1 LinkStack的实现
1.1 StaticStack的缺陷
由于StaticStack内部使用了原声数组,当存储的元素为类类型时,StaticStack的对象在创建时,会多次调用元素类型的构造函数,影响效率。因此,我们需要链式栈来避免这种缺陷。
1.2 链式栈的存储实现
1.3 链式栈的设计要点
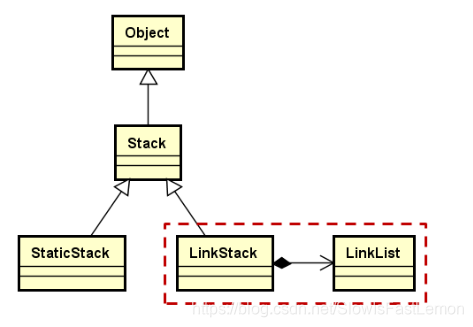
- 类模板,抽象父类Stack的直接子类。
- 在内部组合使用LinkList类,实现栈的链式存储。
- 只在单链表成员对象的头部进行操作。
1.4 继承关系图
2 代码实现
#ifndef LINKSTACK_H
#define LINKSTACK_H
#include "Stack.h"
#include "LinkList.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace LemonLib
{
template <typename T>
class LinkStack : Stack<T>
{
protected:
LinkList<T> m_list;
public:
void push(const T& e)
{
m_list.insert(0, e);
}
void pop()
{
if (m_list.length() > 0)
{
m_list.remove(0);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No element in current stack ...");
}
}
T top() const
{
if (m_list.length() > 0)
{
return m_list.get(0);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No element in current stack ...");
}
}
void clear()
{
m_list.clear();
}
int size() const
{
return m_list.length();
}
};
}
#endif // LINKSTACK_H
3 栈的应用实践
符号匹配问题:
在C语言中有一些成对匹配出现的符号:
- 括号:(),[],{},<>
- 引号:’’,""
那么我们如何实现编译器中的符号成对检测呢?
算法思路:
-
从第一个字符开始扫描
- 当遇见普通字符时忽略
- 当遇见左符号时压入栈中
- 当遇见右符号时弹出栈顶符号,并进行匹配
-
结束
- 成功:所有字符扫描完毕,并且栈为空
- 失败:匹配失败或所有字符扫描完毕但栈非空
#include <iostream>
#include "LinkStack.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace LemonLib;
bool is_left(char c)
{
return ((c == '{') || (c == '(') || (c == '[') || (c == '<'));
}
bool is_right(char c)
{
return ((c == '}') || (c == ')') || (c == ']') || (c == '>'));
}
bool is_quote(char c)
{
return ((c == '\'') || (c == '\"'));
}
bool is_match(char l, char r)
{
return ((l == '{') && (r == '}')) ||
((l == '(') && (r == ')')) ||
((l == '[') && (r == ']')) ||
((l == '<') && (r == '>')) ||
((l == '\'') && (r == '\'')) ||
((l == '\"') && (r == '\"'));
}
bool scan(const char* str)
{
bool ret = true;
LinkStack<char> stack;
int i = 0;
str = (str == NULL) ? "" : str;
while (ret && (str[i] != '\0'))
{
if (is_left(str[i]))
{
stack.push(str[i]);
}
else if (is_right(str[i]))
{
if ((stack.size() > 0) && is_match(stack.top(), str[i]))
{
stack.pop();
}
else
{
ret = false;
}
}
else if (is_quote(str[i]))
{
if ((stack.size() > 0) && (is_match(stack.top(), str[i])))
{
stack.pop();
}
else
{
stack.push(str[i]);
}
}
i++;
}
return (ret && (stack.size() == 0));
}
int main()
{
cout << scan("<a{b(\'x\')c}d>") << endl;
return 0;
}
4 小结
- 链式栈的实现组合使用了单链表对象。
- 在单链表的头部进行操作能够实现高效的入栈和出栈操作。
- 栈“后近先出”的特性适用于检测成对出现的符号。
- 栈非常适合于需要“就近匹配”的场合。





















 840
840

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








