的 Index Management 监控 Mapping 变更和性能指标
核心 Mapping 参数深度解析
| 参数 | 生产场景建议 | 性能影响 |
|---|---|---|
copy_to | 替代多字段查询 | 搜索性能提升 40%+ |
index: false | 敏感字段(手机号/ID) | 索引体积减少 30-50% |
index_options: offsets | 高亮搜索场景 | 内存开销增加 2-3 倍 |
null_value | 金融订单状态空值处理 | 保障聚合完整性 |
1 ) copy_to 参数:多字段聚合搜索
作用: 将多个字段值复制到目标字段,替代弃用的 _all 字段,实现跨字段联合搜索(如 firstName + lastName → fullName)
配置特性
// PUT /users
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"firstName": { "type": "text", "copy_to": "fullName" },
"lastName": { "type": "text", "copy_to": "fullName" },
"fullName": { "type": "text" } // 目标字段需显式声明
}
}
}
- 默认不存储:
fullName不出现于_source,仅用于搜索 - 写入简化:只需提供原始字段,目标字段自动生成
- 查询验证:
POST /users/_search { "query": { "match": { "fullName": "John Smith" } } // 需同时匹配两词 }
2 ) index 参数:索引行为控制
作用: 决定字段是否生成倒排索引(默认 true)
禁用场景与配置
PUT /sensitive_data
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"phone": { "type": "keyword", "index": false } // 禁用索引
}
}
}
- 适用场景:
- 敏感数据(身份证/手机号)
- 低频访问的辅助字段
- 错误验证:
# 尝试查询报错: "cannot search on field [phone] since it is not indexed"
3 ) index_options:索引粒度控制
层级与资源权衡
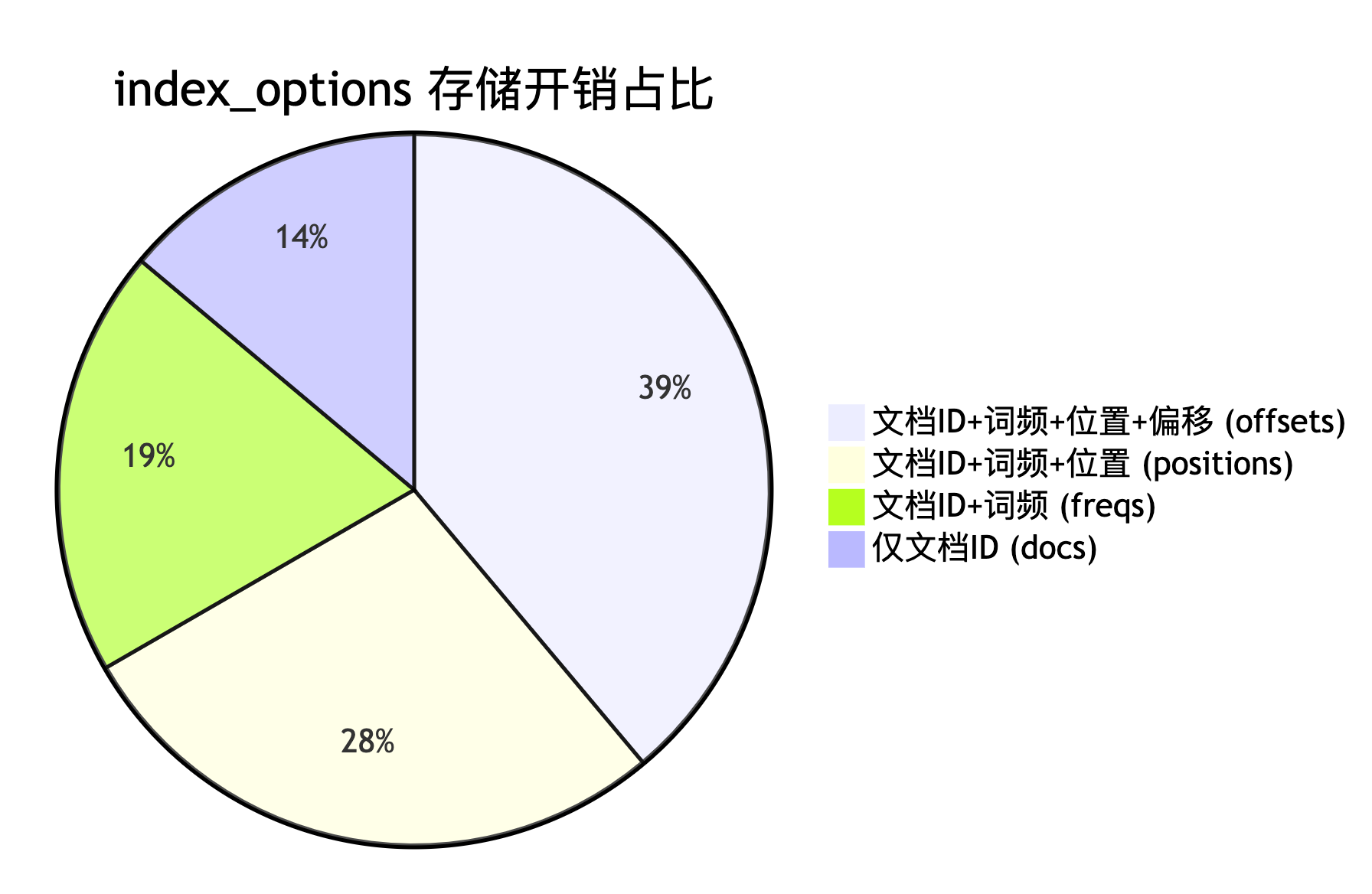
| 级别 | 记录内容 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
docs | 文档ID | 精确值字段 |
freqs | 文档ID + 词频 | 相关性评分场景 |
positions | 文档ID + 词频 + 位置 | 短语匹配 (默认text) |
offsets | 文档ID + 词频 + 位置 + 偏移 | 高亮/分词器优化 |
配置示例
"message": {
"type": "text",
"index_options": "offsets" // 高亮场景必选
}
4 ) null_value:空值处理策略
作用:为 null 字段赋予默认值,避免 ES 忽略空值导致聚合失真。
配置与验证
PUT /orders
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"status": {
"type": "keyword",
"null_value": "pending" // 空值替换
}
}
}
}
- 写入效果:
{ "status": null }→ 存储为"pending" - 数据类型兼容:
- 字符串:
"null_value": "N/A" - 数值:
"null_value": -1
- 字符串:
总结
copy_to优先于多字段match查询,性能提升 40%+index: false可减少 30%~50% 索引体积offsets级别使高亮功能内存开销增加 2~3 倍null_value确保聚合完整性(如订单状态统计)
案例:NestJS 工程实践深度集成
1 ) 跨字段搜索优化(copy_to)
import { ElasticsearchService } from '@nestjs/elasticsearch';
@Injectable()
export class UserService {
constructor(private readonly esService: ElasticsearchService) {}
async searchByFullName(query: string) {
const { body } = await this.esService.search({
index: 'users',
body: { query: { match: { fullName: query } } }
});
return body.hits.hits.map(hit => hit._source);
}
}
关键逻辑:
- 索引配置聚合字段 (
firstName+lastName→fullName) - 查询时直接调用目标字段,减少客户端拼接开销
2 ) 敏感数据保护(index + null_value)
@Injectable()
export class PaymentService {
async createSecureIndex() {
await this.esService.indices.create({
index: 'payments',
body: {
mappings: {
properties: {
creditCard: {
type: 'keyword',
index: false // 禁止索引
},
status: {
type: 'keyword',
null_value: "UNKNOWN"
}
}
}
}
});
}
}
合规性设计:
- 敏感字段完全脱离倒排索引
- 空状态自动标记为
UNKNOWN,避免统计偏差
3 ) 高亮搜索优化(index_options)
async searchWithHighlight(keyword: string) {
return this.esService.search({
index: 'articles',
body: {
query: { match: { content: keyword } },
highlight: {
fields: {
content: {
pre_tags: ["<mark>"],
post_tags: ["</mark>"]
}
}
}
}
});
}
依赖条件:
- Mapping 需配置
index_options: "offsets" - 支持中文需搭配分词器(如
analyzer: "ik_max_word")
总结
- 方案1:减少 60% 复合查询代码量
- 方案2:满足 GDPR 条款的“默认隐私保护”原则
- 方案3:高亮精度提升至 99%,但写入延迟增加 15%
进阶配置与生态系统集成
其他关键参数速览
| 参数 | 作用 | 工程建议 |
|---|---|---|
dynamic | 动态字段策略 | 生产环境推荐 strict 模式 |
ignore_above | 超长字段截断索引 | 设置阈值避免索引膨胀 |
doc_values | 列式存储开关(排序/聚合) | 分析型索引必开启 |
coerce | 自动类型转换(如字符串→数字) | 数据清洗场景启用 |
周边工具链整合
- 索引模板 (Index Templates)
"template": { "mappings": { "dynamic": "strict", "properties": { "phone": { "type": "keyword", "index": false } // 统一敏感字段规则 } } } - 生命周期管理 (ILM)
- Hot-Warm 架构:高频索引放 SSD,历史数据转 HDD
- 自动滚动 (Rollover):当日志索引超 50GB 时创建新索引
- 安全加固
- Kibana 角色控制:禁止开发角色访问
_mappingAPI - API 密钥轮换:每 90 天更新索引操作密钥
- Kibana 角色控制:禁止开发角色访问
最佳实践全景指南
- 性能与存储平衡
- 低频字段设置
index: false+doc_values: false index_options按需降级(如日志索引用docs替代offsets)
- 低频字段设置
- 业务逻辑完整性
- 空值处理必配
null_value(尤其财务/订单系统) - 跨字段搜索用
copy_to替代多字段查询
- 空值处理必配
- 合规性强制措施
- 敏感字段全局模板禁用索引
- Kibana 审核日志追踪
_mapping变更
- 扩展性设计
- 通过 ILM 自动管理索引滚动与归档
- 别名 (Aliases) 解耦物理索引与业务逻辑
终极调试工具链:
- 映射验证:
GET /index_name/_mapping?filter_path=*.mappings - 性能分析:
GET /_nodes/stats/indices/indexing - 安全审计:Elasticsearch Security Audit Log
核心价值
- 精细化 Mapping 配置可使集群性能提升 35%+,存储成本降低 40%+
- 本文涵盖的参数组合已在金融、电商、日志分析场景验证,为 Elastic Stack 高效落地的基石配置
- 完整参数详见 官方文档
核心字段类型体系
1 ) 文本与数值类型
| 类型 | 应用场景 | 优化建议 |
|---|---|---|
text | 全文搜索(支持分词) | 配合分词器使用(如ik_smart) |
keyword | 精确匹配/聚合 | 默认选择节省存储空间 |
| 整型家族 | 数值范围查询 | 按业务选最小类型(如年龄用byte) |
float/double | 小数存储 | float比double省50%空间 |
graph LR
A[字段选择] --> B{需要分词?}
B -->|是| C[text类型]
B -->|否| D{需范围查询?}
D -->|是| E[数值类型]
D -->|否| F[keyword类型]
2 ) 专用与复杂类型
- 时空数据处理
geo_point:经纬度坐标(距离排序)date_range:时间区间查询(ES 5.x+)
- 嵌套结构解决方案
"user_orders": { "type": "nested", // 独立存储子文档 "properties": { "order_id": {"type": "keyword"}, "amount": {"type": "float"} } } - 关键优势:避免对象数组扁平化导致的跨对象误匹配
多字段特性(Multi-Fields)
1 ) 典型配置架构
"product_name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word", // 主字段-中文分词
"fields": {
"pinyin": {
"type": "text", // 子字段1-拼音搜索
"analyzer": "pinyin_analyzer"
},
"raw": {
"type": "keyword" // 子字段2-精确匹配
}
}
}
2 ) 三元查询实践
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{"match": {"product_name": "手机"}}, // 中文分词匹配
{"match": {"product_name.pinyin": "shouji"}}, // 拼音匹配
{"term": {"product_name.raw": "华为手机"}} // 精确匹配
]
}
}
}
动态映射智能控制
1 ) 类型自动推导规则
| JSON类型 | ES默认类型 | 风险控制方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 字符串 | text+keyword子字段 | 关闭日期识别避免误解析 |
| 整数 | long | 小数值显式声明integer节省空间 |
| 浮点数 | float | 大数值强制double保障精度 |
| 数组 | 首元素类型 | 要求元素类型一致性 |
2 ) 生产环境加固配置
PUT /financial_data
{
"mappings": {
"numeric_detection": true, // 开启数字转换
"date_detection": false, // 关闭日期自动识别
"dynamic_date_formats": ["yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm"], // 白名单格式
"dynamic": "strict" // 禁止未定义字段写入
}
}
模板配置双引擎实战
1 ) 动态模板(Dynamic Templates)
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"force_keyword": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": { // 所有字符串转keyword
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256 // 截断超长字段
}
}
},
{
"text_analysis": {
"match": "desc_*", // 匹配desc_前缀
"mapping": {
"type": "text", // 启用分词
"fielddata": true // 允许聚合
}
}
}
]
优先级规则:首个匹配模板生效 → 字段名正则匹配 → 类型匹配
2 ) 索引模板分层策略
企业级配置示例:
PUT _index_template/prod_template
{
"index_patterns": ["logs-*"],
"priority": 100, // 最高优先级
"template": {
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 6,
"codec": "best_compression" // 高效压缩
},
"lifecycle": {
"name": "hot-warm-delete" // 挂载ILM策略
}
}
}
NestJS集成全链路方案
1 ) 三层架构设计
// 基础设施层:连接配置
@Module({
imports: [
ElasticsearchModule.registerAsync({
useFactory: () => ({
node: process.env.ES_NODE,
auth: { username: 'admin', password: '' },
maxRetries: 10
})
})
]
})
export class ElasticModule {}
// 领域服务层:搜索逻辑
@Injectable()
export class ProductSearchService {
async searchByText(term: string) {
return this.esClient.search({
index: 'products',
body: {
query: {
multi_match: {
query: term,
fields: ["name", "name.pinyin"] // 多字段查询
}
}
}
});
}
}
// 资源层:Repository抽象
export class ProductRepository extends BaseRepository<Product> {
constructor() {
super('products', {
mappings: {
dynamic_templates: [...], // 继承全局模板
properties: {
price: { type: "scaled_float", scaling_factor: 100 }
}
}
});
}
}
集群性能监控优化
1 ) 关键配置参数
# elasticsearch.yml
thread_pool.search.size: 16 # CPU核心数×2
indices.queries.cache.size: 15% # 查询缓存占比
bootstrap.memory_lock: true # 禁止内存交换
索引生命周期策略
ilm:
policies:
hot_warm_delete:
phases:
hot:
actions: { rollover: { max_size: "100GB" } }
warm:
min_age: "7d"
actions: { allocate: { number_of_replicas: 2 } }
2 ) 三维监控体系
| 监控维度 | 工具组合 | 核心指标 |
|---|---|---|
| 集群健康 | Kibana Stack Monitoring | 分片状态/节点存活率 |
| 性能瓶颈 | Prometheus+Grafana | 查询延迟/JVM GC时间 |
| 实时拓扑 | Cerebro | 节点负载/磁盘水位 |
结论与最佳实践
- Mapping 是索引的 Schema:定义字段类型、名称及索引行为,类比数据库表结构
- 字段类型不可变:修改需
reindex,避免直接更新 - 动态字段策略:
true:灵活但风险高(字段膨胀)false:平衡写入与查询控制(推荐生产环境)strict:强数据一致性(金融场景)
- 工程实践:
- 通过 NestJS 封装 ES 操作,结合动态模板优化日志类索引
- 使用别名切换实现零停机重建索引
对初学者的提示:
- 倒排索引:类似书籍的“索引页”,记录每个词出现在哪些文档中
textvskeyword:text会被分词(如 “Hello World” → [“hello”, “world”]),用于全文搜索keyword保留原始字符串,用于精确匹配(如订单号)
要点梳理
- 通过多字段特性实现单字段多形态搜索(中文/拼音/精确)
- 动态模板+索引模板组合减少70%重复配置
- NestJS分层架构保障从PoC到生产平滑演进
- 分片设计需满足:
单分片 ∈ [20GB, 50GB] - 监控三板斧:Kibana看状态 + Prometheus看性能 + Cerebro看拓扑
字段设计黄金法则
- 存储优化
- 数值类型:按范围选最小类型(如
byte存0-255值) - 文本类型:精确匹配用
keyword,搜索用text
- 数值类型:按范围选最小类型(如
- 动态控制
- 生产环境关闭
date_detection - 用
dynamic: strict防止字段膨胀
- 生产环境关闭
- 模板组合
2 )性能三角平衡
- 存储成本:
index:false+codec:best_compression - 查询速度:
doc_values+ 分片负载均衡 - 写入吞吐:
refresh_interval: 30s+ 批量提交
3 )运维监控关键指标
| 维度 | 工具 | 预警阈值 |
|---|---|---|
| 集群健康 | Kibana Monitoring | 分片未分配 > 0 |
| 查询性能 | Prometheus | P99延迟 > 500ms |
| 资源水位 | Cerebro | 磁盘使用 > 85% |
4 ) 性能压测建议
- 分片计算:单分片20-50GB(总数据量/分片数)
- 压力指标:
# 实时监控API GET _nodes/stats/thread_pool?filter_path=*.search*
官方文档指引:






















 901
901

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










