torch.compile解析系列——TorchDynamo解析
基本介绍
在上一篇【编译系列】Torch.compile()流程解析——1. torch.compile介绍,我们解释了torch.compile出现的背景并初步了解了其使用和基础组成(感兴趣的小伙伴可以去翻一翻哦~~~)。本章我们将解释四个基础组件中的TorchDynamo。
TorchDynamo的基本工作流程是基于PEP 523(Python Enhancement Proposal)在函数执行前拿到Python字节码,通过解析并模拟执行每条Python字节码逐步创建FX Graph,对if/else、loop或不支持的操作,会触发graph break生成sub-graph。例如对于上面的my_func()函数会生成三个subgraph。其中opcode有六种:placeholder对应输入、call_method/call_function/call_module对应函数/方法/模型调用、output对应输出;target是函数调用,name是op结果名称,args和kwargs是参数。
# 原始函数
def my_func(x, y):
if x.sum() > y.sum():
loss = torch.cos(torch.cos(x))
else:
loss = torch.cos(torch.cos(y))
return loss
# 判断语句及之前的代码对应一个subgraph
===============my compiler=================
opcode name target args kwargs
------------- ------ ---------------------- -------------- --------
placeholder l_x_ L_x_ () {}
placeholder l_y_ L_y_ () {}
call_method sum_1 sum (l_x_,) {}
call_method sum_2 sum (l_y_,) {}
call_function gt <built-in function gt> (sum_1, sum_2) {}
output output output ((gt,),) {}
# 对应的python代码
code is:
def forward(self, L_x_ : torch.Tensor, L_y_ : torch.Tensor):
l_x_ = L_x_
l_y_ = L_y_
sum_1 = l_x_.sum(); l_x_ = None
sum_2 = l_y_.sum(); l_y_ = None
gt = sum_1 > sum_2; sum_1 = sum_2 = None
return (gt,)
# if为True对应一个subgraph
===============my compiler=================
opcode name target args kwargs
------------- ------ ------------------------------------------------------ ---------- --------
placeholder l_x_ L_x_ () {}
call_function cos <built-in method cos of type object at 0x7f0f1017b500> (l_x_,) {}
call_function loss <built-in method cos of type object at 0x7f0f1017b500> (cos,) {}
output output output ((loss,),) {}
# 对应的python代码
code is:
def forward(self, L_x_ : torch.Tensor):
l_x_ = L_x_
cos = torch.cos(l_x_); l_x_ = None
loss = torch.cos(cos); cos = None
return (loss,)
# if为False对应一个subgraph
===============my compiler=================
opcode name target args kwargs
------------- ------ ------------------------------------------------------ ---------- --------
placeholder l_y_ L_y_ () {}
call_function cos <built-in method cos of type object at 0x7f1254470500> (l_y_,) {}
call_function loss <built-in method cos of type object at 0x7f1254470500> (cos,) {}
output output output ((loss,),) {}
# 对应的python代码
code is:
def forward(self, L_y_ : torch.Tensor):
l_y_ = L_y_
cos = torch.cos(l_y_); l_y_ = None
loss = torch.cos(cos); cos = None
return (loss,)
优点:
- 动态优化:能够处理包含动态控制流的模型,如循环和条件语句,适用于动态计算图。
- 自动化:用户无需手动编写转换代码,可以自动识别和优化执行路径。
- 灵活性:支持多种后端优化器,如 TorchInductor,提供多样化的性能提升方案。
缺点:
- 新兴工具:作为较新的优化工具,可能在某些极端场景下还不够稳定或全面支持所有 PyTorch 功能,尚未提供序列化/反序列化API。
- 依赖后端:最终性能提升依赖于所使用的后端优化器,某些后端可能在特定硬件或模型上表现不佳。
和其他静态图构建方式相比,TorchDynamo更为灵活且支持更多复杂的操作,而不需要用户做大量的代码修改适配。
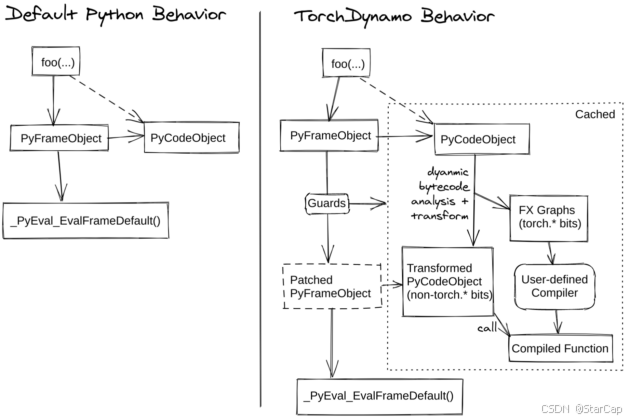
CPython代码的执行过程 & PEP 523:
在正式进入TorchDynamo工作过程之前先了解CPython的工作流程。首先介绍Cpython中两个重要的对象——PyCodeObject和PyFrameObject。PyCodeObject保存二进制字节码、常量表、变量名表等静态信息;而PyFrameObject 是一个用于表示执行环境的对象,每次函数调用时,Python都会创建一个新的PyFrameObject,其中包含了该函数的PyCodeObject,以及一些其他运行需要的信息,如存放局部变量的内存空间和evaluation stake(函数调用栈)等。
CPython在执行Python函数前会将Python代码编译为字节码,由Python虚拟机(PVM)中_PyEval_EvalFrameDefault()函数逐条执行编译好的字节码,而PEP 523提供了一个API接口让用户在PVM执行字节码之前获得待执行的字节码,从而可以对字节码进行优化修改实现即时编译(JIT Compiler)的效果。
TorchDynamo正是基于PEP 523把TorchDynamo的编译逻辑引入到Python代码的解释执行过程中,通过 CPython 提供的_PyInterpreterState_SetEvalFrameFunc()函数把CPython中用于执行字节码的默认函数给替换为custom_eval_frame_shim()。
在执行用户想要编译的函数时便会进入_custom_eval_frame_shim(),在_custom_eval_frame函数中,会先通过lookup函数检查cache中是否有已编译代码,若存在则直接调用eval_custom_code函数执行,从而避免重复编译相同函数。若cache未命中,则通过call_callback调用回调函数进行编译,并通过set_extra()将编译结果保存在PyFrameObject中,最后调用eval_custom_code继续进行执行。而这里的回调函数也即前面在torch._dynamo.optimize传入的回调函数convert_frame.convert_frame(backend, hooks=hooks)(包含编译入口compile_fn)。
因此torch.compile只有在第一次正式执行代码前才会进行编译,这也导致测试编译代码的时间时需要考虑数据预热。
到此,解释了torch.compile是如何在Python代码执行过程中引入TorchDynamo的,接下来回到torch._dynamo.optimize解析是如何一步步从字节码构建FX Graph。
static PyObject* _custom_eval_frame_shim(
PyThreadState* tstate,
THP_EVAL_API_FRAME_OBJECT* frame,
int throw_flag) {
// Shims logic into one of three states. Can probably be refactored into a
// single func, later:
// - None: disables TorchDynamo
// - False: run-only mode (reuse existing compiles)
// - Python callable(): enables TorchDynamo
PyObject* callback = eval_frame_callback_get();
if (callback == Py_None) {
return eval_frame_default(tstate, frame, throw_flag);
}
return _custom_eval_frame(tstate, frame, throw_flag, callback); # 调用编译函数
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static PyObject* _custom_eval_frame(
PyThreadState* tstate,
THP_EVAL_API_FRAME_OBJECT* frame,
int throw_flag,
PyObject* callback) {
// 省略中间代码,只展示核心函数调用...
PyObject* maybe_cached_code = lookup(extra, frame, NULL);
if (maybe_cached_code == NULL) {
// Python error
return NULL;
} else if (maybe_cached_code != Py_None) {
PyCodeObject* cached_code = (PyCodeObject*)maybe_cached_code;
// used cached version
DEBUG_TRACE("cache hit %s", name(frame));
// Re-enable custom behavior
eval_frame_callback_set(callback);
return eval_custom_code(tstate, frame, cached_code, throw_flag); //命中cache,直接eval_custom_code函数执行frame中的代码
}
// cache miss
PyObject* result =
call_callback(callback, frame, cache_size(extra)); // 未命中则调用回调函数进行编译
if (result == NULL) {
return NULL;
} else if (result != Py_None) {
DEBUG_TRACE("create cache %s", name(frame));
extra = create_cache_entry(extra, result);
Py_DECREF(result);
set_extra(frame->f_code, extra); // 将编译完成代码添加到frame中
// Re-enable custom behavior
eval_frame_callback_set(callback);
return eval_custom_code(tstate, frame, extra->code, throw_flag);
}
}
后续TorchDynamo的代码逻辑如下,感兴趣的小伙伴也可以看看后面的代码解析部分

TorchDynamo模拟执行 & FX Graph构建:
回到torch._dynamo.optimize设置的回调函数convert_frame.convert_frame(backend, hooks=hooks),其核心函数是_compile(),用于负责对字节码进行编译。在_compile()中会对缓存大小进行判断,如果缓存大小超过配置会有警告信息,默认值为 64,含义是对于同一个 Python 函数,如果函数的输入张量信息组合变化超过 64 种,TorchDynamo 则不会继续编译用户指定的函数。
在_compile中通过transform_code_object(code, transform)对用户代码进行优化转换,其中code是PyCodeObject类型,即待编译优化的字节码,transformer是转换函数。在transform_code_object函数中,cleaned_instructions()用来预处理字节码指令,通过 Python 标准库 dis.get_instructions(code) 获取字节码指令,对字节码进行清洗(例如对跳转指令做标准化处理),并转为结构化数据表示 Instruction,方便后续的优化。
#ps:只展示核心函数调用
# path:torch/_dynamo/convert_frame.py
@compile_time_strobelight_meta(phase_name="_compile")
@_use_lazy_graph_module(config.use_lazy_graph_module)
def _compile(
code: types.CodeType,
globals: Dict[str, object],
locals: Dict[str, object],
builtins: Dict[str, object],
compiler_fn: CompilerFn,
one_graph: bool,
export: bool,
export_constraints,
hooks: Hooks,
cache_entry,
cache_size: CacheSizeRelevantForFrame,
frame: Optional[types.FrameType] = None,
frame_state=None,
compile_id=None,
*,
skip: int = 0,
) -> Optional[GuardedCode]:
exceeded, limit_type = exceeds_cache_size_limit(cache_size) # 判断缓存大小是否超过阈值,默认为64
try:
guarded_code = compile_inner(code, one_graph, hooks, transform)
return guarded_code
except ...
finally:
tracer.output.call_cleanup_hooks()
output = tracer.output
assert output is not None
assert output.output_instructions
instructions[:] = output.output_instructions
code_options.update(output.code_options)
if config.dead_code_elimination:
propagate_inst_exn_table_entries(instructions)
check_inst_exn_tab_entries_valid(instructions)
instructions[:] = remove_pointless_jumps(remove_dead_code(instructions)) # 根据FX Graph分析未调用的代码,并进行剔除
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def compile_inner(
code: types.CodeType,
one_graph: bool,
hooks: Hooks,
transform: Callable[[List[Instruction], Dict[str, Any]], Any],
) -> Optional[GuardedCode]:
for attempt in itertools.count():
CompileContext.get().attempt = attempt
try:
out_code = transform_code_object(code, transform) # 编译用户想要优化的函数
break
except ...
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def transform_code_object(code, transformations, safe=False) -> types.CodeType:
keys = get_code_keys()
code_options = {k: getattr(code, k) for k in keys}
assert len(code_options["co_varnames"]) == code_options["co_nlocals"]
instructions = cleaned_instructions(code, safe)
propagate_line_nums(instructions)
transformations(instructions, code_options)
return clean_and_assemble_instructions(instructions, keys, code_options)[1]
def cleaned_instructions(code, safe=False) -> List[Instruction]:
instructions = list(map(convert_instruction, dis.get_instructions(code)))
check_offsets(instructions)
if sys.version_info >= (3, 11):
populate_kw_names_argval(instructions, code.co_consts)
virtualize_exception_table(code.co_exceptiontable, instructions)
virtualize_jumps(instructions)
strip_extended_args(instructions)
if not safe:
if sys.version_info < (3, 11):
remove_load_call_method(instructions)
if sys.version_info < (3, 12):
explicit_super(code, instructions)
if sys.version_info >= (3, 11):
remove_jump_if_none(instructions)
if sys.version_info >= (3, 12):
remove_binary_store_slice(instructions)
update_offsets(instructions)
devirtualize_jumps(instructions)
return instructions
例如对我们的样例函数my_func进行cleaned_instructions()后的结果如下。
Instruction(opcode=113, opname='JUMP_ABSOLUTE', arg=18, argval=18, offset=0, starts_line=13, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=Instruction(opcode=116, opname='LOAD_GLOBAL', arg=1, argval='torch', offset=18, starts_line=14, is_jump_target=True, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None), exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=124, opname='LOAD_FAST', arg=0, argval='x', offset=2, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=106, opname='LOAD_ATTR', arg=0, argval='sum', offset=4, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=131, opname='CALL_FUNCTION', arg=0, argval=0, offset=6, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=124, opname='LOAD_FAST', arg=1, argval='y', offset=8, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=106, opname='LOAD_ATTR', arg=0, argval='sum', offset=10, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=131, opname='CALL_FUNCTION', arg=0, argval=0, offset=12, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=107, opname='COMPARE_OP', arg=4, argval='>', offset=14, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=114, opname='POP_JUMP_IF_FALSE', arg=36, argval=36, offset=16, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=Instruction(opcode=116, opname='LOAD_GLOBAL', arg=1, argval='torch', offset=36, starts_line=16, is_jump_target=True, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None), exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=116, opname='LOAD_GLOBAL', arg=1, argval='torch', offset=18, starts_line=14, is_jump_target=True, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=106, opname='LOAD_ATTR', arg=2, argval='cos', offset=20, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=116, opname='LOAD_GLOBAL', arg=1, argval='torch', offset=22, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=106, opname='LOAD_ATTR', arg=2, argval='cos', offset=24, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=124, opname='LOAD_FAST', arg=0, argval='x', offset=26, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=131, opname='CALL_FUNCTION', arg=1, argval=1, offset=28, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=131, opname='CALL_FUNCTION', arg=1, argval=1, offset=30, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=125, opname='STORE_FAST', arg=2, argval='loss', offset=32, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=110, opname='JUMP_FORWARD', arg=16, argval=52, offset=34, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=Instruction(opcode=124, opname='LOAD_FAST', arg=2, argval='loss', offset=52, starts_line=17, is_jump_target=True, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None), exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=116, opname='LOAD_GLOBAL', arg=1, argval='torch', offset=36, starts_line=16, is_jump_target=True, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=106, opname='LOAD_ATTR', arg=2, argval='cos', offset=38, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=116, opname='LOAD_GLOBAL', arg=1, argval='torch', offset=40, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=106, opname='LOAD_ATTR', arg=2, argval='cos', offset=42, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=124, opname='LOAD_FAST', arg=1, argval='y', offset=44, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=131, opname='CALL_FUNCTION', arg=1, argval=1, offset=46, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=131, opname='CALL_FUNCTION', arg=1, argval=1, offset=48, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=125, opname='STORE_FAST', arg=2, argval='loss', offset=50, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=124, opname='LOAD_FAST', arg=2, argval='loss', offset=52, starts_line=17, is_jump_target=True, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
Instruction(opcode=83, opname='RETURN_VALUE', arg=None, argval=None, offset=54, starts_line=None, is_jump_target=False, positions=None, target=None, exn_tab_entry=None)
清理后的字节码通过transformations(instructions, code_options)函数进行处理,核心transform()函数实现如下。首先实例化了InstructionTranslator对象,在InstructionTranslator中有一个 OutputGraph 的实例,用于保存InstructionTranslator编译后的输出,以 torch.fx.Graph表示。
其中transform()(也即TorchDynamo)构建FX Graph的核心模块有两个:
- InstructionTranslator的初始化过程,负责对变量构建对应的Proxy,对应FX Graph中的placeholder部分;
- InstructionTranslator.run()负责模拟运行字节码并构建对应的Node添加到FX Graph中;
def transform(instructions, code_options):
nonlocal output
nonlocal tracer
speculation_log.restart()
tracer = InstructionTranslator(
instructions,
code,
locals,
globals,
builtins,
code_options,
compiler_fn,
one_graph,
export,
export_constraints,
mutated_closure_cell_contents,
frame_state=frame_state,
speculation_log=speculation_log,
)
try:
with tracing(tracer.output.tracing_context), tracer.set_current_tx():
tracer.run()
except ...
在InstructionTranslator的初始化过程中,通过PyCodeObject对象的co_varnames字段获取待编译函数中的变量名,并为每一个变量创建一个LazyVariableTracker,作为symbolic_locals。其中LazyVariableTracker是一种推迟创建给定底层值的VariableTracker,直到访问该值才创建用于节省空间资源,而VariableTracker被用于记录每个Python变量对应的类型信息用于构建静态图。
vars = list(code_options["co_varnames"])
cells_and_freevars = [x for x in self.cell_and_freevars() if x not in vars]
vars.extend(cells_and_freevars)
cells_and_freevars_set = set(cells_and_freevars)
self.symbolic_locals = {
k: variables.LazyVariableTracker.create(
f_locals[k],
source=LocalSource(k, cell_or_freevar=k in cells_and_freevars_set),
)
for k in vars
if k in f_locals
}
其中LazyVariableTracker通过 VariableBuilder 来生成实际对象。以torch.Tensor为例,VariableBuilder的创建逻辑如下:
- 首先通过create_graph_input()在FX Graph中创建了类型为placeholder的FX Proxy(FX Proxy是FX symbolic tracing中的symbol,placeholder对应变量,即前面的opcode)。
- install_guards()函数创建了类型为GuardBuilder.TYPE_MATCH的Guard对象,Guard在TorchDynamo中负责检测被编译函数所引用的外部数据信息是否发生变化,如果没有发生变化则可以复用之前编译好的函数,否则需要重新编译该函数。TYPE_MATCH主要判断两者的数据类型是否一致,TENSOR_MATCH主要对输入Tensor的shape、stride等信息进行检查是否发生改变。
- wrap_fx_proxy()为刚刚创建的Proxy建立实际的VariableTracker,核心逻辑实现在wrap_fx_proxy_cls()函数:
- 在wrap_fx_proxy_cls()函数中首先通过wrap_to_fake_tensor_and_record()函数为运行时获得的torch.Tensor创建 FakeTensor(默认情况下,TorchDynamo使用FakeTensor捕获计算图而不是真实的torch.Tensor,FakeTensor具有和真实torch.Tensor相同的张量信息,但没有实际的数据和张量内存分配);
- 通过specialize()函数特化张量信息(包括dtype、device等),在static shape模式下还会特化size、stride、is_contiguous信息,而在dynamic shape模式下则不会特化这部分信息。
- 最后通过target_cls创建对应的VariableTracker对象,例如这里的是torch.Tensor,则创建的是TensorVariable(VariableTracker的子类),用于记录Pytorch中的torch.Tensor类型数据的相关信息。
因此,在InstructionTranslator对象初始化创建VariableTracker的过程中,TorchDynamo完成了在FX Graph中创建FXProxy、添加Guard和FakeTensor相关操作并初始化VariableTracker,由于并不是所有的局部变量都会被当前frame用到,为了节省资源开销这里采用LazyVariableTracker,只有到实际使用的时候才会进行创建。到此完成输入对应的VariableTracker创建,会在后续一直带着Guard、FakeTensor等信息用于跟踪Tensor的后续操作。
tensor_proxy = self.tx.output.root_tracer.create_graph_input(
re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z0-9]+", "_", self.name), type(value), source=source
)
options = {}
if type(value) in config.traceable_tensor_subclasses:
options["torch_function_fn"] = build_torch_function_fn(
self.tx, value, self.source
)
self.install_guards(GuardBuilder.TYPE_MATCH)
tensor_variable = wrap_fx_proxy(
tx=self.tx,
proxy=tensor_proxy,
example_value=value,
subclass_type=subclass_type,
source=source,
**options,
)
guard_type = GuardBuilder.TENSOR_MATCH
if isinstance(source, GradSource) and is_from_optimizer_source(source):
guard_type = GuardBuilder.NOT_NONE_MATCH
self.install_guards(
functools.partial(
guard_type,
value=value
if isinstance(source, NumpyTensorSource)
else TensorWeakRef(value),
)
)
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 节省篇幅,这里只展示核心函数调用
def wrap_fx_proxy_cls(
target_cls, tx, proxy, example_value=None, subclass_type=None, **options
):
example_value = wrap_to_fake_tensor_and_record(example_value, tx=tx, **kwargs)
if isinstance(example_value, torch.Tensor):
set_example_value(proxy.node, example_value)
specialized_props = target_cls.specialize(example_value)
options.update(specialized_props)
return target_cls(proxy, **options)
完成InstructionTranslator对象的初始化,回到InstructionTranslator.run()函数,由于InstructionTranslator继承于class InstructionTranslatorBase,所以这里实际调用的是InstructionTranslatorBase.run()函数。InstructionTranslatorBase的本质是一个Python虚拟机的模拟器,在循环中对字节码逐条解析模拟执行,对其核心函数step()进行分析,首先基于instruction_pointer获取待执行的字节码指令,通过dispatch_table映射表获取到每个op对应的函数调用并进入函数解析当前字节码指令,当遇到循环、if/else等跳转相关的字节码指令时会触发compile_subgraph()函数进入子图编译相关操作。
def run(self):
with self.run_ctx_mgr():
try:
self.output.push_tx(self)
while self.step(): # 循环调用step()函数模拟执行python字节码
pass
except BackendCompilerFailed:
raise
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def step(self):
"""Process exactly one instruction, return False we should exit"""
ip = self.instruction_pointer # Python虚拟机的PC(Program Counter),表明当前正在执行的字节码指令所处位置;
if ip is None:
return False
self.current_instruction = inst = self.instructions[ip]
self.instruction_pointer = ip + 1
if inst.starts_line:
self.starts_line(inst.starts_line)
# stack:Python虚拟机的数据栈,Python虚拟机中字节码之间通过数据栈交换数据
if (
not self.stack
and self.should_compile_partial_graph()
and self.is_non_empty_graph()
):
self.current_speculation = self.speculate()
# 循环、if/else等语句都会触发,进入step_graph_break进行子图编译
if self.current_speculation.failed:
return self.step_graph_break(inst)
self.update_block_stack(inst)
try:
self.dispatch_table[inst.opcode](self, inst) # 逐条执行指令
return not self.output.should_exit # 执行结束退出
except exc.ObservedException:
self.exception_handler()
return True
except ReturnValueOp:
return False # 返回指令
except Unsupported:
if self.current_speculation is None:
log.debug("empty checkpoint")
raise
log.debug("step triggered compile", exc_info=True)
对于每条字节码的模拟执行和解析,以上面的CALL_FUNCTION函数调用为例,会先根据argval弹出对应的函数参数,并进一步调用TensorVariable.call_method()函数。在call_method()函数中,proxy_args_kwargs()函数从symbolic_locals中获取相应的函数参数Proxy,然后调用create_proxy()创建新的Proxy,类型是call_method,并有对应的method名(如my_func中的x.sum(),对应TorchDynamo中的target项)和参数。最后通过wrap_fx_proxy()(和前面创建局部变量一样)创建新的TensorVariable来保存结果,中间收集到的Guard信息也附加了上去,最后在call_function()函数中将结果压栈。到此完成当前字节码的模拟执行并在此过程中将对应的Proxy添加到FX Graph中。
@break_graph_if_unsupported(push=1)
def CALL_FUNCTION(self, inst):
args = self.popn(inst.argval)
fn = self.pop()
self.call_function(fn, args, {})
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TensorVariable
def call_method(
self,
tx,
name,
args: "List[VariableTracker]",
kwargs: "Dict[str, VariableTracker]",
) -> "VariableTracker":
# 省略中间代码...
return wrap_fx_proxy(
tx,
tx.output.create_proxy(
"call_method",
name,
*proxy_args_kwargs([self, *args], kwargs),
),
)
因此,TorchDynamo在字节码的分析过程中并没有真正地执行指令,而是以符号分析的方式从字节码中提取相应的符号和函数,创建相应的Proxy并添加到FX Graph中,通过指令逐条模拟执行(解析)不断构建FX Graph,直到触发compile_subgraph()。
子图编译
在前面的分析中,TorchDynamo都是逐条执行指令然后不断地构建FX Graph,但当遇到例如jump字节码指令(对应if/else、循环等)时,会触发compile_subgraph()函数,因为在TorchDynamo中是以子图为单位进行编译的(除了设置full_graph=True),在compile_subgraph()中完成FX Graph一个完整子图的构建,并调用backend compiler对该子图进行编译。
分析compile_subgraph()的核心函数compile_and_call_fx_graph()实现:
- 调用create_node创建类型为output的Proxy(对应输出返回值),到此一张完整的FX Graph构建完毕。
- 基于完整的FX Graph创建对应的GraphModule作为编译函数的入参,并通过call_user_compiler()函数调用backend compiler对GraphModule进行编译(在这里开始进入inductor编译函数)。
- 通过PyCodegen.get_instructions()函数获得编译后函数对应的Instructions,到此完成整个子图的编译部分。
# ps:只展示核心函数调用,省略中间过程
def compile_and_call_fx_graph(self, tx, rv, root):
"""
Generate code from self.graph and return the Instruction()s to
call that generated code.
"""
self.create_node(
"output",
"output",
(self.current_tracer.create_arg(tuple(x.as_proxy() for x in rv)),),
{},
)
gm = _make_graph_module(root, self.graph) # 创建GraphModule,对应编译函数的传入参数,用于编译
with self.restore_global_state():
compiled_fn = self.call_user_compiler(gm) # 这里调用用户指定的backend compiler进行编译,如inductor等
compiled_fn = disable(compiled_fn) # 禁止TorchDynamo再次编译已编译的函数
cg = PyCodegen(tx)
cg.make_call_generated_code(name) # 生成字节码
return cg.get_instructions() # 获取编译后代码的Instructions
最后调用add_output_instructions()函数将should_exit属性置为True,这意味回到InstructionTranslatorBase.run()循环中会退出。
一路回退到_compile(),,在transform_code_object()中会调用clean_and_assemble_instructions()将Instruction汇编为Python可执行的字节码。
Guard生成
对于静态图的生成,特别是static shape,TorchDynamo中还有一个重要的组成部分——Guard。随着上述提及的函数调用栈一路回退到_compile(),此时已经完成了FX Graph的构建、调用backend compiler进行了编译并对编译后代码生成字节码,TorchDynamo最后需要为之前构建FX Graph过程中收集的Guard生成检测代码(Python代码),从而在后续执行代码时检测代码是否已编译过。
TorchDynamo通过CheckFunctionManager的compile_check_fn()函数为Guard生成可执行Python代码,为了降低运行时检测输入是否发生变化的函数开销,TorchDynamo把Guard检测功能实现在了C++中。(具体实现可以查阅 /usr/local/lib/python3.9/dist-packages/torch/_dynamo/guards.py )
回到_compile()函数,check_fn即生成的Guard检查函数,GuardedCode保存编译好的子图out_code和check_fn。
check_fn = CheckFunctionManager(
output,
hooks.guard_fail_fn if hooks else None,
)
guarded_code = GuardedCode(out_code, check_fn.check_fn)
到此完成了一个完整的子图的全部构建和编译工作,最终回到最开始的_custom_eval_frame()函数,对编译完的代码调用eval_custom_code(),送入CPython默认的执行函数入口_PyEval_EvalFrameDefault进行执行,完成编译后子图的执行(和Pytorch eager模式执行一样)。
后续函数的执行过程
回到_custom_eval_frame()函数,此时拿到了编译好的GuardedCode,create_cache_entry()和set_extra()往当前用户函数的frame->f_code里写入了一跳CacheEntry,记录了check_fn和编译好的code。eval_custom_code()创建了一个新的 Python Frame,并运行编译好的函数。
eval_custom_code() 中直接调用了eval_frame_default()来执行上面的字节码,所以此处不会再次触发 TorchDynamo 定制的 Frame Evaluation 函数custom_eval_frame_shim()。执行完编译过的子图,程序返回到 Python 解释器,下一条字节码是 if/else对应的跳转指令,会再次触发TorchDynamo 设置的 Frame Evaluation 函数 custom_eval_frame_shim()继续进行子图的捕获和编译。























 13万+
13万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








