Let's play the minesweeper game (Wikipedia, online game)!
You are given a 2D char matrix representing the game board. 'M' represents an unrevealed mine, 'E' represents an unrevealed empty square, 'B' represents a revealed blank square that has no adjacent (above, below, left, right, and all 4 diagonals) mines, digit ('1' to '8') represents how many mines are adjacent to this revealed square, and finally 'X' represents a revealed mine.
Now given the next click position (row and column indices) among all the unrevealed squares ('M' or 'E'), return the board after revealing this position according to the following rules:
- If a mine ('M') is revealed, then the game is over - change it to 'X'.
- If an empty square ('E') with no adjacent mines is revealed, then change it to revealed blank ('B') and all of its adjacent unrevealed squares should be revealed recursively.
- If an empty square ('E') with at least one adjacent mine is revealed, then change it to a digit ('1' to '8') representing the number of adjacent mines.
- Return the board when no more squares will be revealed.
Example 1:
Input: [['E', 'E', 'E', 'E', 'E'], ['E', 'E', 'M', 'E', 'E'], ['E', 'E', 'E', 'E', 'E'], ['E', 'E', 'E', 'E', 'E']] Click : [3,0] Output: [['B', '1', 'E', '1', 'B'], ['B', '1', 'M', '1', 'B'], ['B', '1', '1', '1', 'B'], ['B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B']] Explanation: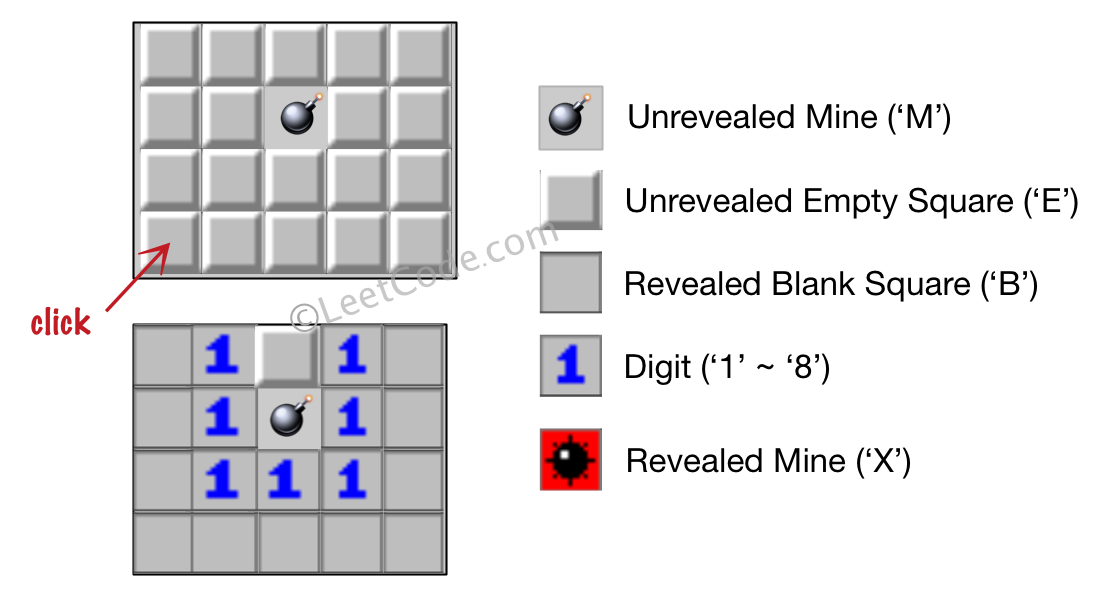
Example 2:
Input: [['B', '1', 'E', '1', 'B'], ['B', '1', 'M', '1', 'B'], ['B', '1', '1', '1', 'B'], ['B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B']] Click : [1,2] Output: [['B', '1', 'E', '1', 'B'], ['B', '1', 'X', '1', 'B'], ['B', '1', '1', '1', 'B'], ['B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B']] Explanation: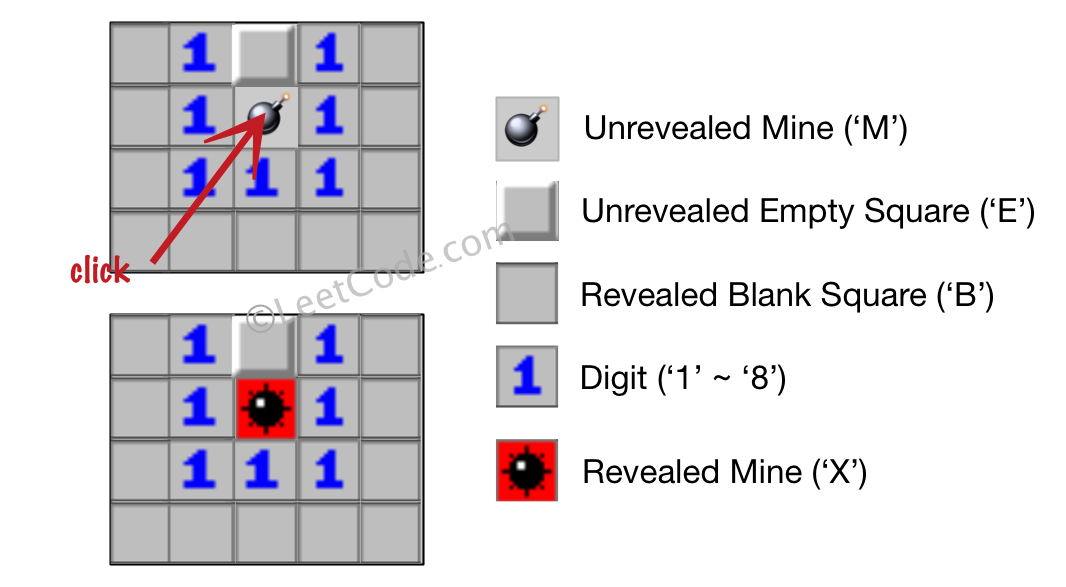
Note:
- The range of the input matrix's height and width is [1,50].
- The click position will only be an unrevealed square ('M' or 'E'), which also means the input board contains at least one clickable square.
- The input board won't be a stage when game is over (some mines have been revealed).
- For simplicity, not mentioned rules should be ignored in this problem. For example, you don't need to reveal all the unrevealed mines when the game is over, consider any cases that you will win the game or flag any squares.
这道题是小游戏扫雷,题目难度为Medium。
这类题目可以分别通过广度优先搜索和深度优先搜索两种方法来解决。
广度优先搜索在搜索过程中借助队列,将遍历位置相邻的位置逐个存入队列来完成广度优先搜索。游戏规则不再详述,题目复杂的地方在点到‘E’且相邻位置没有‘M’时,需要将相邻位置的‘E’依次做同样的操作,这也是需要做广度优先搜索的原因。搜索过程中要避免将同一位置重复存入队列中,注意代码中board[rr][cc] = 'B'这句,将插入队列待处理的位置先标记为‘B’以避免重复。具体代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<char>> updateBoard(vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<int>& click) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
que.push(make_pair(click[0], click[1]));
int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();
while(!que.empty()) {
pair<int, int> cur = que.front();
que.pop();
int r = cur.first;
int c = cur.second;
if(board[r][c] == 'M') {
board[r][c] = 'X';
return board;
}
else {
int mineCnt = 0;
for(int i=-1; i<=1; ++i) {
for(int j=-1; j<=1; ++j) {
int rr = r + i;
int cc = c + j;
if((i == 0 && j == 0) || rr < 0 || rr >= m || cc < 0 || cc >= n)
continue;
if(board[rr][cc] == 'M') ++mineCnt;
}
}
if(mineCnt) {
board[r][c] = '0' + mineCnt;
}
else {
board[r][c] = 'B';
for(int i=-1; i<=1; ++i) {
for(int j=-1; j<=1; ++j) {
int rr = r + i;
int cc = c + j;
if((i == 0 && j == 0) || rr < 0 || rr >= m || cc < 0 || cc >= n)
continue;
if(board[rr][cc] == 'E') {
que.push(make_pair(rr, cc));
board[rr][cc] = 'B';
}
}
}
}
}
}
return board;
}
};class Solution {
void dfsUpdate(vector<vector<char>>& board, int r, int c, int m, int n) {
if(board[r][c] == 'M') {
board[r][c] = 'X';
}
else if(board[r][c] == 'E') {
int mineCnt = 0;
for(int i=-1; i<=1; ++i) {
for(int j=-1; j<=1; ++j) {
int rr = r + i;
int cc = c + j;
if((i == 0 && j == 0) || rr < 0 || rr >= m || cc < 0 || cc >= n)
continue;
if(board[rr][cc] == 'M') ++mineCnt;
}
}
if(mineCnt == 0) {
board[r][c] = 'B';
for(int i=-1; i<=1; ++i) {
for(int j=-1; j<=1; ++j) {
int rr = r + i;
int cc = c + j;
if((i == 0 && j == 0) || rr < 0 || rr >= m || cc < 0 || cc >= n)
continue;
dfsUpdate(board, rr, cc, m, n);
}
}
}
else board[r][c] = '0' + mineCnt;
}
}
public:
vector<vector<char>> updateBoard(vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<int>& click) {
dfsUpdate(board, click[0], click[1], board.size(), board[0].size());
return board;
}
};




















 595
595

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








