| Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 15120 | Accepted: 4817 |
Description
Write a program that takes as input a rooted tree and a list of pairs of vertices. For each pair (u,v) the program determines the closest common ancestor of u and v in the tree. The closest common ancestor of two nodes u and v is the node w that is an ancestor of both u and v and has the greatest depth in the tree. A node can be its own ancestor (for example in Figure 1 the ancestors of node 2 are 2 and 5)
Input
The data set, which is read from a the std input, starts with the tree description, in the form:
nr_of_vertices
vertex:(nr_of_successors) successor1 successor2 ... successorn
...
where vertices are represented as integers from 1 to n ( n <= 900 ). The tree description is followed by a list of pairs of vertices, in the form:
nr_of_pairs
(u v) (x y) ...
The input file contents several data sets (at least one).
Note that white-spaces (tabs, spaces and line breaks) can be used freely in the input.
nr_of_vertices
vertex:(nr_of_successors) successor1 successor2 ... successorn
...
where vertices are represented as integers from 1 to n ( n <= 900 ). The tree description is followed by a list of pairs of vertices, in the form:
nr_of_pairs
(u v) (x y) ...
The input file contents several data sets (at least one).
Note that white-spaces (tabs, spaces and line breaks) can be used freely in the input.
Output
For each common ancestor the program prints the ancestor and the number of pair for which it is an ancestor. The results are printed on the standard output on separate lines, in to the ascending order of the vertices, in the format: ancestor:times
For example, for the following tree:
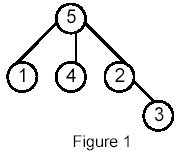
For example, for the following tree:

Sample Input
5
5:(3) 1 4 2
1:(0)
4:(0)
2:(1) 3
3:(0)
6
(1 5) (1 4) (4 2)
(2 3)
(1 3) (4 3)
Sample Output
2:1 5:5
Hint
Huge input, scanf is recommended.
Source
下面算法出处:http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/u012860428/article/details/38306327
- 该算法利用树中每个节点最多只有一个前驱。
- 寻找A,B的最近祖先,假设C为A的祖先,那么沿着A一定能到C。(B也同样如此)
因为是从下到上找的,所以最先找到的,就是最近的。
给出节点连接的子节点,根据此来建树,然后再给出一些数对,计算这两个节点的最近的公共节点并计数,最后全部查询完后,输出计数的个数;
- #include <iostream>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #define MAX 1000
- using namespace std;
- int p[MAX];
- int cnt[MAX];
- void init(int n)
- {
- int i;
- for(i=0; i<=n; i++)
- p[i]=i;
- }
- int query(int x,int y)
- {
- int i,j;
- if(p[x]==y)
- return y;
- if(p[y]==x)
- return x;
- for(i=x; p[i]!=i; i=p[i])//从当前节点开始,分别遍历x,y的父节点查找
- {
- for(j=y; p[j]!=j; j=p[j])
- {
- if(i==j)
- {
- return j;
- }
- }
- }
- return i;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int node,i,num,n,ccnode,x,y,ans,m;
- //freopen("\\input.txt","r",stdin);
- // freopen("\\output.txt","w",stdout);
- while(~scanf("%d",&n))
- {
- memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));//计数数组置零
- init(n);
- m=n;
- while(n--)
- {
- scanf("\t%d\t:\t(\t%d\t)",&node,&num);
- for(i=0; i<num; i++)
- {
- scanf("\t%d\t",&ccnode);//输入节点
- p[ccnode]=node;//指定节点的父亲节点
- }
- }
- scanf("%d",&n);
- for(i=0; i<n; i++)
- {
- getchar();
- scanf("\t(%d\t %d\t)",&x,&y);
- ans=query(x,y);
- cnt[ans]++;计数
- }
- //printf("%d:%d\n",14,cnt[14]);
- for(i=0; i<=m; i++)//遍历输出
- {
- if(cnt[i]!=0)
- printf("%d:%d\n",i,cnt[i]);
- }
- }
- return 0;
- }





 本文介绍了一个算法,用于解决给定树结构中两个节点的最近公共祖先问题。通过递归向上查找的方式确定最近的共同祖先,并统计每一对节点的查询结果。
本文介绍了一个算法,用于解决给定树结构中两个节点的最近公共祖先问题。通过递归向上查找的方式确定最近的共同祖先,并统计每一对节点的查询结果。
















 599
599

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








