快速排序的基本思想:
通过一趟排序将待排序记录分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分记录的关键字均比另一部分关键字小,则分别对这两部分继续进行排序,直到整个序列有序。
先看一下这幅图:
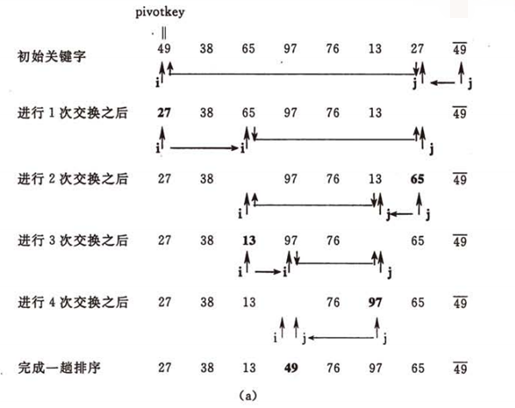
把整个序列看做一个数组,把第零个位置看做中轴,和最后一个比,如果比它小交换,比它大不做任何处理;交换了以后再和小的那端比,比它小不交换,比他大交换。这样循环往复,一趟排序完成,左边就是比中轴小的,右边就是比中轴大的,然后再用分治法,分别对这两个独立的数组进行排序。
1 public int getMiddle(Integer[] list, int low, int high) {
2 int tmp = list[low]; //数组的第一个作为中轴
3 while (low < high) {
4 while (low < high && list[high] > tmp) {
5 high--;
6 }
7 list[low] = list[high]; //比中轴小的记录移到低端
8 while (low < high && list[low] < tmp) {
9 low++;
10 }
11 list[high] = list[low]; //比中轴大的记录移到高端
12 }
13 list[low] = tmp; //中轴记录到尾
14 return low; //返回中轴的位置
15 }
递归形式的分治排序算法:
16 public void _quickSort(Integer[] list, int low, int high) {
17 if (low < high) {
18 int middle = getMiddle(list, low, high); //将list数组进行一分为二
19 _quickSort(list, low, middle - 1); //对低字表进行递归排序
20 _quickSort(list, middle + 1, high); //对高字表进行递归排序
21 }
22 }
23 public void quick(Integer[] str) {
24 if (str.length > 0) { //查看数组是否为空
25 _quickSort(str, 0, str.length - 1);
26 }
27 }
编写测试方法:
28 public class TestMain {
29
30 /**
31 * @param args
32 */
33 public static void main(String[] args) {
34 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
35 Integer[] list={34,3,53,2,23,7,14,10};
36 QuicSort qs=new QuicSort();
37 qs.quick(list);
38 for(int i=0;i<list.length;i++){
39 System.out.print(list[i]+" ");
40 }
41 System.out.println();
42 }
43
44 }
看一下打印结果吧:
2 3 7 10 14 23 34 53
这样就排序好了,快速排序是对冒泡排序的一种改进,平均时间复杂度是O(nlogn)





















 1709
1709

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








