在车载HMI(人机交互界面)开发中,OpenGL ES 凭借其硬件加速能力和跨平台特性,成为实现高帧率、低延迟图形渲染的首选方案。本文将深入解析一个基于OpenGL ES 2.0的汽车仪表盘实现,涵盖图形渲染管线设计、矩阵变换优化和动画控制逻辑等核心技术。
一、核心实现原理
1. 渲染管线架构
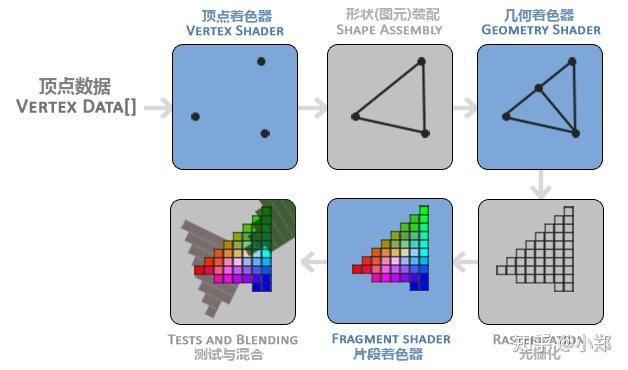
-
顶点着色器:完成坐标变换(模型-视图-投影矩阵)
-
片段着色器:处理颜色插值与抗锯齿
-
帧缓冲:双缓冲机制避免画面撕裂
2. 关键数据结构
// 顶点数据存储优化
private val vertices = FloatArray(2000) // 预分配顶点空间
private lateinit var vertexBuffer: FloatBuffer // 直接内存缓冲区
// 矩阵栈管理
private val projectionMatrix = FloatArray(16)
private val viewMatrix = FloatArray(16)
private val modelMatrix = FloatArray(16)
通过预分配顶点缓冲区和矩阵栈,减少GC压力,提升渲染效率。
3. 矩阵变换
// 投影矩阵计算(透视投影)
Matrix.frustumM(projectionMatrix, 0, -ratio, ratio, -1f, 1f, 3f, 7f)
// 视图矩阵设置(摄像机位置)
Matrix.setLookAtM(viewMatrix, 0, 0f, 0f, 4f, 0f, 0f, 0f, 0f, 1f, 0f)
-
透视投影:通过
frustumM实现16:9宽高比适配 -
视锥体裁剪:近裁剪面(0.1f)与远裁剪面(10f)设置
-
模型矩阵:通过旋转实现仪表盘方向调整
4. 顶点数据动态生成
private fun drawCircle(centerX: Float, centerY: Float, radius: Float, color: Int, segments: Int) {
val angleStep = 2 * Math.PI / segments
vertices.forEachIndexed { i, _ ->
val angle = angleStep * i
vertices[i*3] = (centerX + radius * cos(angle)).toFloat()
vertices[i*3+1] = (centerY + radius * sin(angle)).toFloat()
}
}
-
参数化生成:通过分段数控制圆弧精度
-
内存复用:固定大小顶点数组避免频繁内存分配
5. 动画控制逻辑
private fun updateSpeed() {
speed = when {
speed < targetSpeed -> min(speed + 2f, targetSpeed)
speed > targetSpeed -> max(speed - 2f, targetSpeed)
else -> speed
}
}
-
线性插值:实现平滑速度过渡
-
帧率无关:通过固定时间步长保证动画流畅性
二 渲染代码
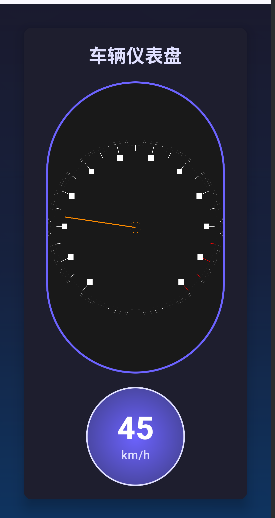
package com.example.openglcarpannel.graphics
import android.graphics.Color
import android.opengl.GLES20
import android.opengl.GLSurfaceView
import android.opengl.Matrix
import java.nio.ByteBuffer
import java.nio.ByteOrder
import java.nio.FloatBuffer
import javax.microedition.khronos.egl.EGLConfig
import javax.microedition.khronos.opengles.GL10
import kotlin.math.cos
import kotlin.math.sin
class CarDashboardRenderer : GLSurfaceView.Renderer {
private val projectionMatrix = FloatArray(16)
private val viewMatrix = FloatArray(16)
private val modelMatrix = FloatArray(16)
private val mvpMatrix = FloatArray(16)
private var speed = 0f // 当前速度
private var targetSpeed = 0f // 目标速度
private val speedIncrement = 2f // 速度增加步长,用于动画效果
// 着色器程序
private var programId = 0
// 着色器位置
private var positionHandle = 0
private var colorHandle = 0
private var mvpMatrixHandle = 0
// 顶点数据存储 - increased size to handle more segments
private val vertices = FloatArray(2000)
private var vertexCount = 0
private lateinit var vertexBuffer: FloatBuffer
override fun onSurfaceCreated(unused: GL10?, config: EGLConfig?) {
// 设置背景颜色
GLES20.glClearColor(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f, 1.0f)
// 创建和编译着色器程序
programId = createProgram()
// 获取着色器变量位置
positionHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(programId, "vPosition")
colorHandle = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(programId, "vColor")
mvpMatrixHandle = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(programId, "uMVPMatrix")
// 初始化顶点缓冲区
val byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(vertices.size * 4) // 每个float占4字节
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
vertexBuffer = byteBuffer.asFloatBuffer()
}
override fun onSurfaceChanged(unused: GL10?, width: Int, height: Int) {
GLES20.glViewport(0, 0, width, height)
// 计算投影矩阵
val ratio = width.toFloat() / height.toFloat()
Matrix.frustumM(projectionMatrix, 0, -ratio, ratio, -1f, 1f, 3f, 7f)
// 设置视图矩阵
Matrix.setLookAtM(viewMatrix, 0, 0f, 0f, 4f, 0f, 0f, 0f, 0f, 1f, 0f)
}
override fun onDrawFrame(unused: GL10?) {
// 清除颜色缓冲区
GLES20.glClear(GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT)
// 使用着色器程序
GLES20.glUseProgram(programId)
// 更新速度(动画效果)
updateSpeed()
// 保存当前模型矩阵,准备应用旋转
val tempModelMatrix = FloatArray(16)
// 绘制仪表盘背景
Matrix.setIdentityM(modelMatrix, 0)
// 顺时针旋转270度(90+180),调整仪表盘方向
Matrix.rotateM(modelMatrix, 0, -270f, 0f, 0f, 1f)
System.arraycopy(modelMatrix, 0, tempModelMatrix, 0, 16)
drawDashboardBackground()
// 绘制刻度
System.arraycopy(tempModelMatrix, 0, modelMatrix, 0, 16)
drawSpeedMarkings()
// 绘制指针
System.arraycopy(tempModelMatrix, 0, modelMatrix, 0, 16)
drawSpeedPointer()
// 速度文本已移除
}
private fun updateSpeed() {
// 平滑过渡到目标速度
if (speed < targetSpeed) {
speed = kotlin.math.min(speed + speedIncrement, targetSpeed)
} else if (speed > targetSpeed) {
speed = kotlin.math.max(speed - speedIncrement, targetSpeed)
}
}
private fun drawDashboardBackground() {
// 绘制外圈(更亮的颜色提高可见性)
drawCircle(0f, 0f, 0.8f, Color.rgb(120, 120, 120), 120)
// 绘制中间圈(增加对比度)
drawCircle(0f, 0f, 0.78f, Color.WHITE, 120)
// 绘制内圈
drawCircle(0f, 0f, 0.75f, Color.rgb(40, 40, 40), 120)
}
// 速度文本相关功能已移除
private fun drawSpeedMarkings() {
// 绘制刻度和数字
val startAngle = 140f // 起始角度(左侧)
val endAngle = 40f // 结束角度(右侧)
val angleRange = 280f // 总角度范围(140到40度,实际是280度)
val maxSpeed = 220f // 最大速度
for (i in 0..maxSpeed.toInt() step 10) {
val angle = startAngle - (i / maxSpeed) * angleRange
val radians = Math.toRadians(angle.toDouble())
// 刻度长度
val length = if (i % 20 == 0) 0.1f else 0.05f
// 刻度颜色
val color = if (i > 180) Color.RED else Color.WHITE
// 绘制刻度线
drawLine(
(0.75f - length) * cos(radians).toFloat(),
(0.75f - length) * sin(radians).toFloat(),
0.75f * cos(radians).toFloat(),
0.75f * sin(radians).toFloat(),
color,
2f
)
// 绘制数字(每20单位)
if (i % 20 == 0) {
// 简化:这里不绘制实际文本,使用小方块代替
drawSmallSquare(
(0.65f) * cos(radians).toFloat(),
(0.65f) * sin(radians).toFloat(),
Color.WHITE
)
}
}
}
private fun drawSpeedPointer() {
// 计算指针角度
val startAngle = 140f
val angleRange = 280f
val maxSpeed = 220f
val currentAngle = startAngle - (speed / maxSpeed) * angleRange
val radians = Math.toRadians(currentAngle.toDouble())
// 绘制指针
drawLine(
0f,
0f,
0.65f * cos(radians).toFloat(),
0.65f * sin(radians).toFloat(),
Color.rgb(255, 140, 0),
4f
)
// 绘制中心圆点
drawCircle(0f, 0f, 0.05f, Color.rgb(255, 140, 0), 30)
}
private fun drawCircle(centerX: Float, centerY: Float, radius: Float, color: Int, segments: Int) {
vertexCount = segments * 3
// 生成圆形顶点数据
for (i in 0 until segments) {
val angle = 2.0 * Math.PI * i / segments
val x = centerX + radius * cos(angle).toFloat()
val y = centerY + radius * sin(angle).toFloat()
vertices[i * 3] = centerX
vertices[i * 3 + 1] = centerY
vertices[i * 3 + 2] = 0f
vertices[segments * 3 + i * 3] = x
vertices[segments * 3 + i * 3 + 1] = y
vertices[segments * 3 + i * 3 + 2] = 0f
val nextAngle = 2.0 * Math.PI * (i + 1) / segments
val nextX = centerX + radius * cos(nextAngle).toFloat()
val nextY = centerY + radius * sin(nextAngle).toFloat()
vertices[segments * 6 + i * 3] = nextX
vertices[segments * 6 + i * 3 + 1] = nextY
vertices[segments * 6 + i * 3 + 2] = 0f
}
// 更新顶点缓冲区
vertexBuffer.clear()
vertexBuffer.put(vertices, 0, vertexCount * 3)
vertexBuffer.position(0)
// 使用已设置好的模型矩阵(包含旋转)
// 计算MVP矩阵
Matrix.multiplyMM(mvpMatrix, 0, viewMatrix, 0, modelMatrix, 0)
Matrix.multiplyMM(mvpMatrix, 0, projectionMatrix, 0, mvpMatrix, 0)
// 设置顶点数据
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(
positionHandle, 3, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 12, vertexBuffer
)
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(positionHandle)
// 设置颜色
GLES20.glUniform4f(
colorHandle,
Color.red(color) / 255f,
Color.green(color) / 255f,
Color.blue(color) / 255f,
Color.alpha(color) / 255f
)
// 设置MVP矩阵
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(mvpMatrixHandle, 1, false, mvpMatrix, 0)
// 绘制三角形
GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_TRIANGLES, 0, vertexCount)
// 禁用顶点属性数组
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(positionHandle)
}
private fun drawLine(startX: Float, startY: Float, endX: Float, endY: Float, color: Int, width: Float) {
// 设置线宽
GLES20.glLineWidth(width)
// 设置顶点数据
vertices[0] = startX
vertices[1] = startY
vertices[2] = 0f
vertices[3] = endX
vertices[4] = endY
vertices[5] = 0f
vertexCount = 2
// 更新顶点缓冲区
vertexBuffer.clear()
vertexBuffer.put(vertices, 0, vertexCount * 3)
vertexBuffer.position(0)
// 使用已设置好的模型矩阵(包含旋转)
// 计算MVP矩阵
Matrix.multiplyMM(mvpMatrix, 0, viewMatrix, 0, modelMatrix, 0)
Matrix.multiplyMM(mvpMatrix, 0, projectionMatrix, 0, mvpMatrix, 0)
// 设置顶点数据
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(
positionHandle, 3, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 12, vertexBuffer
)
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(positionHandle)
// 设置颜色
GLES20.glUniform4f(
colorHandle,
Color.red(color) / 255f,
Color.green(color) / 255f,
Color.blue(color) / 255f,
Color.alpha(color) / 255f
)
// 设置MVP矩阵
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(mvpMatrixHandle, 1, false, mvpMatrix, 0)
// 绘制线段
GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_LINES, 0, vertexCount)
// 禁用顶点属性数组
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(positionHandle)
}
private fun drawSmallSquare(x: Float, y: Float, color: Int, customWidth: Float = 0.05f, customHeight: Float = 0.05f) {
val width = customWidth
val height = customHeight
// 设置顶点数据
vertices[0] = x - width / 2
vertices[1] = y - height / 2
vertices[2] = 0f
vertices[3] = x + width / 2
vertices[4] = y - height / 2
vertices[5] = 0f
vertices[6] = x - width / 2
vertices[7] = y + height / 2
vertices[8] = 0f
vertices[9] = x + width / 2
vertices[10] = y + height / 2
vertices[11] = 0f
vertexCount = 4
// 更新顶点缓冲区
vertexBuffer.clear()
vertexBuffer.put(vertices, 0, vertexCount * 3)
vertexBuffer.position(0)
// 使用已设置好的模型矩阵(包含旋转)
// 计算MVP矩阵
Matrix.multiplyMM(mvpMatrix, 0, viewMatrix, 0, modelMatrix, 0)
Matrix.multiplyMM(mvpMatrix, 0, projectionMatrix, 0, mvpMatrix, 0)
// 设置顶点数据
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(
positionHandle, 3, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 12, vertexBuffer
)
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(positionHandle)
// 设置颜色
GLES20.glUniform4f(
colorHandle,
Color.red(color) / 255f,
Color.green(color) / 255f,
Color.blue(color) / 255f,
Color.alpha(color) / 255f
)
// 设置MVP矩阵
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(mvpMatrixHandle, 1, false, mvpMatrix, 0)
// 绘制四边形
GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, 0, vertexCount)
// 禁用顶点属性数组
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(positionHandle)
}
private fun createProgram(): Int {
val vertexShaderCode = """
attribute vec4 vPosition;
uniform mat4 uMVPMatrix;
void main() {
gl_Position = uMVPMatrix * vPosition;
}
"""
val fragmentShaderCode = """
precision mediump float;
uniform vec4 vColor;
void main() {
gl_FragColor = vColor;
}
"""
// 编译着色器
val vertexShader = loadShader(GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER, vertexShaderCode)
val fragmentShader = loadShader(GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, fragmentShaderCode)
// 创建程序
val program = GLES20.glCreateProgram()
GLES20.glAttachShader(program, vertexShader)
GLES20.glAttachShader(program, fragmentShader)
GLES20.glLinkProgram(program)
return program
}
private fun loadShader(type: Int, shaderCode: String): Int {
val shader = GLES20.glCreateShader(type)
GLES20.glShaderSource(shader, shaderCode)
GLES20.glCompileShader(shader)
return shader
}
// 设置目标速度
fun setTargetSpeed(newSpeed: Float) {
targetSpeed = newSpeed.coerceIn(0f, 220f) // 限制在0-220之间
}
// 获取当前速度
fun getCurrentSpeed(): Float {
return speed
}
}





















 2026
2026

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








