一、依赖注入(将spring容器中的组件注入到bean中)
我们之前学习了怎么将bean注入到容器中,接下来我们来研究一下怎么将容器中的组件注入到bean中。
1、属性注入(将组件注入到属性中)
1.1、spring提供的方式
1、spring为我们提供了一个注解@Autowire,将@Autowired注解放到JavaBean对应类的属性上,该属性的值会在JavaBean对应类创建实例之前,去看容器中是不是存在属性对应类型的组件,有的话就从容器中取,并注入到该属性中。 如果不存在就报错,要想没有不报错,可以使用@Autowired的一个属性require=false。如果容器中存在多个同类型的组件,那么就会用属性的名字去匹配组件名。
2、;@Autowire还可以与@Qualifier注解连用。直接指定组件名去注入。
3、@Autowire支持@Primary【标注了@Primary注解的组件在按类型注入时会被优先选择】
@Component("qinglong")
public class PersonPojo {
private String title = "青龙";//称号
private String name = "宁仲";//真实姓名
@Autowired//将容器中SkillPojo类型组件的注入到属性中
@Qualifier("skillPojo")
private SkillPojo skillPojo;//武器类
}
@Component("ghost")
@Primary//按类型注入时,这个组件会被优先选择
public class SkillPojo {
private String name="以身饲鬼术";//武器名称
private String type="召唤类";//武器功能
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SkillPojo{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
}
1.2、jdk提供的方式
jdk为我们提供了@Resoure注解。它可以直接指定组件名注入也可以指定类型注入,不需要与其他注解连用。但是它不支持@Primary注解
@Component("qinglong")
public class PersonPojo {
private String title = "青龙";//称号
private String name = "宁仲";//真实姓名
//@Resource(type = SkillPojo.class)//按组件类型注入
@Resource(value="skillPojo")//按组件名称注入
private SkillPojo skillPojo;//武器类
}
1.3、第三方提供的方式
既然是第三方提供的,我们就要导入第三方jar包。它的提供注解是@Inject。@Inject功能基本和@AutoWire注解一致。
它支持@Primary注解
它默认是按类型注入的,可以与@Qualifier注解连用。直接指定组件名去注入。
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.inject</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId>
<version>1</version>
</dependency>
2、方法注入(将组件注入到属性中)
将@Autowired注解放在方法上,方法可以有任意名称和任意数量的参数;每个参数都将与Spring容器中的匹配bean自动连接。Bean属性setter方法实际上只是这种通用配置方法的一个特例。这样的配置方法不必是公共的。
public class PersonPojo {
private String title = "青龙";//称号
private String name = "宁仲";//真实姓名
private SkillPojo skillPojo;//武器类
@Autowired
private void setSkillPojo(SkillPojo skillPojo) {//skillPojo取的是spring容器中组件的值
this.skillPojo = skillPojo;
}
3、构造器注入
如果一个bean有且只有一个有参构造,那么有参构造每个参数都将与Spring容器中的匹配bean自动连接(假如有参构造的参数包含基本数据类型或容器中没有的组件类型,会报注入失败错误)
public class PersonPojo {
private String title = "青龙";//称号
private String name = "宁仲";//真实姓名
private SkillPojo skillPojo;//武器类
//只有一个有参构造,spring容器对应的组件会自动注册到构造器参数中
public PersonPojo(SkillPojo skillPojo) {
this.skillPojo = skillPojo;
this.name=name;
}
}
4、将组件注入到被@Bean修饰的方法参数中
在配置类中,标准了@Bean方法中的方法参数,每个参数都将与Spring容器中的匹配bean自动连接
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = {"com.tellhow.review.spring_annotation.di"})
@Slf4j
public class DIConfig {
@Bean("zhuque")
public PersonPojo personPojo2(SkillPojo martial) {//martial会自动注入容器中相同类型的组件值
PersonPojo personPojo = new PersonPojo();
personPojo.setName("陆言");
personPojo.setTitle("朱雀");
return personPojo;
}
5、spring容器通过回调样式的方法获取特定框架对象
5.1、基本操作
spring为我们提供了一些xxxAware接口,实现了这些接口我们通过通过回调样式方法获取到spring特定的框架对象。
/**
* 向bean注入Spring底层组件.
* 1、操作:Spring 提供了各种各样的xxxAware接口。只要实现了这些接口,就可以通过回调样式的方法获取到相应Spring的内置组件。
* 2、原理:将Spring内置组件注入到javabean的属性中。它的底层原理是对应的ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(前置处理器)在创建组件对象进行初始化前进行一些判断,符合条件的就会将内置组件放到方法的参数中取
* @author wujianghao
* @date 2022年11月18日 15:42
*/
@Component
public class BuiltInComponents implements ApplicationContextAware, EnvironmentAware {
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
Environment environment;
private String osName;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {//实现了ApplicationContextAware方法,就会通过回调方法setApplicationContext,获取到spring容器对象。
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
public Environment getEnvironment() {
return environment;
}
public String getOsName() {
return osName;
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
this.osName = environment.getProperty("os.name");
}
}
5.2、原理解析(以ApplicationContextAware为例)
1、我们知道bean的生命周期是bean的创建->初始化->销毁。
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();//实例化bean
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);//用来自bean定义的属性值填充给定BeanWrapper中的bean实例
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);//初始化bean
}
}
2、我们想将spring特定的框架对象绑定到属性中,是通过前置处理器完成的,前置处理器的方法会在bean的初始化前后执行。将spring框架对象的值暴露給属性是在初始化之前进行的。所以接下来进入applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization方法。
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);//执行前置处理器,在初始化之前
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);//执行初始化方法
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);//执行前置处理器,在初始化之前
}
return wrappedBean;
}
我们来看看前置处理器在执行bean初始化前做了什么操作。
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
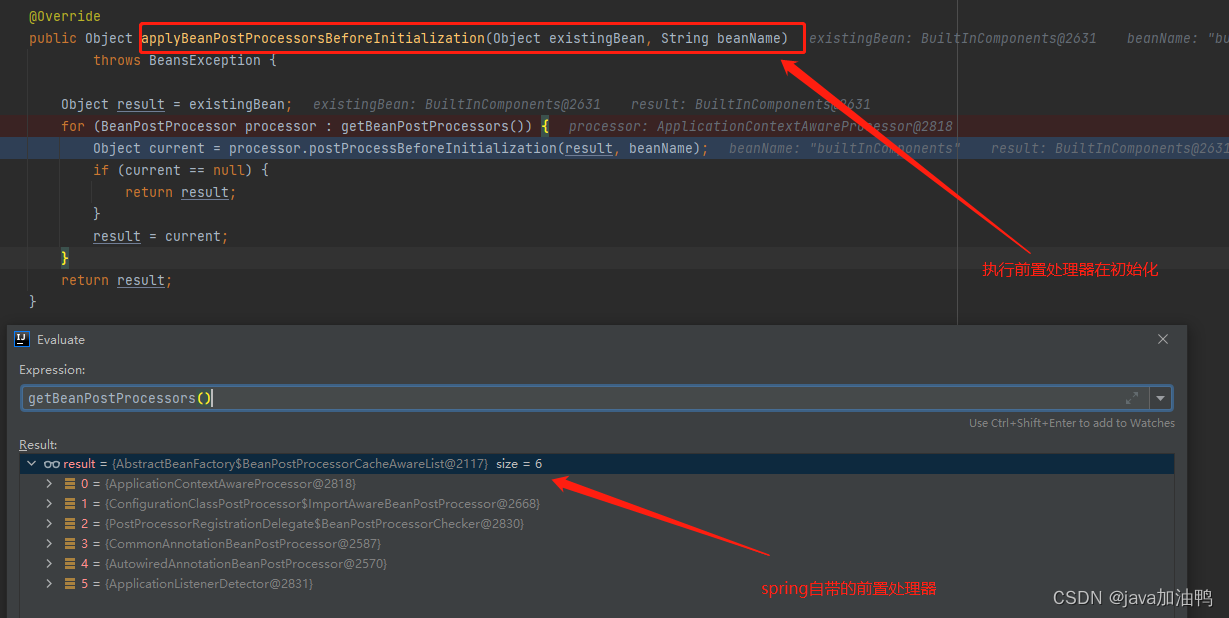 spring内置了6个前置处理器,他们在bean执行之前先执行这些BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法。我们进入查看一下ApplicationContextAwareProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
spring内置了6个前置处理器,他们在bean执行之前先执行这些BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法。我们进入查看一下ApplicationContextAwareProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
@Override
@Nullable
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (!(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||
bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||
bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware ||
bean instanceof ApplicationStartupAware)) {//bean是不是这些类型的
return bean;
}
AccessControlContext acc = null;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext();
}
if (acc != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
return null;
}, acc);
}
else {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);//执行Aware接口的方法,原理在这里
}
return bean;
}
beans实现ApplicationContextAware接口,将spring框架对象与重写的set方法的参数进行了连接。
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationStartupAware) {
((ApplicationStartupAware) bean).setApplicationStartup(this.applicationContext.getApplicationStartup());
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
@Component
public class BuiltInComponents implements ApplicationContextAware, EnvironmentAware {
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
Environment environment;
private String osName;
@Override//所以applicationContext对象,已经被前置处理器赋值了(ApplicationContextAwareProcessor)
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
public Environment getEnvironment() {
return environment;
}
public String getOsName() {
return osName;
}
@Override////所以applicationContext对象,已经被前置处理器赋值了(ApplicationContextAwareProcessor)
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
this.osName = environment.getProperty("os.name");
}
}
实现xxxAware接口,可以获取对应的框架对象。底层原理就是前置处理器(xxxAwareProcessor)





 本文详细介绍了Spring框架中的依赖注入(DI),包括属性注入、方法注入、构造器注入、组件注入到@Bean修饰的方法参数中,以及通过回调样式的方法获取特定框架对象。通过@Autowire、@Resource和@Inject等注解,以及xxxAware接口,实现组件间的依赖管理。
本文详细介绍了Spring框架中的依赖注入(DI),包括属性注入、方法注入、构造器注入、组件注入到@Bean修饰的方法参数中,以及通过回调样式的方法获取特定框架对象。通过@Autowire、@Resource和@Inject等注解,以及xxxAware接口,实现组件间的依赖管理。
















 1315
1315

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








