PY001 - PY010 WriteUp
网上随便找的python练习,完成任务加复健一下python,顺手发到博客上。
个人觉得题目符合由简至难的规律,涵盖方面较多,新手入门非常合适的选择。
学习新编程语言最好的方式就是逼着自己写代码解决算法题。
PY001 – 输入两个数相加
题目:
•输入两个数字,输出他们相加的和
输出示例:
•a + b = 28
考点:
•input()print()语句输入输出
•变量赋值
a = int(input("input a here:"))
b = int(input("input b here:"))
c = a + b
print("a + b = ",c)
运行结果:

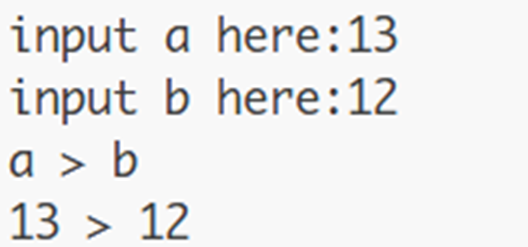
PY002 – 输入两个数比较
题目:
•输入两个数字,输出他们比较大小的结果
•输出两次,第一次
输出示例:
•a > b
•13 > 12
考点:
•If-elif-else 语句
•f格式化输出
笔记:
•print(f“{a} > {b}),格式化输出情况下,把变量放入{}中以正常在字符串中输出变量
a = int(input("input a here:"))
b = int(input("input b here:"))
if a > b:
print("a > b")
print(f"{a} > {b}")
elif a == b:
print("a = b")
print(f"{a} = {b}")
else:
print("a < b")
print(f"{a} < {b}")
运行结果:
PY003 – 1~100数字求和
题目:
•求1~100所有整数的和(包括1和100)
输出示例:
•5050
考点:
•range循环
笔记:
•For I in range(首项,尾项+1,步长)
•Eg. Range(1, 100, 2)输出从1到99所有的奇数
i, sum = 0, 0
for i in range(100):
i += 1
sum += i
print("The sum is:", sum)
运行结果:
![]()
PY004 – 组成不重复三位数
题目:
•一个三位数的个位,十位,百位都在列表[1, 2, 3, 4]中
•输出一共有多少种可能且三位数不重复
输出示例:
•There are 24 possibilities.
•All possible three digit numbers are as follows:
• [123, 124, 132, 134, 142, 143, 213, 214, 231, 234, 241, 243, 312, 314, 321, 324, 341, 342, 412, 413, 421, 423, 431, 432]
考点:
•嵌套循环
•append()函数
笔记:
•list.append(temp)函数把变量加入列表
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
lst = []
temp = 0
for i in numbers:
for j in numbers:
for k in numbers:
if i != j and j != k and i != k:
temp = i*100 + j*10 + k
if not temp in lst:
lst.append(temp)
print("There are", len(lst), "possibilities.")
print("All possible three digit numbers are as follows:\n", lst)
运行结果:

PY005 – 工整输出九九乘法表
题目:
•输出九九乘法表
•格式美观,与输出样例相同
输出示例:
•1*1=1
•1*2=2 2*2=4
•1*3=3 2*3=6 3*3=9
•1*4=4 2*4=8 3*4=12 4*4=16
•1*5=5 2*5=10 3*5=15 4*5=20 5*5=25
•1*6=6 2*6=12 3*6=18 4*6=24 5*6=30 6*6=36
•1*7=7 2*7=14 3*7=21 4*7=28 5*7=35 6*7=42 7*7=49
•1*8=8 2*8=16 3*8=24 4*8=32 5*8=40 6*8=48 7*8=56 8*8=64
•1*9=9 2*9=18 3*9=27 4*9=36 5*9=45 6*9=54 7*9=63 8*9=72 9*9=81
考点:
•不重复双循环
•格式制表符
•print()换行
笔记:
•\t为制表符,用于对齐
•Print(n, end = “/t”)end=表示以“”结尾,如果没有这个语句,值默认\n,即输出后换行
for i in range(1, 10):
for j in range(1, i + 1):
print(f"{j}*{i}={i * j}", end = "\t") # \t为制表符,用于对齐
if j == i:
print()
运行结果:

PY006 – 猴子吃桃
题目:
•猴子偷了一堆桃,每天早上吃一半,嘴馋再吃一个,如此重复,第十天早上想吃时发现只有一个桃子了。
•问第一天猴子偷了多少桃子?
输出示例:
•1534
考点:
•Def()自定义函数
•逆向思维
def backday(latter):
former = (latter + 1) * 2
return former
temp = 1
for i in range(9):
temp = backday(temp)
print("First day the monkey had", temp, "peaches.")
运行结果:
![]()
PY007 – 水仙花数
题目:
•水仙花数一个3位正整数,它的每个位上的数字的3次幂之和等于它本身。
•输出所有的水仙花数。
输出示例:
•There are 4 narcissistic numbers.
•All possible narcissistic numbers are as follows: [153, 370, 371, 407]
考点:
•整数切片
•算术运算符
笔记:
•a/b表示a除以b的结果,a//b表示a除以b取整,a%b表示a除以b取余
count = 0
lst = []
for i in range(100,1000):
x = i//100
y = i//10%10
z = i%10
if x**3 + y**3 + z**3 == i:
count += 1
lst.append(i)
print("There are", count ,"narcissistic numbers.")
print("All possible narcissistic numbers are as follows:", lst)
运行结果:

PY008 – 不同类型字符数量统计
题目:
•给一个字符串,分别统计这个字符串里数字,字母,空格,其他字符的数量。
输出示例:
•input here:3, 2, 1, Hello World!
•In this string, there're 10 letters, 3 numbers, 4 blanks and 4 other characters.
考点:
•Isalpha(), isspace(), isdigit()函数
笔记:
•i.isalpha()判断是否是字母,isdigit判断数字,isspace判断空格
text = input("input here:")
alpha, digit, space, others = 0, 0, 0, 0
for i in text:
if i.isalpha():
alpha += 1
elif i.isdigit():
digit += 1
elif i.isspace():
space += 1
else:
others += 1
print(f"In this string, there're {alpha} letters, {digit} numbers, {space} blanks and {others} other characters.")
运行结果:

PY009 – 简单列表排序
题目:
•给一个字符串,分别统计这个字符串里数字,字母,空格,其他字符的数量。
测试用例:
[20, 50, 10, 40, 30]
[‘bb’, ‘ee’, ‘aa’, ‘dd’, ‘cc’]
输出示例:
•[10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
•['aa', 'bb', 'cc', 'dd', 'ee’]
考点:
•Sort和sorted函数
笔记:
•列表的排序方法
•1 使用sort(原地排序)
•list.sort(key = None, reverse = False)
•key(可选): 接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会在每个元素上调用,其返回值将作为排序的依据。未提供默认为None,即直接比较元素本身
•reverse(可选): reverse = True降序排列,不给的话默认值为False,即升序排列
•2 使用sorted(不改变原列表顺序,在新列表中排序)
•sorted(iterable, key = None, reverse = False)
•iterable可迭代对象,不局限于列表
•调用方法与sort有明显区别
•3 区别
•sort是列表的成员方法,sorted 可以对所有可迭代的对象进行排序操作
•list 的 sort 方法返回的是对已经存在的列表进行操作,而内建函数 sorted 方法返回的是一个新的 list,而不是在原来的基础上进行的操作
•sort使用方法为lst.sort(),而sorted使用方法为sorted(lst)
list1 = [20, 50, 10, 40, 30]
list2 = ['bb', 'ee', 'aa', 'dd', 'cc']
list1.sort() # 不能直接在print框中进行list.sort()
# list.sort()可以理解为是一种自我迭代行为
print(list1)
print(sorted(list2))
运行结果:
![]()
PY009 – 简单列表排序
题目:
•给出学生成绩列表,将学生信息按成绩降序排列
•复杂列表排序,元素是字典或元组
测试用例:
[
{‘sno’: 101, ‘name’: ‘张三’, ‘grade’: 88}
{‘sno’: 101, ‘name’: ‘李四’, ‘grade’: 77}
{‘sno’: 101, ‘name’: ‘钱五’, ‘grade’: 99}
{‘sno’: 101, ‘name’: ‘周六’, ‘grade’: 66}
]
输出示例:
•{'sno': 101, 'name': '钱五', 'grade': 99}
•{'sno': 101, 'name': '张三', 'grade': 88}
•{'sno': 101, 'name': '李四', 'grade': 77}
•{'sno': 101, 'name': '周六', 'grade': 66}
考点:
•复杂列表排序
•Sort和sorted函数中key和reverse的用法
笔记:
•匿名函数lambda,调用方法lambda 形参: 返回值
•lambda只能处理简单逻辑,一般只有一句表达式和一个返回值的函数才可以用lambda简化
•匿名函数的调用次数很少,一般只调用一次
•# 形参(形式参数)是在函数定义时声明的变量,用于接收传递给函数的值
•# 实参(实际参数)是在函数调用时传递给函数的具体值或表达式
students_list = [
{'sno': 101, 'name': '张三', 'grade': 88},
{'sno': 101, 'name': '李四', 'grade': 77},
{'sno': 101, 'name': '钱五', 'grade': 99},
{'sno': 101, 'name': '周六', 'grade': 66}
]
list_new = sorted(students_list, key = lambda x: x["grade"], reverse = True)
for i in list_new:
print(i)
迷你彩蛋(林)
《十日终焉》张三,李四,钱五,周六
运行结果:

#记录:指针-月羽,林,木舟
#时间:2025/11/14
#灵感:python算法解题指导和笔记






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








