这也是刚看,仅供参考~
1、Linux内核bdi系统
bdi是backing device info的缩写,它用于描述后端存储(如磁盘)设备相关的信息。相对于内存来说,后端存储的I/O比较慢,因此写盘操作需要通过page cache进行缓存延迟写入。
与bdi_writeback机制相关的主要数据结构有三个:
1)backing_dev_info:该数据结构描述了backing_dev的所有信息,通常块设备的request queue中会包含backing_dev对象。
2)bdi_writeback:该数据结构封装了writeback的内核线程以及需要操作的inode队列。
3)wb_writeback_work:该数据结构封装了writeback的工作任务。
在include/linux/backing-dev-defs.h中定义了前两个结构。
1.1 backing_dev_info
其中backing_dev_info结构定义如下:

struct backing_dev_info {
struct list_head bdi_list;
unsigned long ra_pages; /* max readahead in PAGE_CACHE_SIZE units */
unsigned int capabilities; /* Device capabilities */
congested_fn *congested_fn; /* Function pointer if device is md/dm */
void *congested_data; /* Pointer to aux data for congested func */
char *name;
unsigned int min_ratio;
unsigned int max_ratio, max_prop_frac;
atomic_long_t tot_write_bandwidth;
struct bdi_writeback wb; /* the root writeback info for this bdi */
struct list_head wb_list; /* list of all wbs */
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_WRITEBACK
struct radix_tree_root cgwb_tree; /* radix tree of active cgroup wbs */
struct rb_root cgwb_congested_tree; /* their congested states */
atomic_t usage_cnt; /* counts both cgwbs and cgwb_contested's */
#else
struct bdi_writeback_congested *wb_congested;
#endif
wait_queue_head_t wb_waitq;
struct device *dev;
struct timer_list laptop_mode_wb_timer;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FS
struct dentry *debug_dir;
struct dentry *debug_stats;
#endif
};
1.2 bdi_writeback
bdi_writeback对象封装了需要处理的inode队列。当page cache/buffer cache需要刷新radix tree上的inode时,可以将该inode挂载到writeback对象的b_dirty队列上,然后唤醒writeback线程。在处理过程中,inode会被移到b_io队列上进行处理。
bdi_writeback定义如下:

struct bdi_writeback {
struct backing_dev_info *bdi; /* our parent bdi */
unsigned long state; /* Always use atomic bitops on this */
unsigned long last_old_flush; /* last old data flush */
struct list_head b_dirty; /* dirty inodes */
struct list_head b_io; /* parked for writeback */
struct list_head b_more_io; /* parked for more writeback */
struct list_head b_dirty_time; /* time stamps are dirty */
spinlock_t list_lock; /* protects the b_* lists */
struct percpu_counter stat[NR_WB_STAT_ITEMS];
struct bdi_writeback_congested *congested;
unsigned long bw_time_stamp; /* last time write bw is updated */
unsigned long dirtied_stamp;
unsigned long written_stamp; /* pages written at bw_time_stamp */
unsigned long write_bandwidth; /* the estimated write bandwidth */
unsigned long avg_write_bandwidth; /* further smoothed write bw, > 0 */
unsigned long dirty_ratelimit;
unsigned long balanced_dirty_ratelimit;
struct fprop_local_percpu completions;
int dirty_exceeded;
spinlock_t work_lock; /* protects work_list & dwork scheduling */
struct list_head work_list;
struct delayed_work dwork; /* work item used for writeback */
struct list_head bdi_node; /* anchored at bdi->wb_list */
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_WRITEBACK
struct percpu_ref refcnt; /* used only for !root wb's */
struct fprop_local_percpu memcg_completions;
struct cgroup_subsys_state *memcg_css; /* the associated memcg */
struct cgroup_subsys_state *blkcg_css; /* and blkcg */
struct list_head memcg_node; /* anchored at memcg->cgwb_list */
struct list_head blkcg_node; /* anchored at blkcg->cgwb_list */
union {
struct work_struct release_work;
struct rcu_head rcu;
};
#endif
};
1.3 wb_writeback_work
在fs/fs-writeback.c中定义了wb_writeback_work结构体,该数据结构封装了writeback的工作任务,其内容如下:

struct wb_writeback_work {
long nr_pages;
struct super_block *sb;
unsigned long *older_than_this;
enum writeback_sync_modes sync_mode;
unsigned int tagged_writepages:1;
unsigned int for_kupdate:1;
unsigned int range_cyclic:1;
unsigned int for_background:1;
unsigned int for_sync:1; /* sync(2) WB_SYNC_ALL writeback */
unsigned int auto_free:1; /* free on completion */
enum wb_reason reason; /* why was writeback initiated? */
struct list_head list; /* pending work list */
struct wb_completion *done; /* set if the caller waits */
};
wb_writeback_work数据结构是对writeback任务的封装,不同的任务可以采用不同的刷新策略。writeback线程的处理对象就是wb_writeback_work。如果writeback_work队列为空,那么内核线程就可以睡眠。
nr_pages:待回写页面数量;
sb: 该 writeback 任务所属的 super_block;
for_background: 若值为 1,表示后台回写;否则值为 0;
1.4 bdi-default内核线程
1.4.1 default_bdi_init

Linux内核启动时,会执行bdi模块default_bdi_init(),代码定义在文件mm/backing-dev.c中。主要工作如下:
1)创建名为writeback的线程,此线程由定时器来唤醒。
2)调用bdi_init,定义默认数据结构noop_backing_dev_info。

1.4.2 bdi_init
初始化bdi,其内容定义在mm/backing-dev.c中,内容如下:
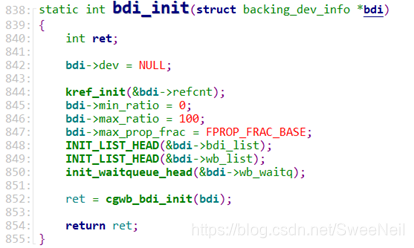
1.4.3 cgwb_bdi_init
cgwb_bdi_init有两个接口,都定义在mm/backing-dev.c下:
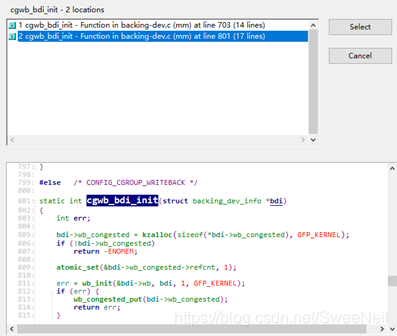
这两个接口中都调用了wb_init,整个调用流程如下:
内核启动
——default_bdi_init
————bdi_init
——————cgwb_bdi_init
————————wb_init
接下来进行第二部分分析。
2、delayed_work接口
writeback是通过delayed_work来实现的,在wb_init()函数里初始化了这个delayed_work。
2.1 wb_init()
wb_init()函数,定义在mm/backing-dev.c中,其内容如下:
![]()
static int wb_init(struct bdi_writeback *wb, struct backing_dev_info *bdi,int blkcg_id, gfp_t gfp)
{
int i, err;
memset(wb, 0, sizeof(*wb));
if (wb != &bdi->wb)
bdi_get(bdi);
wb->bdi = bdi;<





 本文深入探讨了Linux内核的缓存回写机制,详细介绍了backing_dev_info、bdi_writeback和wb_writeback_work等关键数据结构,以及Linux内核启动时如何初始化默认的writeback线程。同时,分析了delayed_work接口在writeback过程中的作用,特别是wb_workfn()、wb_do_writeback()和writeback_sb_inodes()等核心函数的工作流程。通过对ext4_writepages函数的解析,展示了实际文件系统如何执行写回操作。
本文深入探讨了Linux内核的缓存回写机制,详细介绍了backing_dev_info、bdi_writeback和wb_writeback_work等关键数据结构,以及Linux内核启动时如何初始化默认的writeback线程。同时,分析了delayed_work接口在writeback过程中的作用,特别是wb_workfn()、wb_do_writeback()和writeback_sb_inodes()等核心函数的工作流程。通过对ext4_writepages函数的解析,展示了实际文件系统如何执行写回操作。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 535
535

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








