文章目录
1 线性表的链式存储结构
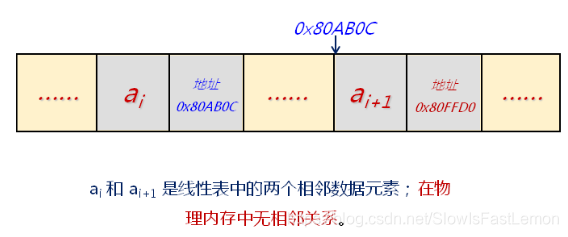
顺序存储结构的最大问题就是插入和删除时需要移动大量的元素,这个时候就需要链式存储结构的线性表出场了。
1.1 链式存储的定义
为了表示每个数据元素与其直接后继元素之间的逻辑关系,数据元素除了存储本身的信息外,还需要存储直接后继的信息。
1.2 链式存储逻辑结构
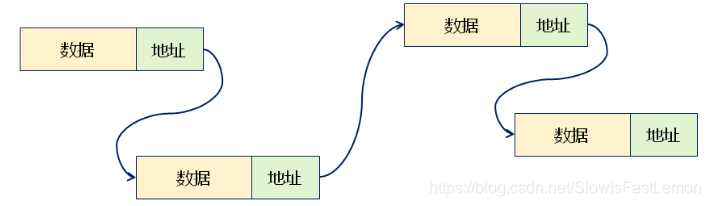
基于链式存储结构的线性表中,每个结点都包含数据域和指针域。
- 数据域:存储数据元素本身。
- 指针域:存储相邻结点的地址。
1.3 专业术语的统一
顺序表
- 基于顺序存储结构的线性表
链表
- 基于链式存储结构的线性表
- 单链表:每个结点只包含直接后继的地址信息
- 循环链表:单链表中的最后一个结点的直接后继为第一个结点
- 双向链表:单链表中的结点包含直接前驱和直接后继的地址信息
1.4 链表中的基本概念
头结点: 链表中的辅助结点,包含指向第一个数据元素的指针。
数据结点: 链表中代表数据元素的结点,表现形式为:(数据元素,地址)。
尾结点: 链表中的最后一个数据结点,包含的地址信息为空。
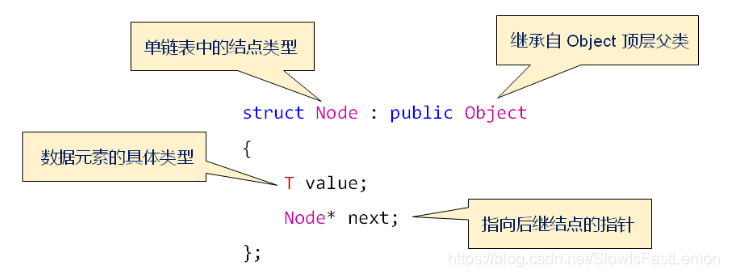
1.5 单链表中的结点定义
1.6 单链表的内部结构
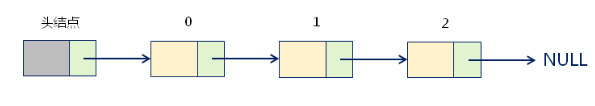
头结点在单链表中的意义: 辅助数据元素的定位,方便插入和删除操作;因此,头结点不存储实际的数据元素。
1.7 在目标位置处插入数据元素
- 从头结点开始,通过current指针定位到目标位置。
- 从堆空间申请新的Node结点。
- 执行操作:
node->value = e;
node->next = current->next;
current->next = node;
1.8 在目标位置处删除数据元素
- 从头结点开始,通过current指针定位到目标位置。
- 使用toDel指针指向需要删除的结点。
- 执行操作:
toDel = current->next;
current->next = toDel->next;
delete toDel;
注意: 插入和删除操作一定要保证链表的完整性。
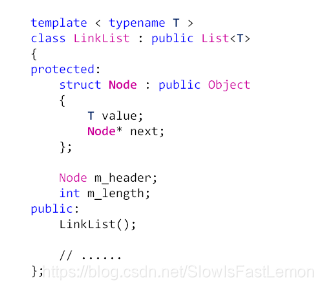
2 LinkList设计要点
- 类模板,通过头结点访问后继结点。
- 定义内部结点类型Node,用于描述数据域和指针域。
- 实现线性表的关键操作(增,删,查,等)。
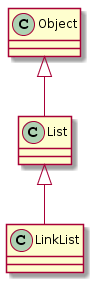
3 继承关系图和接口实现
继承关系图
接口实现
4 代码实现
LinkList.h
#ifndef LINKLIST_H
#define LINKLIST_H
#include "List.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace LemonLib
{
template < typename T >
class LinkList : public List<T>
{
protected:
struct Node : public Object
{
T value;
Node* next;
};
mutable Node m_header;
int m_length;
Node* position(int index) const
{
Node* ret = &m_header;
for (int i=0; i<index; i++)
{
ret = ret->next;
}
return ret;
}
public:
LinkList()
{
m_header.next = NULL;
m_length = 0;
}
bool insert(int index, const T& e)
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index <= m_length);
if (ret)
{
Node* node = new Node();
if (node != NULL)
{
Node* current = position(index);
node->value = e;
node->next = current->next;
current->next = node;
m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No enough memory to inset element ...");
}
}
return ret;
}
bool insert(const T& e)// 插入到尾部
{
return insert(m_length, e);
}
bool remove(int index)
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < m_length);
if (ret)
{
Node* current = position(index);
Node* toDel = current->next;
current->next = toDel->next;
m_length--;
delete toDel;
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int index, const T& e)
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < m_length);
if (ret)
{
position(index)->next->value = e;
}
return ret;
}
bool get(int index, T& e) const
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < m_length);
if (ret)
{
e = position(index)->next->value;
}
return ret;
}
T get(int index) const
{
T ret;
if (get(index, ret))
{
return ret;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidParameterException, "Invalid parameter in get element...");
}
}
int find(const T& e) const
{
int ret = -1;
int index = 0;
Node* current = m_header.next;
while (current)
{
if (current->value == e)
{
ret = index;
break;
}
else
{
index++;
current = current->next;
}
}
return ret;
}
int length() const
{
return m_length;
}
void clear()
{
while (m_header.next)
{
Node* toDel = m_header.next;
m_header.next = toDel->next;
m_length--;
delete toDel;
}
}
~LinkList()
{
clear();
}
};
}
#endif // LINKLIST_H
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Object.h"
#include "Exception.h"
#include "List.h"
#include "Seqlist.h"
#include "Staticlist.h"
#include "Dynamiclist.h"
#include "Staticarray.h"
#include "DynamicArray.h"
#include "Linklist.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace LemonLib;
int main()
{
LinkList<int> list;
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
list.insert(i);
}
for (int i=0; i<list.length(); i++)
{
int val = 0;
if (list.get(i, val))
{
cout << val << endl;
}
}
cout << endl;
list.remove(1);
for (int i=0; i<list.length(); i++)
{
cout << list.get(i) << endl;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
5 头结点存在的隐患
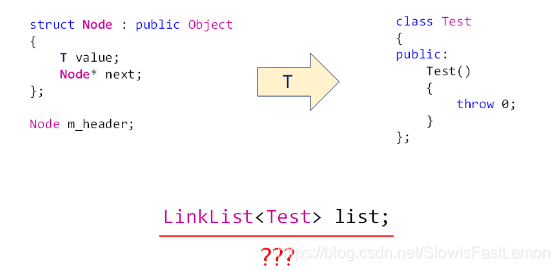
如果写出如上的代码将会直接抛出异常,这显然是不合适的,因为这个时候仅仅创建了单链表类而没有创建有问题的Test类,因此我们需要对头结点进行优化。
优化后的代码如下:
LinkList.h
template < typename T >
class LinkList : public List<T>
{
protected:
struct Node : public Object
{
T value;
Node* next;
};
/* 注意:当前结构体必须继承自Object类,否则会导致和Node的内存布局不同,直接抛出异常 */
mutable struct : public Object
{
char reserved[sizeof(T)];
Node* next;
}m_header;
int m_length;
Node* position(int index) const
{
Node* ret = reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header);
for (int i=0; i<index; i++)
{
ret = ret->next;
}
return ret;
}
public:
// 和之前代码完全相同
};
6 顺序表和单链表分析
6.1 时间复杂度对比分析
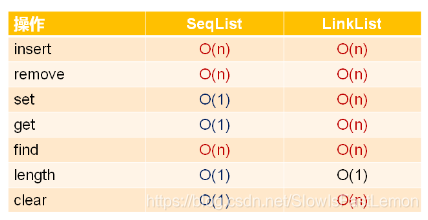
顺序表的整体时间复杂度比单链表要低,那么单链表还有使用价值吗?
6.2 效率深度分析
注意:在实际工程开发中,时间复杂度只是效率的一个参考指标。
| 对比点 | 顺序表 | 单链表 |
|---|---|---|
| 内置基础类型 | 顺序表和链表效率不相上下 | 顺序表和链表效率不相上下 |
| 自定义类型 | 顺序表在效率上低于单链表 | 顺序表在效率上低于单链表 |
| 插入和删除 | 涉及大量数据对象的复制操作 | 只涉及指针操作,效率与数据对象无关 |
| 数据访问 | 随机访问,可直接定位数据对象 | 顺序访问,必须从头访问数据,无法直接定位 |
工程开发中的实际选择:
- 顺序表:数据元素类型相对简单,不涉及深拷贝;数据元素相对稳定,访问操作远多于插入和删除操作。
- 单链表:数据元素类型相对复杂,复制操作相对耗时;数据元素不稳定,需要经常插入和删除,访问操作较少。
7 单链表的遍历与优化
7.1 当前遍历的问题
问题: 如何遍历单链表中每一个元素?
对于当前实现的链表来说,可以用如下的方式进行遍历:

可以看到通过上面的遍历方法我们不能以线性的时间复杂度完成单链表的遍历,目前遍历链表的时间复杂度是O(n2),这显然是有改进的空间的。我们需要为单链表提供新的方法,以便实现在线性的时间内完成遍历。
7.2 优化的思路
设计思路
- 在单链表内部定义一个游标(Node* m_current)
- 遍历开始前将游标指向位置为0的数据元素
- 获取游标指向的数据元素
- 通过结点中的next指针移动游标
我们可以提供如下的一组函数,从而以线性的时间复杂度遍历链表。

遍历函数原型设计

注意:遍历相关的成员函数是相互依赖、相互配合的关系,一定要按照规则使用,否则将有可能出现错误!
7.3 代码实现
为了实现单链表类的扩展,我们对当前单链表内部再进行一次封装。

为了提高扩展性,我们对结点的申请和释放进行封装,这样我们就可以自己指定结点分配的空间。这里我们为静态单链表(StaticLinkList)的实现做准备,StaticLinkList与LinkList的不同仅在于链表结点在内存分配上的不同。因此,只需要将仅有不同封装在父类和子类的虚函数中。
LinkList.h
#ifndef LINKLIST_H
#define LINKLIST_H
#include "List.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace LemonLib
{
template < typename T >
class LinkList : public List<T>
{
protected:
struct Node : public Object
{
T value;
Node* next;
};
/* 注意:当前结构体必须继承自Object类,否则会导致和Node的内存布局不同,直接抛出异常 */
mutable struct : public Object
{
char reserved[sizeof(T)];
Node* next;
}m_header;
int m_length;
Node* m_current;
int m_step;
Node* position(int index) const
{
Node* ret = reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header);
for (int i=0; i<index; i++)
{
ret = ret->next;
}
return ret;
}
virtual Node* create()
{
return new Node();
}
virtual void destroy(Node* pn)
{
delete pn;
}
public:
LinkList()
{
m_header.next = NULL;
m_length = 0;
m_current = NULL;
m_step = 0;
}
bool insert(int index, const T& e)
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index <= m_length);
if (ret)
{
Node* node = create();
if (node != NULL)
{
Node* current = position(index);
node->value = e;
node->next = current->next;
current->next = node;
m_length++;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No enough memory to inset element ...");
}
}
return ret;
}
bool insert(const T& e)// 插入到尾部
{
return insert(m_length, e);
}
bool remove(int index)
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < m_length);
if (ret)
{
Node* current = position(index);
Node* toDel = current->next;
current->next = toDel->next;
if (m_current == toDel)
{
m_current = toDel->next;
}
m_length--;
destroy(toDel);
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int index, const T& e)
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < m_length);
if (ret)
{
position(index)->next->value = e;
}
return ret;
}
bool get(int index, T& e) const
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index < m_length);
if (ret)
{
e = position(index)->next->value;
}
return ret;
}
virtual T get(int index) const
{
T ret;
if (get(index, ret))
{
return ret;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidParameterException, "Invalid parameter in get element...");
}
}
int find(const T& e) const
{
int ret = -1;
int index = 0;
Node* current = m_header.next;
while (current)
{
if (current->value == e)
{
ret = index;
break;
}
else
{
index++;
current = current->next;
}
}
return ret;
}
virtual bool move(int index, int step = 1)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= index) && (index < m_length) && (step > 0));
if (ret)
{
m_current = position(index)->next;
m_step = step;
}
return ret;
}
virtual bool end()
{
return (m_current == NULL);
}
virtual T current()
{
if (!end())
{
return m_current->value;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "Invalid operation to get current value ...");
}
}
virtual bool next()
{
int i = 0;
while ((i < m_step) && (!end()))
{
m_current = m_current->next;
i++;
}
return (i == m_step);
}
int length() const
{
return m_length;
}
void clear()
{
while (m_header.next)
{
Node* toDel = m_header.next;
m_header.next = toDel->next;
m_length--;
destroy(toDel);
}
}
~LinkList()
{
clear();
}
};
}
#endif // LINKLIST_H
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Object.h"
#include "Exception.h"
#include "List.h"
#include "Seqlist.h"
#include "Staticlist.h"
#include "Dynamiclist.h"
#include "Staticarray.h"
#include "DynamicArray.h"
#include "Linklist.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace LemonLib;
int main()
{
LinkList<int> list;
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
list.insert(0, i);
}
for (list.move(0); !list.end(); list.next())
{
cout << list.current() << endl;
}
return 0;
}





 本文深入探讨了链式存储结构的定义、逻辑结构及其在单链表中的应用,包括结点定义、内部结构、插入与删除操作。同时,分析了链表与顺序表在时间复杂度、效率及工程开发中的优劣,提出了链表遍历的优化方法。
本文深入探讨了链式存储结构的定义、逻辑结构及其在单链表中的应用,包括结点定义、内部结构、插入与删除操作。同时,分析了链表与顺序表在时间复杂度、效率及工程开发中的优劣,提出了链表遍历的优化方法。
















 1459
1459

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








