C++STL—unordered_map和unordered_set介绍和使用
unordered_set和unordered_map的使用类似set和map。unordered_set是key模型。unordered_map是key/value模型,存储的数据类型是一个pair<key, value>。
map和set的底层是红黑树,unordered_map和unordered_set的底层是哈希表。他们的函数接口大部分相同,所以会使用map和set,也会使用unordered_map、unordered_set。
1、unordered_set
1.1、unordered_set简介
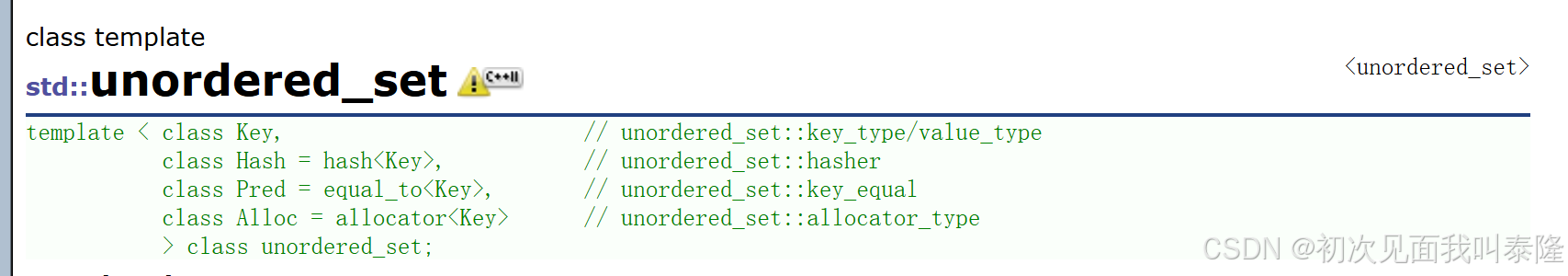
如果:第一个模板参数就是存储的数据类型Key,因为给了缺省值,所以我们使用的时候只要给出数据类型即可。包含于头文件<unordered_set>
第二个模板参数是哈希函数,unordered_set默认要求Key支持转换为整形,如果不支持或者想按自己的需求走可以自行实现支持将Key转成整形的仿函数传给第二个模板参数。
unordered_set默认要求Key支持比较相等,如果不支持或者想按自己的需求走可以自行实现支持将Key比较相等的仿函数传给第三个模板参数。
unordered_set底层是用哈希桶实现,增删查平均效率是O(1) ,迭代器遍历不再有序,为了跟set区分,所以取名unordered_set。
1.2、接口介绍及其使用
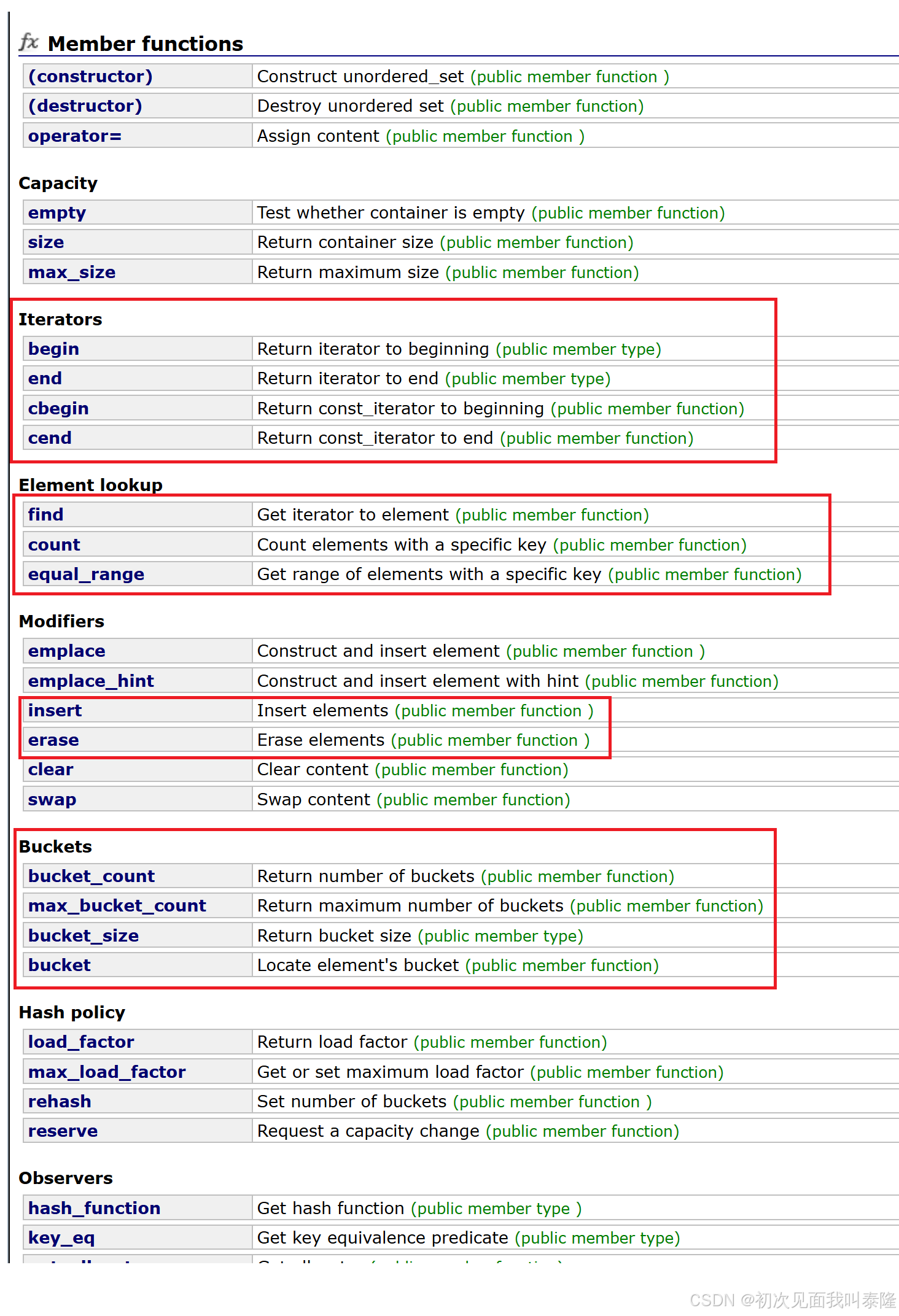
注意:unordered_set和unordered_map这里的迭代器是单向迭代器,没有反向迭代器。而且迭代器遍历是无序的(因为底层是哈希表),而map和set的迭代器遍历是有序的(中序遍历),因为map和set底层是红黑树。
find、count、equal_range使用类似前面map和set中的使用,有疑问移步前面写的map和set的介绍和使用。
相比于map和set多了Buckets中四个函数,因为底层是哈希桶(拉链法),函数取名都带了bucket(桶),但是用处并不大。
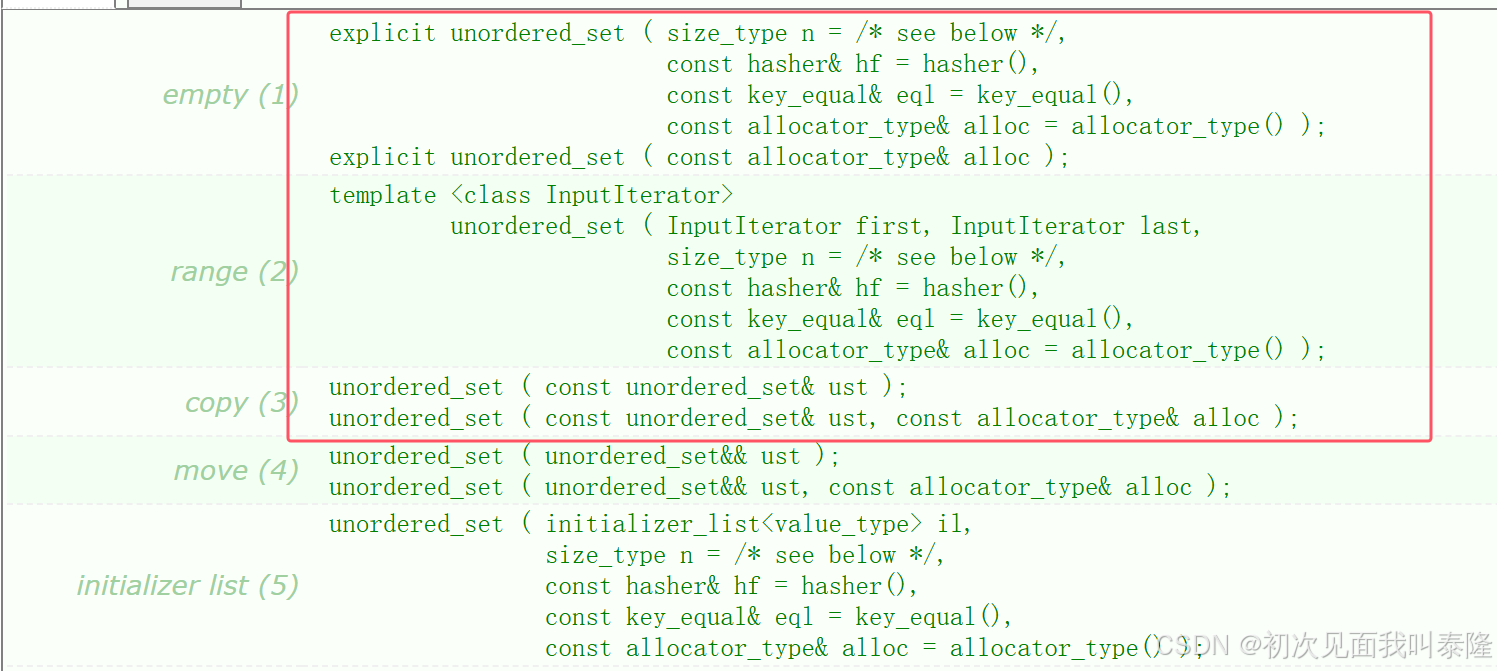
构造函数支持无参构造、迭代器区间构造、拷贝构造,后面两个需要到C++11才能看懂,因此unordered_set和unordered_map是C++11的产物,所以多了下面两个构造函数。
下面来看看基本使用方式:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
unordered_set<int> us;
us.insert(1);
us.insert(3);
us.insert(31);
us.insert(15);
us.insert(22);
unordered_set<int>::iterator it = us.begin();
while (it != us.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
us.erase(31);
us.erase(1);
for (auto& e : us)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
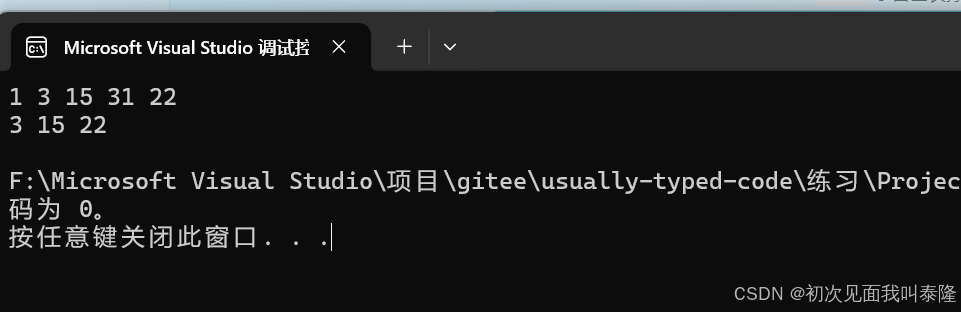
注意到:这里insert的返回值跟set一样返回的是pair<iterator, bool>。
2、unordered_map
2.1、unordered_map简介

后面三个模板参数跟前面set是一样的,但是unordered_map是key/value模型,所以数据类型有Key和T(Value)。包含于头文件<unordered_map>。
2.2、接口介绍及其使用
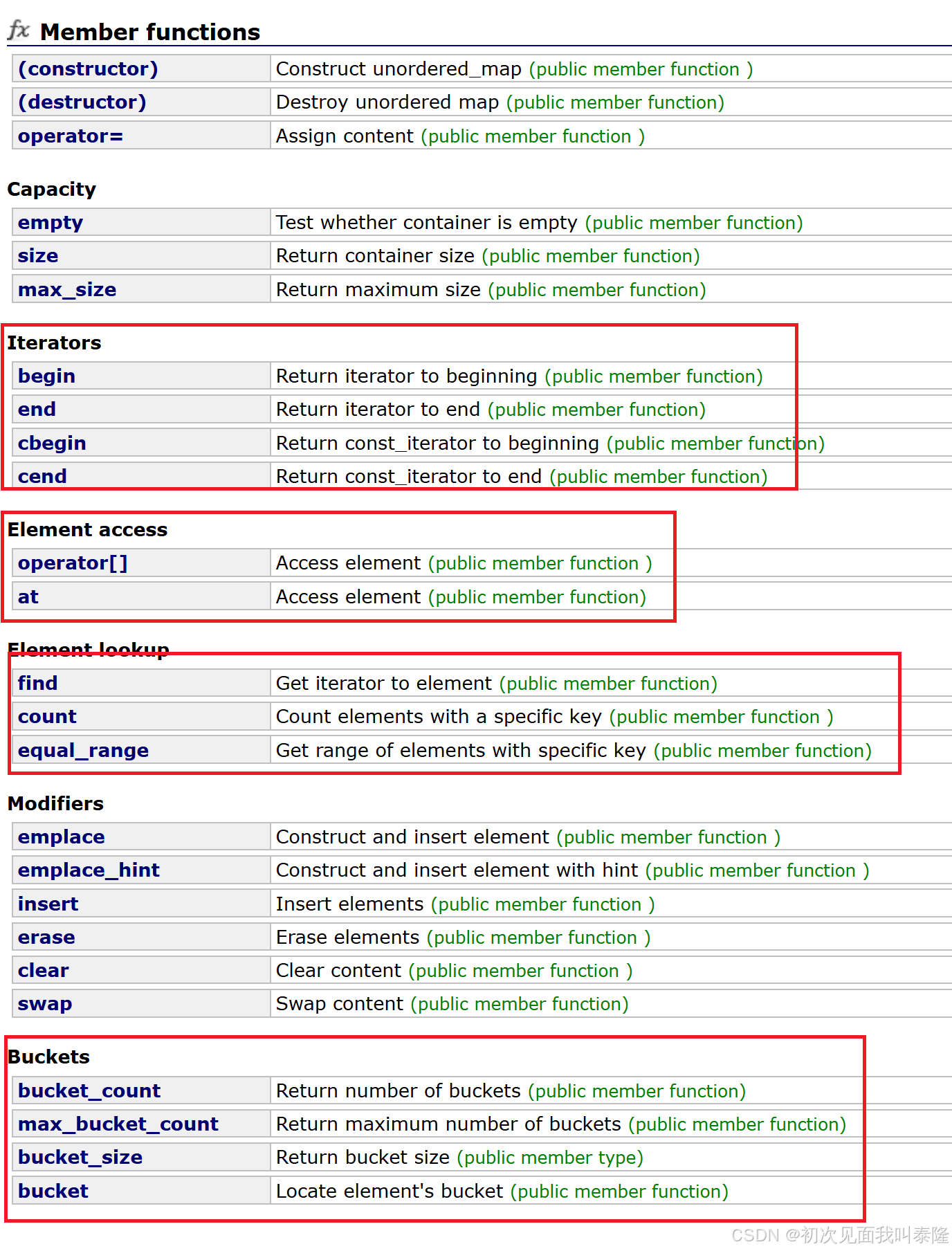
可以看到这里的接口跟unordered_set是一样的,同样是单向迭代器,只不过类似map,比unordered_set多了operator[]和at函数。通过实现operator[]可以插入和修改。
使用如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
unordered_map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("insert", "插入"));
dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));
dict["left"]; // 插入
dict["right"] = "右边"; // 插入+修改
dict["left"] = "左边"; // 修改
unordered_map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
dict.erase("sort");
for (const auto& e : dict)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1、支持迭代器就支持范围for,因为范围for的底层就是替换成迭代器。
2、it->这里本质上是因为迭代器重载了operator->,返回的是数据类型的指针,也就是pair<K, V>*,正常应该写成it->->first,但是为了可读性优化成了一个->即可。
这些我们之前都有讲过,这里就不再赘述了。






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








