一、创建一个界面
第一个 没用的 故 删除
二、vue 关键字
2.1 v-if条件判断
<div id="app">
<label>
<h2 v-if="isShow">test</h2>
<h2 v-else>1010101 else</h2>
</label>
<button type="button" @click="btnClick">btn</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isShow:true
},
methods:{
btnClick(){
this.isShow=!this.isShow
}
}
})
</script>
2.2 v-show
<div id="app">
<label>
<!-- v-if: 条件为false时 将包含的元素从dom中删掉
v-show: 只仅仅隐藏 加了个 display:none
-->
<h2 v-show="isShow">test</h2>
</label>
<button type="button" @click="btnClick">btn</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isShow:true
},
methods:{
btnClick(){
this.isShow=!this.isShow
}
}
})
2.3 created 和 mounted
Vue中实例或者组件从创建到消灭中间经过的一系列过程。

-
created:在模板渲染成html前调用,即通常初始化某些属性值(从后端获取数据),然后再渲染成视图。
-
mounted:在模板渲染成html后调用,通常是初始化页面完成后,再对html的dom节点进行一些需要的操作。
2.3 mustache(胡须)
mustache{{}}不仅仅可以写变量 也可以写简单的表达式。
<template>
<div id="app">
<h2>{{a+''+b}}</h2>
<h2>{{count*2}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Choice",
data(){
return{
a:"11",
b:"22",
count:100
}
},
create:function () {
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2.4 v-once
<h2 v-once>{{count}}</h2> 只会改变一次
2.5 v-html
解析变量html内容
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2 v-html="a"></h2>
</div>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
a:'<h1>太帅了/h1>',
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.6 v-text
与mustache相似 显示文本 不够灵活不建议使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 会直接覆盖,you不够灵活-->
<h2 v-text="a">,you</h2>
</div>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
a:'<h1>太帅了</h1>',
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.7 v-pre
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>{{a}}</h2>
<!-- 会原封不动的显示里面的内容 不作任何的解析-->
<h2 v-pre>{{a}}</h2>
</div>
<script>
const vm=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
a:'<h1>太帅了</h1>',
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.8 cloak
翻译为斗篷
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
[v-cloak]{
display: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 一旦vue对app进行解析 v-cloak会将对app进行自定义的样式操作 直到完成解析并且v-cloak在div中删除-->
<div id="app" v-cloak>
<h2>{{a}}</h2>
</div>
<script>
//设置延时1000ms
setTimeout(function () {
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
a: '<h1>太帅了</h1>',
}
})
}, 1000)
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.9 v-bind 动态绑定属性
动态地显示图片 也就是可以控制图片内容显示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>{{url}}</h2>
<!-- 这里不可以使用胡须,只有内容位置才可以插入-->
<img src="{{url}}" alt="">
<!-- 在html关键字前面加入v-bind: 动态绑定到data里面的url中 变成可以变化的src-->
<img v-bind:src="url" alt="">
<!-- 可以缩写成 :-->
<!-- <img :src="url" alt="">-->
<a :href="url">图片地址</a>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
url: 'https://t7.baidu.com/it/u=1819248061,230866778&fm=193&f=GIF'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.9.1 动态绑定css
对象语法(常用)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
.s1{
color: red;
}
.s2{
color: blue;
}
.s3{
font-family: 宋体;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- {里面是对象 key:value} isS1 为true时加入到class里-->
<h2 :class="{s1:isS1,s2:isS2}">TEST</h2>
<button @click="btn">变色</button>
<!--vue 会将两个class合并 不会覆盖-->
<h2 class="s3" :class="{s1:isS1,s2:isS2}">TEST</h2>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isS1:true,
isS2:false,
},
methods:{
btn:function () {
this.isS1=!this.isS1;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
数组语法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
.s1{
color: red;
}
.s2{
color: blue;
}
.s3{
font-family: 宋体;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2 class="s3" :class="getClass()">TEST</h2>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isS1:true,
isS2:false,
s1:'s1',
s2:'s2',
},
methods:{
btn:function () {
this.isS1=!this.isS1;
},
getClass:function () {
//别忘了this
return [this.s1,this.s2];
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.9.2 动态绑定style
对象语法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 不加引号 vue会当变量去解析-->
<h3 :style="getStyles()">test</h3>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
num:0,
fontSize1: 90
myColor:'red'
},
methods:{
getStyles:function () {
return {fontSize:this.fontSize1 + 'px',color:this.myColor}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
数组语法(不常用 参考上面)
2.10 Computed
2.10.1 基本用法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h3>{{name}}</h3>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName:'Big',
lastName:'Boy'
},
computed:{
name:function () {
return this.firstName+' '+this.lastName
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.10.2 复杂使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 不加引号 vue会当变量去解析-->
<h3>{{totalPrice}}</h3>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
books:[
{id:1,name:'book1',price:98},
{id:2,name:'book2',price:998},
{id:3,name:'book3',price:998},
{id:4,name:'book4',price:998}
]
},
computed:{
totalPrice:function () {
let sum=0;
for(let i of this.books){//es6
sum+=i.price;
}
return sum
}
},
methods:{
getStyles:function () {
return {fontSize:this.fontSize1 + 'px',color:this.myColor}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
getter and setter
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h3>{{name}}</h3>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName:'Big',
lastName:'Boy'
},
computed:{
//只读属性
name:{
//计算属性一般是没有set方法
set:function (newValue) {
const names=newValue.split(' ');
this.firstName=names[0];
this.lastName=names[1];
},
get:function () {
return this.firstName+' '+this.lastName
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
计算属性(computed)对比方法(methods)
- 第一 在界面上可以当一个属性引用不需要加()直接引用
- 第二 计算属性的结果放在缓存中,复用效率高于方法
2.11 v-on
参数问题
如果函数需要参数 但是调用的时候没有输入 vue会将浏览器生产的event对象传到这个函数的第一个参数里
<div id="app">
<h3>{{num}}</h3>
<button @click="add">add</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
num:0
},
methods:{
add(event){
this.num++;
console.log(event);
}
}
})
</script>
多参数时用$event取event
如果不加 event会被当做变量在vue中寻找
<div id="app">
<h3>{{num}}</h3>
<button @click="add(11,$event)">add</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
num:0
},
methods:{
add(abc,event){
this.num+=abc;
console.log(event);
}
}
})
</script>
v-on修饰符
click.stop
阻止点击事件继续传播
点击add divClick不会被打印
<div id="app" @click="divClick">
<h3>div</h3>
<button @click.stop="btnClick">add</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
num:0
},
methods:{
divClick(){
console.log("divClick");
},
btnClick(){
console.log("btnClick")
}
}
})
click.prevent
阻止默认事件行为
<div id="app">
<button type="submit" @click.prevent="btnClick">btn</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
},
methods:{
btnClick(){
console.log("btnClick")
}
}
})
</script>
xx.once
只监听一次事件 如下
keyup.enter
<div id="app">
<label>
<input @keyup.enter="btnClick1"/>
</label>
<button type="submit" @click.once="btnClick2">btn</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
},
methods:{
btnClick1(){
console.log("keyup enter")
},
btnClick2(){
console.log("keyup enter")
}
}
})
</script>
2.12 v-for
<div id="app">
<ul>
<!-- 若是 item in yuge 那item仅仅是值-->
<li v-for="(value,key,index) in yuge">
{{value}} {{key}} {{index}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
yuge:{
height:1.99,
age:18,
name:'shuaiguo'
}
},
methods:{
}
})
</script>
为什么建议使用v-for设置一个:key
在向中间插入元素时 如果没有key 虚拟DOM的diff算法只能一个个将后面元素后移 效率低下 使用key作为数据标识可在中间直接插入数据 高效的更新虚拟DOM
特别:vue中数组哪个方法是响应式
- 1.push()
2.pop()
3.shift()
4.unshift()
5.splice() 拼接
6.sort() 将…分类
7.reverse() 颠倒 反转
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in letters" :key="item">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
<button @click="btnClick">按钮</button>
</div>
<script src="../vue.min.js"></script>
<script>
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'hello',
letters:['a','b','c','d'],
},
methods:{
btnClick(){
// 1.push方法
// this.letters.push('aaa');
// 2.通过索引值修改数组中的元素(不是响应式的)
// this.letters[0]='bbbbb';
//pop():删除数组中的最后一个元素
this.letters.pop();
//shift():删除数组中的第一个元素
this.letters.shift();
// unshift():在数组最前面添加元素
this.letters.unshift('aaa','bbb','ccc');
// splice()作用:删除元素/插入元素/替换元素
//删除元素:第二个参数传入你要删除几个元素(如果没有传参数,就删除后面的所有元素)
//替换元素:第二个参数辨识要替换几个元素,后面是用于替换前面的元素
// 插入元素:第二元素为0,并且后面跟上要插入的元素
// splice(start)
this.letters.splice(1,3,'s','u','n');
// sort():
this.letters.sort();
// reverse()
this.letters.reverse();
// set(要修改的对象,索引值,修改后的值)
//this.letters[0]='bbbb' 这个vue不会响应!!!! 可以用splice
Vue.set(this.letters,0,'bbbb');
}
}
})
//es6可变参数语法
function sum(...num) {
console.log(num);
}
sum(20,30,40,50,60,70);
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.13 v-model
数据双向绑定 注意胡须什么的都是响应式 不会反过来影响数据
CheckBox
<div id="app">
<h2>您的爱好是?:</h2>
<!-- :for="item" 值绑定-->
<label v-for="item in list" :for="item">
<input type="checkbox" v-model="act" :id="item" name="act" :value="item">{{item}}
</label>
<h2>{{act}}</h2>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
//注意这个地方是数组类型 单选框时对应的是boolean值
act:[],
list:['唱','跳','RUP']
}
})
</script>
Select
<div id="app">
<h2>您的爱好是?:</h2>
<select name="nameS" v-model="act">
<option value="1">1</option>
<option value="3">3</option>
<option value="4">4</option>
<option value="2">2</option>
</select>
<h2>{{act}}</h2>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
act:''
}
})
</script>
修饰符
lazy
<div id="app">
<h2>您的爱好是?:</h2>
<!-- v-model.lazy 敲回车才绑定-->
<input type="text" v-model.lazy="act">
<h2>{{act}}</h2>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
act:''
}
})
</script>
number
<div id="app">
<h2>您的爱好是?:</h2>
<!-- v-model.number act将一直保持number类型-->
<input type="number" v-model.number="act">
<h2>{{act+' '+typeof act}}</h2>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
act:0
}
})
</script>
trim
去除左右两边多余空格
v-model.trim
三、组件
3.1 组件内值必须为函数
为什么必须是函数呢?
因为用对象data(){ title:'dasfaa'}会导致所有组件的复用实例的数据是共享的 而用函数每次复用都会创建一个新的数据储存地址
<div id="app">
<t1></t1>
</div>
<template id="t1">
<div>
<h2>qwer</h2>
<h2>111111111111{{title}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//注册一个全局组件
Vue.component('t1',{
template:'#t1',
//组件里必须是 返回函数
data(){
return{
title:'dasfaa'
}
}
})
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
act:0
}
})
</script>
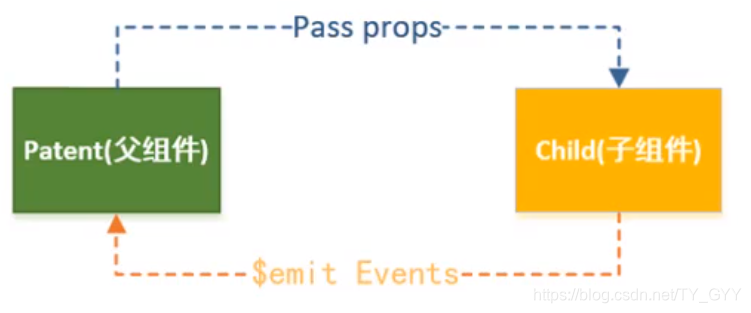
4.2 父子组件通信与访问
4.2.1 父传子 props
props支持的数据验证
String
Number
Boolean
Function
Object
Array
Symbol
<div id="app">
<!-- //模板里多了一个属性 就可以用bind-->
<t1 :act="act" :list1="movies"></t1>
</div>
<template id="t1">
<div>
<h2>Data: {{act}}</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in list1" :key="item">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const t1={
template:'#t1',
//父传子用 props
props:{
//对象可以指定类型
act:{
validator(value) {
console.log(value);
return false;
}
},
list1:{
type:Array,
//可以设置默认值 如果类型是数组或者对象时 默认值必须是一个函数
default(){
return ['1','2']
},
//用来验证数据
validator(value){
console.log(value);
//必须是其中一个
return ['m11','m33','4m'].indexOf(value) !==-1
},
//使用这个组件时候 必须传值给这个属性
required:true
}
},
data(){
return{
list1: []
}
}
}
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
act:77,
movies:['m1','m2','m3']
},
components:{
t1 //cs6
}
})
</script>
4.2.2 子传父 $emit
<div id="app">
<!-- 父组件 vue默认吧item传过去-->
<t1 @btnclick="copyData"></t1>
</div>
<template id="t1">
<div>
<button @click="notifyClick('btn click')">button</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const t1={
template:'#t1',
//父传子用 props
props:{
//对象可以指定类型
act:{
validator(value) {
console.log(value);
return false;
}
}
},
data(){
return{
list1: []
}
},
methods:{
notifyClick(item){
//不能用驼峰命名 发出一个名为btnclick的事件 可以在父组件中调用
this.$emit('btnclick',item)
}
}
}
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
act:77,
movies:['m1','m2','m3']
},
components:{
t1 //cs6
},
methods: {
copyData(v){
console.log(v+"----------copy")
}
}
})
</script>
4.2.3 父访问子 c h i l d r e n / children/ children/refs
<div id="app">
<t1 ref="t01"></t1>
<t1 ref="t02"></t1>
<t1 ref="t03"></t1>
<button @click="btnClick">button</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
num1: 0,
num2: 0
},
components: {
t1:{
data(){
return{
name:'子组件内的name'
}
},
methods: {
message() {
console.log("子组件的message方法...");
}
}
}
},
methods: {
btnClick(){
// 1.$children
//开发中一般不用children 不好维护
// console.log(this.$children);
// for (let t of this.$children){
// console.log(t.name);
// t.message()
// }
//2$refs 对象类型默认为空需要在使用子组件时 加入ref命名
console.log(this.$refs);
}
}
})
</script>
4.3 slot
4.3.1 基本使用
<div id="app">
<t1></t1>
<t1>
<!-- 所有元素替换到slot中-->
<span>data</span>
<p>data2</p>
</t1>
<t1></t1>
</div>
<template id="t1">
<div>
<h2>--1122--</h2>
<!-- 定义个slot相当于html元素占位符-->
<slot>
<!-- 设置默认元素-->
<button>按钮</button>
</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
},
components: {
t1:{
template:'#t1',
data(){
return{
}
},
methods: {
}
}
},
methods: {
}
})
</script>
4.3.2 具名使用
<div id="app">
<t1>
<p slot="s2">t1 test</p>
<p slot="s1">t2 test</p>
</t1>
<!-- 要指定name 要不然什么都不显示-->
<t1><p>t3 test</p></t1>
</div>
<template id="t1">
<div>
<h2>----</h2>
<slot name="s1"><p>1</p></slot>
<slot name="s2"><p>2</p></slot>
<slot name="s3"><p>3</p></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
},
components: {
t1:{
template:'#t1',
data(){
return{
}
},
methods: {
}
}
},
methods: {
}
})
</script>
4.3.3 v-slot 作用域插槽
让父组件的插槽内容能够访问子组件中才有的数据
<div id="app">
<t1></t1>
<t1>
<!-- <template slot-scope="slot">
现在这样写:v-slot:插槽名 =“自定义属性名” 在template中
-->
<template v-slot="slotProps">
<span>{{slotProps.flowers.toString()}}</span>
</template>
</t1>
</div>
<template id="t1">
<div>
<h2>----</h2>
<slot :flowers="flowers">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in flowers" :key="item">
{{item}}
</li>
</ul>
</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
},
components: {
t1:{
template:'#t1',
data(){
return{
flowers:['clover','rose','lily','...']
}
},
methods: {
}
}
},
methods: {
}
})
</script>
四、Vue CLI
安装 创建项目
官网链接 写的很明白
注意
-
先安装node
-
Vue CLI 的包名称由
vue-cli改成了@vue/cli。 如果你已经全局安装了旧版本的vue-cli(1.x 或 2.x),你需要先通过npm uninstall vue-cli -g或yarn global remove vue-cli卸载它。
对Vue中 runtime-compiler 和 runtime-only 两种模式的理解
区别
- runtime-only 比 runtime-compiler 轻 6kb
- runtime-only 运行更快
- runtime-only 只能识别render函数,不能识别template,.vue文件中的template也是被 vue-template-compiler 翻译成了render函数,所以只能在.vue里写 template
五、vue router
5.1 url的hash HTML5的history
通过url的hash HTML5的history可以使页面不刷新
| 浏览器console输入 | 地址栏 |
|---|---|
| location.hash=‘wokao’ | http://localhost:8080/#/wokao |
| history.pushState({},’’,‘wokao2’) | http://localhost:8080/wokao2 |
| history.back()/history.go(-1)/history.forward(1) | http://localhost:8080/#/wokao |
| history.replaceState({},’’,‘wo’) | http://localhost:8080/wo |
- history.pushState是一个栈
- history.replaceState替换当前路由 被替换的路由嗝屁了
- history.go(-2)从栈里出两个 history.go(1) 从栈里压入一个history.forward一个道理 类似go
- 地址中有#表示使用的是hash值
5.2 vue-router 简单使用
-
创建界面文件
Home.vue
<template> <div> <h2>Home</h2> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "home" } </script> <style scoped> </style>About.vue
<template> <div> <h2>About</h2> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "About" } </script> <style scoped> </style> -
书写路由
import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' import Home from "../views/Home"; import About from "../views/About"; Vue.use(VueRouter) const routes = [ { path:'/home', component:Home }, { path:'/about', component:About } ] const router = new VueRouter({ routes }) export default router -
使用路由
在APP.vue中书写
<template> <div id="app"> <router-link to="/home">home </router-link> <router-link to="/about">about</router-link> <router-view/> </div> </template> <style> </style>
5.3 修改路由的默认值 改hash为history
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Home from "../views/Home";
import About from "../views/About";
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path:'',
/*
{
path:'',
component:Home
}这种方式地址栏不会有home
*/
redirect:'/home'
},
{
path:'/home',
component:Home
},
{
path:'/about',
component:About
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
//默认mode为hash
mode:'history'
})
export default router
5.3 router-link属性
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| to="/home" | 指定路由 |
| tag=“button” | 指定渲染成什么元素 |
| replace | 不会留下history记录 |
| active-class="" | 自定义router-link-active的名字 |
router-link-active
当某个路由被激活router自动加入class这个样式router-link-active 所以可以设置激活状态
也可以统一设置class 在router/index.js 下添加linkActiveClass
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
mode:'history',
linkActiveClass:'main'
})
演示代码
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-link style="margin-right: 10px" to="/home" tag="button" replace active-class="main">home</router-link>
<router-link to="/about" tag="button" replace>about</router-link>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<style>
.router-link-active{
color: #42b983;
}
.main{
color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
5.4 代码跳转路由
<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- <router-link style="margin-right: 10px" to="/home" tag="button">home</router-link>-->
<!-- <router-link to="/about" tag="button" replace>about</router-link>-->
<button @click="goHome">home</button>
<button @click="goAbout">about</button>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'APP',
methods: {
goAbout() {
//vue 会给所有的组件内置$router $route为当前活跃的路由
//防止重复点击 添加路由报错
if (this.$route.path !== '/about')
this.$router.replace('/about')
else
console.log('重复点击');
},
goHome() {
if (this.$route.path !== '/home')
this.$router.replace('/home')
else
console.log('重复点击');
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
5.5 动态路由
user.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>userId:{{$route.params.userId}}</h2>
<h2>userId:{{$route.params.username}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "User"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
添加路由
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Home from "../views/Home";
import About from "../views/About";
import User from "../views/User";
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path:'',
redirect:'/home'
},
{
path:'/home',
component:Home
},
{
path:'/about',
component:About
},
{
path:'/user/:userId&:username',
component:User
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
mode:'history',
linkActiveClass:'main'
})
export default router
app.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>APP Components</h1>
<router-link style="margin-right: 10px" to="/home" tag="button">home</router-link>
<router-link style="margin-right: 10px" :to="'/user/'+userId+'&'+username" tag="button">goUser</router-link>
<router-link to="/about" tag="button" replace>about</router-link>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'APP',
data(){
return{
userId:'1',
username:'yuge'
}
},
methods: {}
}
</script>
<style>
.main {
color: blueviolet;
}
</style>
5.6 路由懒加载
当打包构建应用时,JavaScript 包会变得非常大,影响页面加载。如果我们能把不同路由对应的组件分割成不同的代码块,然后当路由被访问的时候才加载对应组件,这样就更加高效了。
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
// import Home from "../views/Home";
// import About from "../views/About";
// import User from "../views/User";
Vue.use(VueRouter)
//路由懒加载 实现动态加载
//一个路由会被分为一个js文件 当使用时动态加载
const Home=()=>import('../views/Home')
const About=()=>import('../views/About')
const User=()=>import('../views/User')
const routes = [
{
path:'',
redirect:'/home'
},
{
path:'/home',
component:Home
},
{
path:'/about',
component:About
},
{
path:'/user/:userId&:username',
component:User
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
mode:'history',
linkActiveClass:'main'
})
export default router
5.7嵌套路由
创建HomeNews.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- // ul>li{新闻$}*4 按一个tab-->
<ul>
<li>新闻1</li>
<li>新闻2</li>
<li>新闻3</li>
<li>新闻4</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "HomeNews"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
配路由
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
//路由懒加载
const Home=()=>import('../views/Home')
const HomeNews=()=>import('../views/HomeNews')
const routes = [
{
path:'',
redirect:'/home'
},
{
path:'/home',
component:Home,
children:[
{
path:'',
redirect:'news'
},
{
// 不能加 / vue会自动加入
path:'news',
component:HomeNews
}
]
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
mode:'history',
linkActiveClass:'main'
})
export default router
home.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>Home</h2>
<router-link to="/home/news">homeNews</router-link>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "home"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
5.8 参数传递
app.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>APP Components</h1>
<router-link style="margin-right: 10px" to="/home" tag="button">home</router-link>
<router-link :to="{path:'/profile',query:{name:'rose',id:2,age:18}}" tag="button">
profile
</router-link>
<button @click="goProfile">goProfile 2.0</button>
<router-link style="margin-right: 10px" :to="'/user/'+id+'&'+name" tag="button">goUser</router-link>
<button @click="goUser">goUser 2.0</button>
<router-link to="/about" tag="button" replace>about</router-link>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'APP',
data() {
return {
id: '1',
name: 'yuge',
age: 18
}
},
methods: {
goUser() {
this.$router.replace( '/user/'+this.id+'&'+this.name)
},
goProfile() {
this.$router.replace({
path: '/profile',
query: {
name: this.name,
id: this.id,
age: this.age
}
})
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
router-link,button{
margin-right: 10px
}
</style>
profile.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>Profile Component</h1>
<p>{{$route.query.name+' '+$route.query.id+' '+$route.query.age}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Profile",
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
router/index
{
path:'/profile',
component:Profile
}
5.9 全局导航守卫
router/index
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
// import Home from "../views/Home";
// import About from "../views/About";
// import User from "../views/User";
Vue.use(VueRouter)
//路由懒加载
const Home=()=>import('../views/Home')
const HomeNews=()=>import('../views/HomeNews')
const About=()=>import('../views/About')
const User=()=>import('../views/User')
const Profile=()=>import('../views/Profile')
const routes = [
{
path:'',
redirect:'/home'
},
{
path:'/home',
component:Home,
//定义元数据
meta:{
title:'首页'
},
children:[
{
path:'',
redirect:'news'
},
{
// 不能加 / vue会自动加入
path:'news',
component:HomeNews,
meta:{
title:'首页-新闻'
}
}
]
},
{
path:'/about',
component:About,
meta:{
title:'关于'
},
beforeEnter:((to,from,next)=>{
console.log('about beforeEnter');
next()
})
},
{
path:'/user/:userId&:username',
component:User,
meta:{
title:'用户'
}
},
{
path:'/profile',
component:Profile,
meta:{
title:'我的'
}
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
mode:'history',
linkActiveClass:'main'
})
//全局前置守卫
router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{
document.title=to.meta.title
next()
})
export default router
5.10 keep-alive
app.vue
keep-alive保持组件不被销毁
<keep-alive exclude="about,profile">
<router-view/>
</keep-alive>
<template>
<div>
<h2>Home</h2>
<router-link to="/home/news">homeNews</router-link>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "home",
data() {
return {
path:'/home/news'
}
},
destroyed(){
console.log('home onDestroyed');
},
//activated 和 deactivated 只有使用keep-alive才会有效
//所以那时候可以用created 和 destroyed
activated(){
console.log('activated');
this.$router.replace(this.path)
},
deactivated () {
console.log('deactivated');
},
beforeRouterLeave(to,from,next){
this.path=this.$route.path
next()
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
六、Vuex
vuex 作用是用来创建和管理全局变量 而且可以实现数据响应式
6.1 vuex基本使用
-
安装
npm install vuex --save -
在src下创建store/index.js
-
import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' //安装插件 Vue.use(Vuex) //创建对象 const store = new Vuex.Store({ state:{ counter:0 } }) export default store -
<template> <div id="app"> <h2>{{$store.state.counter}}</h2> <button @click="$store.state.counter++">+</button> <button @click="$store.state.counter--">-</button> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'APP', components: { }, data() { return {} }, methods: { } } </script> <style> @import "./assets/css/base.css"; button{ width: 50px; margin-right: 10px; } </style>不建议直接修改$store.state的数据,直接修改无法得知是哪个页面修改的数据 不利于找错改错
6.2 Vue Devtools安装
6.3 Vuex-store
6.3.1 响应式规则
- vuex 中store 中的 state是响应式的, 当state 中的数据发生变化的时候, vue 组件会自动更新。当我们修改vuex 中store 对象中的数据,都会加入到 vue 整个响应式中, 在vuex 中 store 对象中state 等价于 单个组件 data 存储数据源的地方; 每一个属性都会有一个依赖, Dep => 对应多个watcher
- vue: 响应式系统: 在 data 数据源中保存的数据都会被保存到vue 的响应式系统中, 而相应式系统会监听属性的变化。 当属性发生变化时, 会通知页面中所有用到该属性的地方。
- 后边追加到响应式系统中: 就不会是响应式的数据。 做到响应式系统数据: 就必须在data 数据初始化好。 被 vue 数据监听。
//info没有address也会增加这个字段并且添加到响应式中
Vue.set(state.info, 'address', '山东省')
//delete state.info.adress 这个做不到响应式
Vue.delete(state.info,'address')
6.3.2 store基本属性
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import {INCREMENT} from "./mutations-type";
//modules
const moduleA={
state:{
name:'shuaige',
address:'shangdong hubaojian'
},
mutations:{
//名字不要重复
updateName(state){
state.name='big shuaige'
}
},
getters: {
fullAddress(state,getters,rootState){
return 'address:'+state.address+rootState.info[0].age
}
},
actions: {
updateANameAsync(context){
setTimeout(()=>context.commit('updateName'),1000)
}
},
modules:{
//最好不要在嵌套
}
}
//安装插件
Vue.use(Vuex)
//创建对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
info: [{
name: 'yuge',
age: 18
}],
counter: 0
},
/**
* 注意 修改state唯一的途径是mutations
* 里面的操作都是响应式的
*/
mutations: {
//自定义参数可以是基本类型 也可以是对象
//[INCREMENT] mutations类型常量 为了防止变量名书写错误 定义变量名全局使用常量
[INCREMENT](state, num) {
state.counter += num
},
decrement(state, payload) {
state.counter -= payload.num
},
updateInfo(state, payload) {
state.info.push(payload)
}
},
/**
* 类似计算属性
*/
getters: {
//可以有两个参数 对应store里的state getters
powerCounter(state, getters) {
// 强行使用
return state.counter * getters.computeCounter(1)
},
// 由于不能接受getters 函数不能接受其他参数 可以返回一个函数来自定义操作
computeCounter(state) {
return (num) => state.counter * num
}
},
/**
* 处理异步操作 一定放到action中
*/
actions: {
//context相当于store
aUpdateInfo(context) {
//Promise 是js新特性 建议百度
return new Promise(((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('updateInfo', {name: 'gyy', age: 21})
//给调用的地方做回调
resolve('update success')
}, 1000)
}))
}
},
/**
*为了避免store过大 vue允许将数据分为模块
*/
modules:{
a:moduleA
}
})
export default store
使用
<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- mutations-->
<h2>{{$store.state.counter}}</h2>
<h2>{{$store.state.info}}</h2>
<!-- getters-->
square:<h2>{{$store.getters.powerCounter}}</h2>
multiply:<h2>{{$store.getters.computeCounter(18)}}</h2>
<button @click="addition(1)">+1</button>
<button @click="subtraction(1)">-1</button>
<button @click="updateInfo">updateInfo</button>
<!-- modules-->
<h2>{{$store.state.a.name}}</h2>
<h2>getters:{{$store.getters.fullAddress}}</h2>
<button @click="updateAName">updateAName</button>
<button @click="updateANameAsync">updateANameAsync</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {INCREMENT} from "./store/mutations-type";
export default {
name: 'APP',
components: {
},
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
addition(num){
this.$store.commit(INCREMENT,num)
},
subtraction(num){
this.$store.commit({
type:'decrement',
//在这种写法下所有的参数会变成一个对象
num
})
},
updateInfo(){
this.$store.dispatch('aUpdateInfo').then(result=>{
console.log(result);
})
},
updateAName(){
this.$store.commit('updateName')
},
updateANameAsync(){
this.$store.dispatch('updateANameAsync')
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "./assets/css/base.css";
button{
width: 150px;
margin-right: 10px;
}
</style>
6.3.3 目录组织
七、网络模块封装(axios)
为了防止 因为过度依赖第三方网络请求而导致项目嗝屁时修改项目难度较大 所以要进行网络请求封装
使用说明 · Axios 中文说明 · 看云 (kancloud.cn)
7.1 axios基本使用
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import axios from 'axios'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
axios({
url:'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/data',
method:'get',
params:{
type:'pop',
page:1
}
}).then(res=>{//内部支持promise
console.log(res);
})
7.2 axios发送并发请求
axios.all([axios(),axios()]).then(results=>{})
const axios1 = {
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/data',
method: 'get',
params: {
type: 'pop',
page: 1
}
}
const axios2 = {
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata',
method: 'get'
}
axios.all([axios(axios1),axios(axios2)]).then(results=>{
console.log(results);
})
//也可以用axios.spread将每个请求分开
axios.all([axios(axios1), axios(axios2)]).then(axios.spread((res1, res2)=> {
console.log(res1);
console.log(res2);
}))
7.3 axios 配置信息
axios.defaults.baseURL='http://123.207.32.32:8000' //默认为 http://localhost:8080
axios.defaults.timeout=5000 //ms
const axios1 = {
url: '/home/data',
method: 'get',
params: {
type: 'pop',
page: 1
}
}
const axios2 = {
url: '/home/multidata',
method: 'get'
}
axios.all([axios(axios1),axios(axios2)]).then(results=>{
console.log(results);
})
//也可以用axios.spread将每个请求分开
axios.all([axios(axios1), axios(axios2)]).then(axios.spread((res1, res2)=> {
console.log(res1);
console.log(res2);
}))
7.3 axios 实例和模块封装
封装1
import axios from 'axios'
export function request(config,success,failure){
const instance=axios.create({
baseURL:'http://123.207.32.32:8000',
timeout:5000
})
instance(config)
.then(res=>success(res))
.catch(err=>failure(err))
}
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import {request} from "./network/request";
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
const axios1 = {
url: '/home/multidata',
method: 'get'
}
request(axios1,res=>{
console.log(res)
},err=>{
console.log(err);
})
封装2
import axios from 'axios'
export function request(config){
const instance=axios.create({
baseURL:'http://123.207.32.32:8000',
timeout:5000
})
instance(config.baseConfig)
.then(res=>config.success(res))
.catch(err=>config.failure(err))
}
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import {request} from "./network/request";
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
const axios2 = {
baseConfig:{
url: '/home/multidata',
method: 'get'
},
success(res){
console.log(res);
},
failure(err){
console.log(err);
}
}
request(axios2)
封装3(建议)
import axios from 'axios'
export function request(config){
const instance=axios.create({
baseURL:'http://123.207.32.32:8000',
timeout:5000
})
return instance(config.baseConfig)
}
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import {request} from "./network/request";
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
const axios2 = {
baseConfig:{
url: '/home/multidata',
method: 'get'
}
}
request(axios2)
.then(res=>console.log(res))
.catch(err=>console.log(err))
7.4 axios拦截器
import axios from 'axios'
export function request(config){
const instance=axios.create({
baseURL:'http://123.207.32.32:8000',
timeout:5000
})
//请求拦截
instance.interceptors.request.use(config=>{
console.log(config);
return config
})
//相应拦截
instance.interceptors.response.use(res=>{
//一般用来过滤数据
console.log(res);
return res.data
},err=>{
console.log(err);
return err
})
return instance(config.baseConfig)
}
作业
4.1 动态绑定css
作业需求:点击列表中的哪一项,那么该项的文字变成红色,默认第一项变红
答案
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
.s1{
color: red;
}
.s2{
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<!-- index渲染时会替换成对应下标 只需控制num即可-->
<li v-for="(item,index) in myList" :class="{s1:index===num}" @click="change(index)">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
myList:['t1111','t1111','t1111','t1111','t1111'],
num:0
},
methods:{
change:function (index) {
this.num=index
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
4.2父子组件数据双向绑定
需求:num1 num2 父子组件数据双向绑定 当num1发生改变 num2变成num1的100倍 当num2发生改变 num1变成num1的100分之一
ans:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>num1:{{num1}}</h2>
<h2>num2:{{num2}}</h2>
<t1 :num1="num1" @num1change="num1Change"
:num2="num2" @num2change="num2Change"></t1>
</div>
<template id="t1">
<div>
<h2>dnum1:{{dnum1}}</h2>
<h2>dnum2:{{dnum2}}</h2>
dnum1<input type="text" :value="dnum1" @input="dnum1Change">
<hr/>
dnum2<input type="text" :value="dnum2" @input="dnum2Change">
</div>
</template>
<script>
const t1={
template:'#t1',
props:{
num1:Number,
num2:Number
},
data(){
return{
dnum1:this.num1,
dnum2:this.num2
}
},
methods:{
dnum1Change(event){
this.dnum1=event.target.value;
this.$emit('num1change',this.dnum1)
this.dnum2=this.dnum1*100;
this.$emit('num2change',this.dnum2)
},
dnum2Change(event){
this.dnum2=event.target.value;
this.$emit('num2change',this.dnum2)
this.dnum1=this.dnum2/100;
this.$emit('num1change',this.dnum1)
}
}
}
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
num1:0,
num2:0
},
components:{
t1
},
methods: {
num1Change(v){
this.num1=v
},
num2Change(v){
this.num2=v
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
拓展用 watch
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>num1:{{num1}}</h2>
<h2>num2:{{num2}}</h2>
<t1 :num1="num1" @num1change="num1Change"
:num2="num2" @num2change="num2Change"></t1>
</div>
<template id="t1">
<div>
<h2>dnum1:{{dnum1}}</h2>
<h2>dnum2:{{dnum2}}</h2>
dnum1<input type="text" v-model="dnum1">
<hr/>
dnum2<input type="text" v-model="dnum2">
</div>
</template>
<script>
const t1 = {
template: '#t1',
//父传子用 props
props: {
num1: Number,
num2: Number
},
data() {
return {
dnum1: this.num1,
dnum2: this.num2
}
},
methods: {},
//用来监听属性变化
watch: {
//函数名要和变量名相同 可以有两个参数一般只用一个
dnum1(newValue, oldValue) {
//因为改变了dnum2 所以dnum2(newValue)将会收到改变 故不用再写发送num2change
this.dnum2 = newValue * 100;
this.$emit('num1change', newValue)
},
dnum2(newValue) {
this.dnum1 = newValue / 100;
this.$emit('num2change', newValue)
}
}
}
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
num1: 0,
num2: 0
},
components: {
t1 //cs6
},
methods: {
num1Change(v) {
this.num1 = v
},
num2Change(v) {
this.num2 = v
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
4.3 tabBar 案例

目录结构
tabbar.vue
<template>
<div id="tab-bar">
<slot></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "TabBar"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
#tab-bar {
display: flex;
background-color: #f6f6f6;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
position: fixed;
box-shadow: 0 -3px 1px rgba(8, 100, 59, 0.08);
}
</style>
TabBarItem.vue
<template>
<div class="tab-bar-item" @click="itemClick">
<slot v-if="!isActive" name="item-icon"></slot>
<slot v-else name="item-icon-active"></slot>
<!-- <slot :class="{name:isActive}" name="item-name"></slot> class会失效因为会被替换
v-if 虽然可以但建议还是用div封一下
-->
<div :style="activeStyle">
<slot name="item-name"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "TabBarItem",
data() {
return {
}
},
props:{
path:{
default:'',
type:String
},
activeColor:{
default: '#00645A',
type: String
}
},
computed:{
isActive(){
return this.$route.path.indexOf(this.path) >=0
},
activeStyle(){
return this.isActive?{color:this.activeColor}:{}
}
},
methods: {
itemClick(){
if (!this.isActive)
this.$router.replace(this.path)
},
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.tab-bar-item {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
height: 49px;
margin-top: 3px;
vertical-align: middle;
}
.tab-bar-item img {
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
}
</style>
MainTabBar.vue
<template>
<div>
<tab-bar>
<tab-bar-item path="/home" active-color="red">
<img slot="item-icon" src="@/assets/img/tabbar/home.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="@/assets/img/tabbar/home-active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-name">Home</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item path="/advance">
<img slot="item-icon" src="@/assets/img/tabbar/advance.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-name">Advance</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item path="/settings">
<img alt="" slot="item-icon" src="@/assets/img/tabbar/settings.svg">
<div slot="item-name">Settings</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item path="/profile">
<img slot="item-icon" src="@/assets/img/tabbar/profile.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-name">Profile</div>
</tab-bar-item>
</tab-bar>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import TabBar from "@/components/tabbar/TabBar"
import TabBarItem from "@/components/tabbar/TabBarItem";
export default {
name: "MainTabBar",
components:{
TabBarItem,
TabBar
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
配置router
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
// import Home from "../views/Home";
// import About from "../views/About";
// import User from "../views/User";
Vue.use(VueRouter)
//路由懒加载
const Home=()=>import('../views/home/Home')
const About=()=>import('../views/About')
const Profile=()=>import('../views/profile/Profile')
const Advance=()=>import('../views/advance/Advance')
const Settings=()=>import('../views/settings/Settings')
const routes = [
{
path:'',
redirect:'/home'
},
{
path:'/home',
component:Home,
meta:{
title:'首页'
}
},
{
path:'/about',
component:About,
meta:{
title:'关于'
}
},
{
path:'/profile',
component:Profile,
meta:{
title:'我的'
}
},
{
path:'/advance',
component:Advance,
meta:{
title:'高级'
}
},
{
path:'/settings',
component:Settings,
meta:{
title:'设置'
}
},
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
mode:'history',
linkActiveClass:''
})
router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{
document.title=to.meta.title
next()
})
export default router
app.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
<MainTabBar></MainTabBar>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MainTabBar from "./components/MainTabBar";
export default {
name: 'APP',
components: {
MainTabBar
},
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "./assets/css/base.css";
</style>
问题与填坑
Cannot read property ‘xx’ of undefined
- 80%是你的变量名是不是少了个 符 号 什 么 的 , 例 如 符号什么的,例如 符号什么的,例如route
vue-devtools 安装
Chrome 新版edge直接下载 打开开发者模式 拖进来安装就行





















 8万+
8万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








