Given an array of integers preorder, which represents the preorder traversal of a BST (i.e., binary search tree), construct the tree and return its root.
It is guaranteed that there is always possible to find a binary search tree with the given requirements for the given test cases.
A binary search tree is a binary tree where for every node, any descendant of Node.left has a value strictly less than Node.val, and any descendant of Node.right has a value strictly greater than Node.val.
A preorder traversal of a binary tree displays the value of the node first, then traverses Node.left, then traverses Node.right.
Example 1:
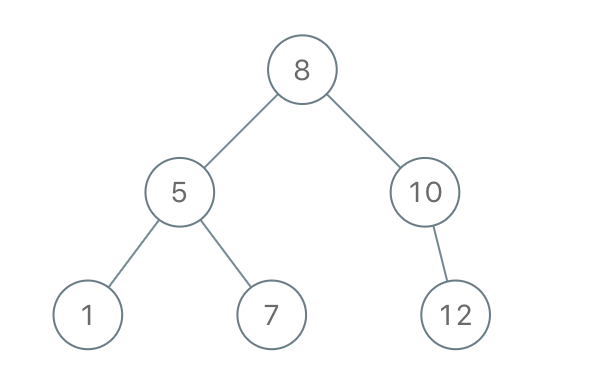
Input: preorder = [8,5,1,7,10,12]
Output: [8,5,10,1,7,null,12]
Example 2:
Input: preorder = [1,3]
Output: [1,null,3]
Constraints:
1 <= preorder.length <= 1001 <= preorder[i] <= 108- All the values of
preorderare unique.
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/construct-binary-search-tree-from-preorder-traversal/
题目大意:根据先序遍历结果恢复二叉搜索树
题目分析:二分找到大于当前根的最小值的下标,然后再分情况二分建树
0ms,时间击败100%
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int bsearch(int[] a, int l, int r, int val) {
int mid = 0, ans = -1;
while (l <= r) {
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (a[mid] > val) {
r = mid - 1;
ans = mid;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
public void solve(TreeNode root, int[] preorder, int l, int r) {
if (l > r || root == null) {
return;
}
int rp = bsearch(preorder, l, r, root.val);
root.right = rp == -1 ? null : new TreeNode(preorder[rp]);
root.left = (rp != -1 && l >= rp) ? null : new TreeNode(preorder[l]);
solve(root.left, preorder, l + 1, rp == -1 ? r : rp - 1);
solve(root.right, preorder, rp + 1, r);
}
public TreeNode bstFromPreorder(int[] preorder) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
solve(root, preorder, 1, preorder.length - 1);
return root;
}
}






 本文解析了如何通过给定的整数先序遍历序列,利用递归策略重建二叉搜索树。重点讲解了查找插入位置的二分搜索法,并提供了Java代码示例。理解这个过程对于解决LeetCode上的相关问题至关重要。
本文解析了如何通过给定的整数先序遍历序列,利用递归策略重建二叉搜索树。重点讲解了查找插入位置的二分搜索法,并提供了Java代码示例。理解这个过程对于解决LeetCode上的相关问题至关重要。
















 3497
3497

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








