文章目录
1 线性表的顺序存储结构
1.1 顺序存储的定义
线性表的顺序存储结构,指的是用一段地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表中的数据元素。

1.2 设计思路
可以用一维数组实现顺序存储结构。
- 存储空间:
T* m_array; - 当前长度:‘int m_length;’
template <typename T>
class SeqList : public List<T>
{
protected:
T* m_array;
int m_length;
// ...
};
1.3 顺序存储结构的元素获取操作
(1)判断目标位置是否合法。
(2)将目标位置作为数据下标获取元素。
bool SeqList<T>::get(int index, T& e) const
{
bool ret = ((0 <= index) && (index < m_length));
if (ret)
{
e = m_array[index];
}
return ret;
}
1.4 顺序存储结构的元素插入操作
(1)判断目标位置是否合法。
(2)将目标位置之后的所有元素后移一个位置。
(3)将新元素插入目标位置。
(4)线性表长度加1。
bool SeqList<T>::insert(int index, const T& e)
{
bool ret = (0 <= index) && (index <= m_length);
ret = ret && ((m_length + 1) <= capacity());
if (ret)
{
for (int p=m_length-1; p>=index; p--)
{
m_array[p+1] = m_array[p];
}
m_array[index] = e;
m_length++;
}
}
1.5 顺序存储结构的元素删除操作
(1)判断目标位置是否合法。
(2)将目标位置后的所有元素前移一个位置。
(3)线性表长度减1。
bool SeqList<T>::remove(int index)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= index) && (index < m_length));
if (ret)
{
for (int p=index; i<m_length-1; i++)
{
m_array[p] = m_array[p+1];
}
m_length--;
}
return ret;
}
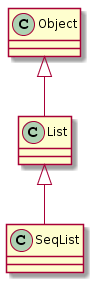
2 继承关系图和接口实现
SeqList实现要点
- 抽象类模板,存储空间的位置和大小由子类完成
- 实现顺序存储结构线性表的关键操作(增,删,查等)
- 提供数组操作符,方便快速获取元素
顺序存储结构线性表继承关系图
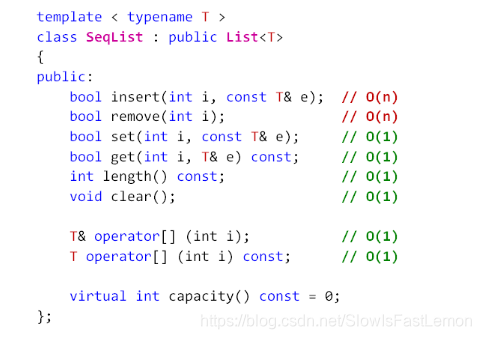
SeqList接口实现:
template < typename T >
class SeqList : public List<T>
{
protected:
T* m_array; // 顺序存储空间
int m_length; // 当前线性表长度
public:
bool insert(int index, const T& e); // O(n)
bool insert(const T& e); // O(1)
bool remove(int index); // O(n)
bool set(int index, const T& e); // O(1)
bool get(int index, T& e) const; // O(1)
int find(const T& e) const; // O(n)
int length() const; // O(1)
void clear(); // O(1)
// 顺序存储线性表的数组访问方式
T& operator[](int index); // O(1)
T operator[](int index) const; // O(1)
// 顺序存储空间的容量
virtual int capacity() const = 0;
};
3 代码实现
SeqList.h
#ifndef SEQLIST_H
#define SEQLIST_H
#include "Exception.h"
namespace LemonLib
{
template < typename T >
class SeqList : public List<T>
{
protected:
T* m_array; // 顺序存储空间
int m_length; // 当前线性表长度
public:
bool insert(int index, const T& e)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= index) && (index <= m_length));
ret = ret && (m_length < capacity());
if (ret)
{
for (int p=m_length-1; p>=index; p--)
{
m_array[p+1] = m_array[p];
}
m_array[index] = e;
m_length++;
}
return ret;
}
bool insert(const T& e)
{
return insert(m_length, e);
}
bool remove(int index)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= index) && (index < m_length));
if (ret)
{
for (int p=index; p<m_length-1; p++)
{
m_array[p] = m_array[p+1];
}
m_length--;
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int index, const T& e)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= index) && (index < m_length));
if (ret)
{
m_array[index] = e;
}
return ret;
}
bool get(int index, T& e) const
{
bool ret = ((0 <= index) && (index < m_length));
if (ret)
{
e = m_array[index];
}
return ret;
}
int find(const T& e) const
{
int ret = -1;
for (int i=0; i<m_length; i++)
{
if (m_array[i] == e)
{
ret = i;
break;
}
}
return ret;
}
int length() const
{
return m_length;
}
void clear()
{
m_length = 0;
}
// 顺序存储线性表的数组访问方式
T& operator[](int index)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= index) && (index < m_length));
if (ret)
{
return m_array[index];
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Param index is invalid...");
}
}
T operator[](int index) const
{
return (const_cast<SeqList<T>&>(*this))[index];
}
// 顺序存储空间的容量
virtual int capacity() const = 0;
};
}
#endif // SEQLIST_H
4 效率分析
5 思考
问题: 长度相同的两个SeqList,插入和删除操作的平均耗时是否相同?
元素的类型不同将导致插入和删除操作的平均耗时不同,比如一个数据类型为原生类型int,另一个数据类型为string,很明显两者的插入和删除操作的平均耗时有很大区别。
6 注意
- 顺序存储线性表的插入和删除操作存在重大效率隐患(跟具体元素的类型有关)。
- 线性表作为容器类,应当避免拷贝构造和拷贝赋值。
- 顺序线性表可能被当成数组误用。
- 工程开发中可以考虑使用数组类代替原生数组使用。







 本文深入探讨了线性表的顺序存储结构,包括定义、设计思路、关键操作的实现如元素获取、插入和删除,以及代码实现和效率分析。通过具体示例,读者将理解顺序存储结构的优缺点。
本文深入探讨了线性表的顺序存储结构,包括定义、设计思路、关键操作的实现如元素获取、插入和删除,以及代码实现和效率分析。通过具体示例,读者将理解顺序存储结构的优缺点。
















 8万+
8万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








