#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define maxLen 1000000
#define F(x, y, z) (((x) & (y)) | ((~x) & (z)))
#define G(x, y, z) (((x) & (z)) | ((y) & (~z)))
#define H(x, y, z) ((x) ^ (y) ^ (z))
#define I(x, y, z) ((y) ^ ((x) | (~z)))
const unsigned int A = 0x67452301;
const unsigned int B = 0xEFCDAB89;
const unsigned int C = 0x98BADCFE;
const unsigned int D = 0x10325476;
const unsigned int T[64] = {
0xd76aa478, 0xe8c7b756, 0x242070db, 0xc1bdceee,
0xf57c0faf, 0x4787c62a, 0xa8304613, 0xfd469501,
0x698098d8, 0x8b44f7af, 0xffff5bb1, 0x895cd7be,
0x6b901122, 0xfd987193, 0xa679438e, 0x49b40821,
0xf61e2562, 0xc040b340, 0x265e5a51, 0xe9b6c7aa,
0xd62f105d, 0x02441453, 0xd8a1e681, 0xe7d3fbc8,
0x21e1cde6, 0xc33707d6, 0xf4d50d87, 0x455a14ed,
0xa9e3e905, 0xfcefa3f8, 0x676f02d9, 0x8d2a4c8a,
0xfffa3942, 0x8771f681, 0x6d9d6122, 0xfde5380c,
0xa4beea44, 0x4bdecfa9, 0xf6bb4b60, 0xbebfbc70,
0x289b7ec6, 0xeaa127fa, 0xd4ef3085, 0x04881d05,
0xd9d4d039, 0xe6db99e5, 0x1fa27cf8, 0xc4ac5665,
0xf4292244, 0x432aff97, 0xab9423a7, 0xfc93a039,
0x655b59c3, 0x8f0ccc92, 0xffeff47d, 0x85845dd1,
0x6fa87e4f, 0xfe2ce6e0, 0xa3014314, 0x4e0811a1,
0xf7537e82, 0xbd3af235, 0x2ad7d2bb, 0xeb86d391
};
const unsigned int k[3] = {0x446b6c6a, 0x49695932, 0x99999999};
const unsigned int s[64] = {
7, 12, 17, 22, 7, 12, 17, 22, 7, 12, 17, 22, 7, 12, 17, 22,
5, 9, 14, 20, 5, 9, 14, 20, 5, 9, 14, 20, 5, 9, 14, 20,
4, 11, 16, 23, 4, 11, 16, 23, 4, 11, 16, 23, 4, 11, 16, 23,
6, 10, 15, 21, 6, 10, 15, 21, 6, 10, 15, 21, 6, 10, 15, 21
};
const unsigned int ipad[16] = {
0x36363636, 0x36363636, 0x36363636, 0x36363636,
0x36363636, 0x36363636, 0x36363636, 0x36363636,
0x36363636, 0x36363636, 0x36363636, 0x36363636,
0x36363636, 0x36363636, 0x36363636, 0x36363636
};
const unsigned int opad[16] = {
0x5c5c5c5c, 0x5c5c5c5c, 0x5c5c5c5c, 0x5c5c5c5c,
0x5c5c5c5c, 0x5c5c5c5c, 0x5c5c5c5c, 0x5c5c5c5c,
0x5c5c5c5c, 0x5c5c5c5c, 0x5c5c5c5c, 0x5c5c5c5c,
0x5c5c5c5c, 0x5c5c5c5c, 0x5c5c5c5c, 0x5c5c5c5c
};
const unsigned int padding[48] = {
0x00000080, 0x00000000, 0x00000000, 0x00000000,
0x00000000, 0x00000000, 0x00000000, 0x00000000,
0x00000000, 0x00000000, 0x00000280, 0x00000000
};
// 将HMAC-MD5的结果从unsigned int 类型的数组CV_out转成128bits的二进制字符串
void transform(unsigned int CV_out[], int num, int *result) {
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
// result[32*i+j] = (CV_out[i] >> (31-j)) & 1;
for (int k = 0; k < 8; ++k) {
result[32*i+j*8+k] = (CV_out[i] >> (j*8+7-k)) & 1;
}
}
}
}
// 将字符串输入形式的明文进行填充并转换成unsigned int 类型的二维数组M
void append(const char *input, unsigned int M[][16], int* num, unsigned long long int* inputLen) {
char *result = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * maxLen);
strcpy(result, input);
*inputLen = strlen(input) * 8;
(*num) = (*inputLen) >> 9;
int index = ((*inputLen) / 8) & 0x3F;
// printf("index: %d\n", index);
unsigned long long int resultLen;
if (index < 56) {
unsigned char a[2];
a[0] = (unsigned char)0x80;
a[1] = '\0';
strcat(result, (const char*)a);
resultLen = (*inputLen) + 64 - index;
(*num) = (*num) + 1;
}
else {
unsigned char a[2];
a[0] = (unsigned char)0x80;
a[1] = '\0';
strcat(result, (const char*)a);
(*num) = (*num ) + 2;
resultLen = (*inputLen) + 128 - index;
}
int index1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (*num); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 16; ++j) {
if (index1 + 3 <= (*inputLen)) {
int word[4];
word[0] = (unsigned int)((unsigned char)result[index1]);
word[1] = (unsigned int)((unsigned char)result[index1+1]);
word[2] = (unsigned int)((unsigned char)result[index1+2]);
word[3] = (unsigned int)((unsigned char)result[index1+3]);
// M[i][j] = (word[0] << 24) + (word[1] << 16) + (word[2] << 8) + word[3];
M[i][j] = (word[3] << 24) + (word[2] << 16) + (word[1] << 8) + word[0];
index1 = index1 + 4;
} else if (index1 <= (*inputLen) && index1 + 3 > (*inputLen)) {
int temp = (*inputLen) - index1;
// for (int k = 0; k < temp+1; ++k) {
// M[i][j] = (M[i][j] << 8) + (unsigned int)((unsigned char)result[index1+k]);
// }
for (int k = temp; k > -1; --k) {
M[i][j] = (M[i][j] << 8) + (unsigned int)((unsigned char)result[index1+k]);
}
// for (int k = temp+1; k < 4; ++k) {
// M[i][j] = M[i][j] << 8;
// }
index1 = index1 + 4;
}
else {
M[i][j] = 0;
index1 = index1 + 4;
}
}
}
M[(*num)-1][14] = ((*inputLen) & 0xff) + ((((*inputLen) >> 8) & 0xff) << 8) + ((((*inputLen) >> 16) & 0xff) << 16) + ((((*inputLen) >> 24) & 0xff) << 24);
M[(*num)-1][15] = (((*inputLen >> 32) & 0xff)) + ((((*inputLen) >> 40) & 0xff) << 8) + ((((*inputLen) >> 48) & 0xff) << 16) + ((((*inputLen) >> 56) & 0xff) << 24);
// for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) {
// for (int j = 0; j < 16; ++j) {
// cout << M[i][j] << endl;
// printf("%0x ===== %d %d\n", M[i][j], i, j);
// }
// }
free(result);
}
// 每轮循环中的一次迭代过程
void iteration_one(unsigned int g, unsigned int input[], unsigned int output[], const unsigned int block[], int* k1, int* k2) {
// g = F(input[1], input[2], input[3]);
// printf("g: %0x\n", g);
unsigned int temp1 = g + input[0];
// printf("temp1: %0x\n", temp1);
unsigned int temp2 = temp1 + block[*k1];
// printf("temp2: %0x\n", temp2);
unsigned int temp3 = temp2 + T[*k2];
// printf("temp3: %0x\n", temp3);
unsigned int temp4_1 = temp3 << s[*k2];
unsigned int temp4_2 = temp3 >> (32-s[*k2]);
unsigned int temp4 = temp4_1 | temp4_2;
// printf("temp4: %0x\n", temp4);
unsigned int temp5 = temp4 + input[1];
// printf("temp5: %0x\n", temp5);
output[0] = input[3];
output[1] = temp5;
output[2] = input[1];
output[3] = input[2];
// for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
// printf("%0x ", output[j]);
// }
// printf("\n");
}
// 第一轮循环运算逻辑
void iteration_1(unsigned int CV_0[], unsigned int CV_1[], const unsigned int block[]) {
unsigned int input[4];
unsigned int output[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
input[i] = CV_0[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {
int k1 = i;
int k2 = i;
unsigned int g = F(input[1], input[2], input[3]);
iteration_one(g, input, output, block, &k1, &k2);
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
input[j] = output[j];
}
// printf("first round %d iteration: ", i);
// for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
// printf("%0x ", output[j]);
// }
// printf("\n");
}
// printf("first round: ");
// for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
// printf("%0x ", output[j]);
// }
// printf("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
CV_1[i] = output[i];
}
}
// 第二轮循环运算逻辑
void iteration_2(unsigned int CV_1[], unsigned int CV_2[], const unsigned int block[]) {
unsigned int input[4];
unsigned int output[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
input[i] = CV_1[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {
int k1 = (1 + 5 * i) % 16;
int k2 = i + 16;
unsigned int g = G(input[1], input[2], input[3]);
iteration_one(g, input, output, block, &k1, &k2);
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
input[j] = output[j];
}
// printf("second round %d iteration: ", i);
// for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
// printf("%0x ", output[j]);
// }
// printf("\n");
}
// printf("second round: ");
// for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
// printf("%0x ", output[j]);
// }
// printf("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
CV_2[i] = output[i];
}
}
// 第三轮循环运算逻辑
void iteration_3(unsigned int CV_2[], unsigned int CV_3[], const unsigned int block[]) {
unsigned int input[4];
unsigned int output[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
input[i] = CV_2[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {
int k1 = (5 + 3 * i) % 16;
int k2 = i + 32;
unsigned int g = H(input[1], input[2], input[3]);
iteration_one(g, input, output, block, &k1, &k2);
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
input[j] = output[j];
}
// printf("third round %d iteration: ", i);
// for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
// printf("%0x ", output[j]);
// }
// printf("\n");
}
// printf("third round: ");
// for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
// printf("%0x ", output[j]);
// }
// printf("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
CV_3[i] = output[i];
}
}
// 第四轮循环运算逻辑
void iteration_4(unsigned int CV_3[], unsigned int CV_4[], const unsigned int block[]) {
unsigned int input[4];
unsigned int output[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
input[i] = CV_3[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {
int k1 = (7 * i) % 16;
int k2 = i + 48;
unsigned int g = I(input[1], input[2], input[3]);
iteration_one(g, input, output, block, &k1, &k2);
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
input[j] = output[j];
}
// printf("fourth round %d iteration: ", i);
// for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
// printf("%0x ", output[j]);
// }
// printf("\n");
}
// printf("fourth round: ");
// for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
// printf("%0x ", output[j]);
// }
// printf("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
CV_4[i] = output[i];
}
}
/*
* MD5压缩函数H_MD5
* 输入:128bits的CV 和 512bits的Yq
* 输出:下一轮输入的128bits的CV
*/
void H_MD5(const unsigned int block[], unsigned int CV_in[], unsigned int CV_out[]) {
unsigned int CV_0[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
CV_0[i] = CV_in[i];
}
unsigned int CV_1[4];
unsigned int CV_2[4];
unsigned int CV_3[4];
unsigned int CV_4[4];
iteration_1(CV_0, CV_1, block);
iteration_2(CV_1, CV_2, block);
iteration_3(CV_2, CV_3, block);
iteration_4(CV_3, CV_4, block);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
CV_out[i] = CV_4[i] + CV_in[i];
// printf("CV_out: %0x\n", CV_out[i]);
}
}
/*
* MD5总控函数H_MD5
* 输入:填充处理后的二维明文数组M
* 输出: 128bits的信息摘要
*/
void MD5(unsigned int IV[], unsigned int M[][16], int* num, unsigned int result[]) {
unsigned int CV_in[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
CV_in[i] = IV[i];
}
unsigned int CV_out[4];
for (int i = 0; i < (*num); ++i) {
H_MD5(M[i], CV_in, CV_out);
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
CV_in[j] = CV_out[j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
result[i] = CV_out[i];
}
}
void HMAC(const unsigned int IV[], const unsigned int k[], unsigned int M[][16], int num, unsigned long long int MLen, int result[]) {
// printf("========================= HMAC ========================\n");
//K+与 ipad 作 XOR,生成 b 位的 Si
unsigned int S_i[16];
unsigned int buf[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {
buf[i] = k[i] ^ ipad[i];
S_i[i] = ((buf[i] & 0xff) << 24) + (((buf[i] >> 8) & 0xff) << 16) + (((buf[i] >> 16) & 0xff) << 8) + ((buf[i] >> 24) & 0xff);
}
//对 (Si ‖ M) 进行 hash 压缩 (例如 MD5),得到 H(Si ‖ M)
unsigned int CV_in[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
CV_in[i] = IV[i];
}
unsigned int CV_out[4];
H_MD5(S_i, CV_in, CV_out);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
CV_in[i] = CV_out[i];
}
unsigned long long int new_MLen = MLen + 512;
// printf("new_MLen: %d", new_MLen);
M[num-1][14] = (new_MLen & 0xff) + (((new_MLen >> 8) & 0xff) << 8) + (((new_MLen >> 16) & 0xff) << 16) + (((new_MLen >> 24) & 0xff) << 24);
M[num-1][15] = (((new_MLen >> 32) & 0xff)) + (((new_MLen >> 40) & 0xff) << 8) + (((new_MLen >> 48) & 0xff) << 16) + (((new_MLen >> 56) & 0xff) << 24);
MD5(CV_in, M, &num, CV_out);
//K+与 opad 作 XOR,生成 b 位的 So
unsigned int S_o[16];
unsigned int buf1[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {
buf1[i] = k[i] ^ opad[i];
S_o[i] = ((buf1[i] & 0xff) << 24) + (((buf1[i] >> 8) & 0xff) << 16) + (((buf1[i] >> 16) & 0xff) << 8) + ((buf1[i] >> 24) & 0xff);
}
//对 So ‖ H(Si ‖ M) 进行 hash 压缩 (例如 MD5),得到HMACK = H(So ‖ H(Si ‖ M))
unsigned int CV_in1[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
CV_in1[i] = IV[i];
}
unsigned int CV_out1[4];
H_MD5(S_o, CV_in1, CV_out1);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
CV_in1[i] = CV_out1[i];
}
unsigned int H[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
H[i] = CV_out[i];
}
for (int i = 4; i < 16; ++i) {
H[i] = padding[i-4];
}
H_MD5(H, CV_in1, CV_out1);
//将结果转换后赋值给result
transform(CV_out1, 4, result);
}
char* bin_to_hex(const int* bin_array, int len) {
if (len < 0) return NULL;
// 处理空数组的特殊情况
if (len == 0) {
char* empty_str = malloc(1);
if (empty_str) empty_str[0] = '\0';
return empty_str;
}
// 计算需要补零的数量
int pad = (4 - (len % 4)) % 4;
int total_bits = len + pad;
int num_groups = total_bits / 4;
// 创建补零后的临时数组
int* temp = malloc(total_bits * sizeof(int));
if (!temp) return NULL;
// 填充前导零
for (int i = 0; i < pad; i++)
temp[i] = 0;
// 复制原始数据
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
temp[pad + i] = bin_array[i];
// 创建结果字符串
char* hex_str = malloc(num_groups + 1);
if (!hex_str) {
free(temp);
return NULL;
}
const char hex_chars[] = "0123456789ABCDEF";
// 转换每个4位组
for (int i = 0; i < num_groups; i++) {
int start = i * 4;
int value = 0;
// 将4位二进制转换为数值
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
value = (value << 1) | (temp[start + j] ? 1 : 0);
hex_str[i] = hex_chars[value];
}
hex_str[num_groups] = '\0';
free(temp);
return hex_str;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
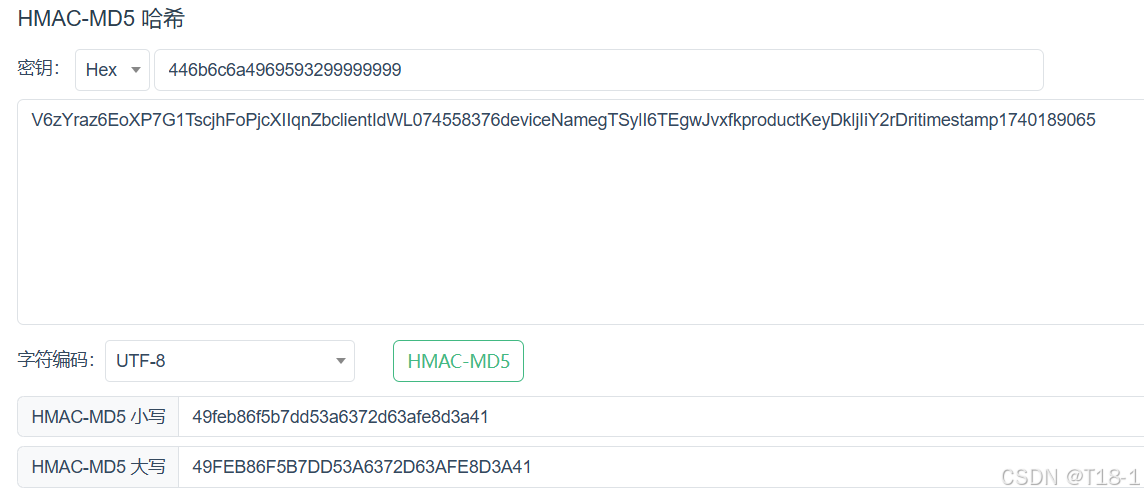
const char *a = "V6zYraz6EoXP7G1TscjhFoPjcXIIqnZbclientIdWL074558376deviceNamegTSylI6TEgwJvxfkproductKeyDkljIiY2rDritimestamp1740189065";
int num = 0;
unsigned long long int inputLen = 0;
unsigned int block[8][16];
append(a, block, &num, &inputLen);
unsigned int CV_in[4];
CV_in[0] = A;
CV_in[1] = B;
CV_in[2] = C;
CV_in[3] = D;
int result[128];
HMAC(CV_in, k, block, num, inputLen, result);
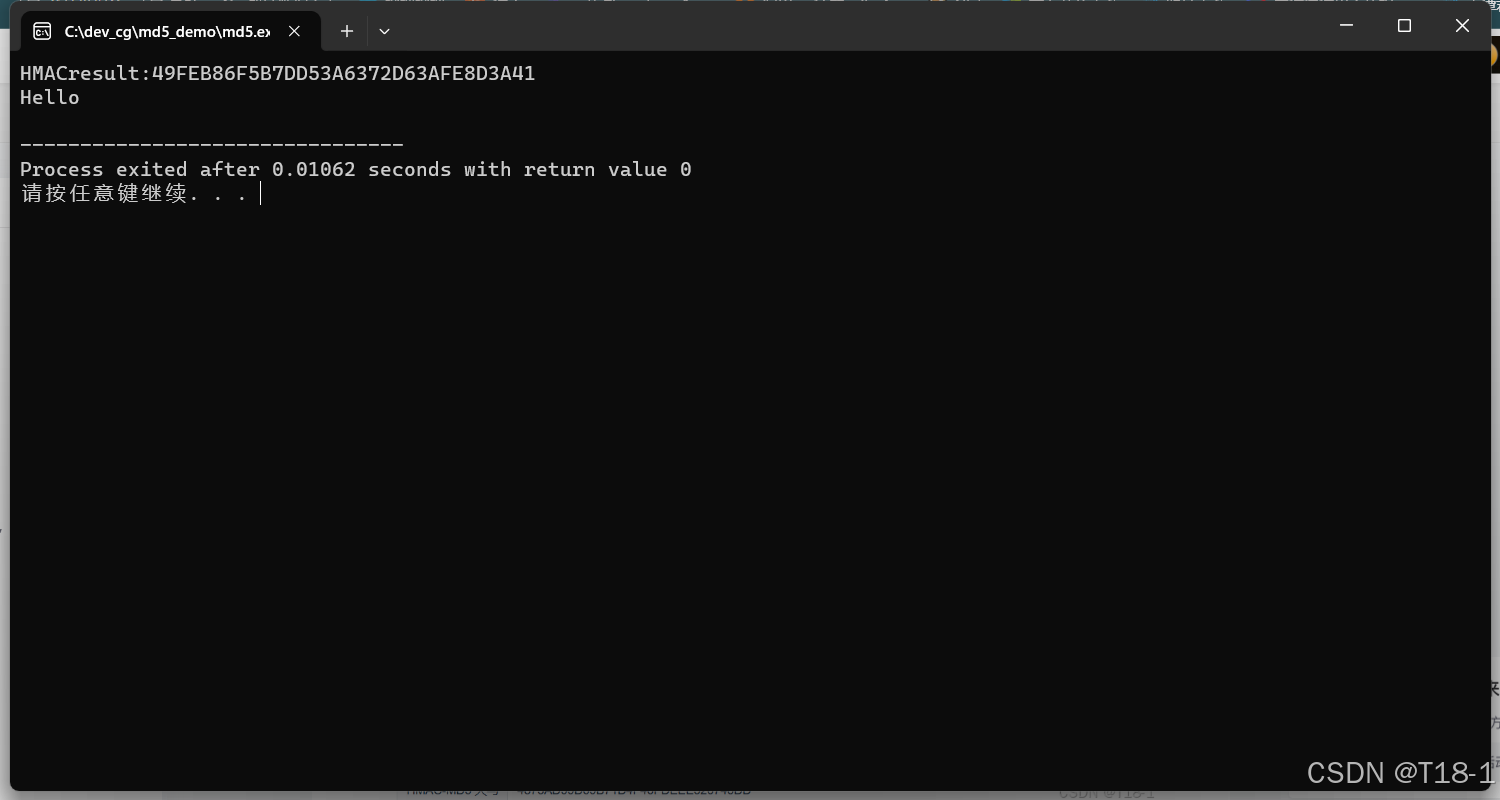
printf("HMACresult:%s\n",bin_to_hex(result,128));
printf("Hello\n");
return 0;
}该源码为简易修改版本,仅有一个main文件作为demo,可自行按需封装
如需更完整的版本,以及源码说明,请点击下方链接进入代码出处
搬运至以下作者,感谢开源
代码出处:MD5: HMAC-MD5消息认证算法
测试环境:Dev-C++ 5.11
经测试可正常使用




















 4906
4906

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








