1 文件从哪里来
在Linux系统中,一切都是“文件”:普通文件、驱动程序、网络通信等等。所有的操作,都是通过“文件IO”来操作的。所以,很有必要掌握文件操作的常用接口。
文件一般从如下来:
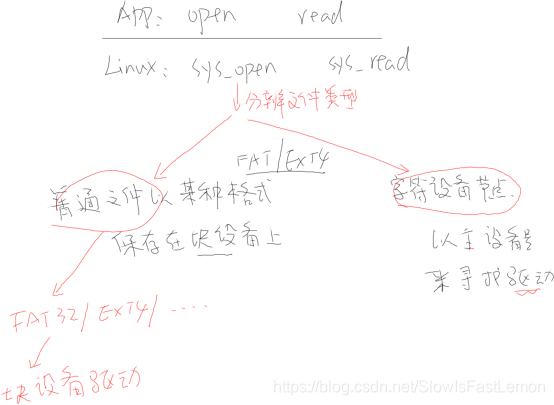
- 磁盘、Flash、SD卡、U盘,这些都是真实文件,是以某种格式(FAT32、EXT4等)保存在某个设备上(/dev/xxxx),要先mount。
- Linux内核提供的虚拟文件系统,也要先mount。
- 特殊文件:/dev/xxx,设备节点(字符设备、块设备),FIFO,socket。
2 怎么访问文件
2.1 通用的IO模型
通用的IO模型有:open/read/write/lseek/close。示例代码如下:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/*
* ./copy 1.txt 2.txt
* argc = 3
* argv[0] = "./copy"
* argv[1] = "1.txt"
* argv[2] = "2.txt"
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd_old, fd_new;
char buf[1024];
int len;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 3)
{
printf("Usage: %s <old-file> <new-file>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开老文件 */
fd_old = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (fd_old == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 3. 创建新文件 */
fd_new = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH);
if (fd_new == -1)
{
printf("can not creat file %s\n", argv[2]);
return -1;
}
/* 4. 循环: 读老文件-写新文件 */
while ((len = read(fd_old, buf, 1024)) > 0)
{
if (write(fd_new, buf, len) != len)
{
printf("can not write %s\n", argv[2]);
return -1;
}
}
/* 5. 关闭文件 */
close(fd_old);
close(fd_new);
return 0;
}
2.2 不是通用的函数
有些函数不是通用的函数:ioctl/mmap。示例代码如下:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
/*
* ./copy 1.txt 2.txt
* argc = 3
* argv[0] = "./copy"
* argv[1] = "1.txt"
* argv[2] = "2.txt"
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd_old, fd_new;
struct stat stat;
char *buf;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 3)
{
printf("Usage: %s <old-file> <new-file>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开老文件 */
fd_old = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (fd_old == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 3. 确定老文件的大小 */
if (fstat(fd_old, &stat) == -1)
{
printf("can not get stat of file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 4. 映射老文件 */
buf = mmap(NULL, stat.st_size, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd_old, 0);
if (buf == MAP_FAILED)
{
printf("can not mmap file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 5. 创建新文件 */
fd_new = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH);
if (fd_new == -1)
{
printf("can not creat file %s\n", argv[2]);
return -1;
}
/* 6. 写新文件 */
if (write(fd_new, buf, stat.st_size) != stat.st_size)
{
printf("can not write %s\n", argv[2]);
return -1;
}
/* 7. 关闭文件 */
close(fd_old);
close(fd_new);
return 0;
}
3 系统调用怎么进入内核
4 内核的sys_open、sys_read会做什么
参考资料:





 本文深入讲解了Linux系统中文件的来源、如何通过通用IO模型访问文件,包括open、read、write等函数的使用,并介绍了非通用函数如ioctl、mmap的应用。同时,探讨了系统调用如何进入内核及内核中sys_open、sys_read的工作原理。
本文深入讲解了Linux系统中文件的来源、如何通过通用IO模型访问文件,包括open、read、write等函数的使用,并介绍了非通用函数如ioctl、mmap的应用。同时,探讨了系统调用如何进入内核及内核中sys_open、sys_read的工作原理。

















 2694
2694

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








