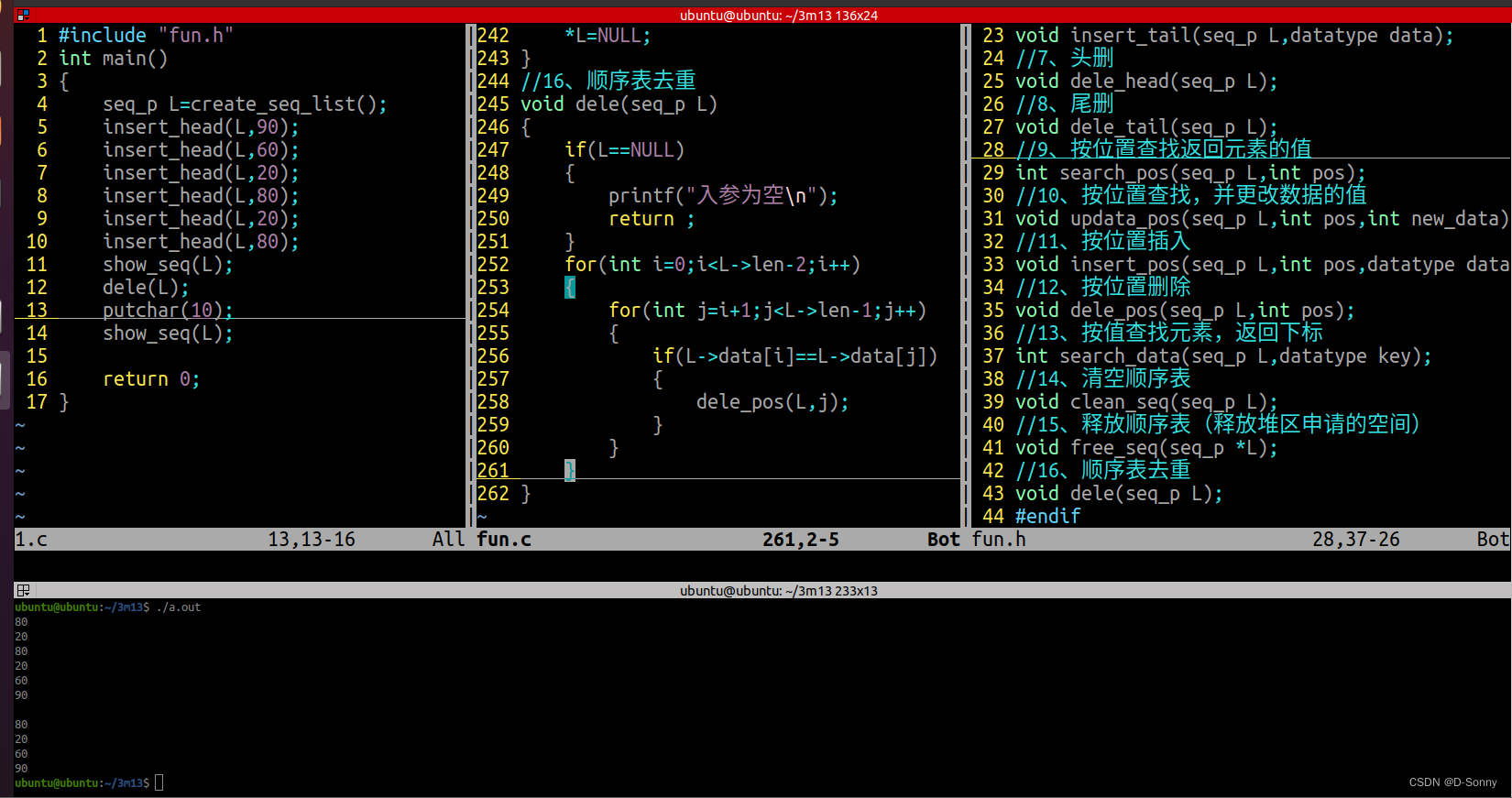
顺序表去重
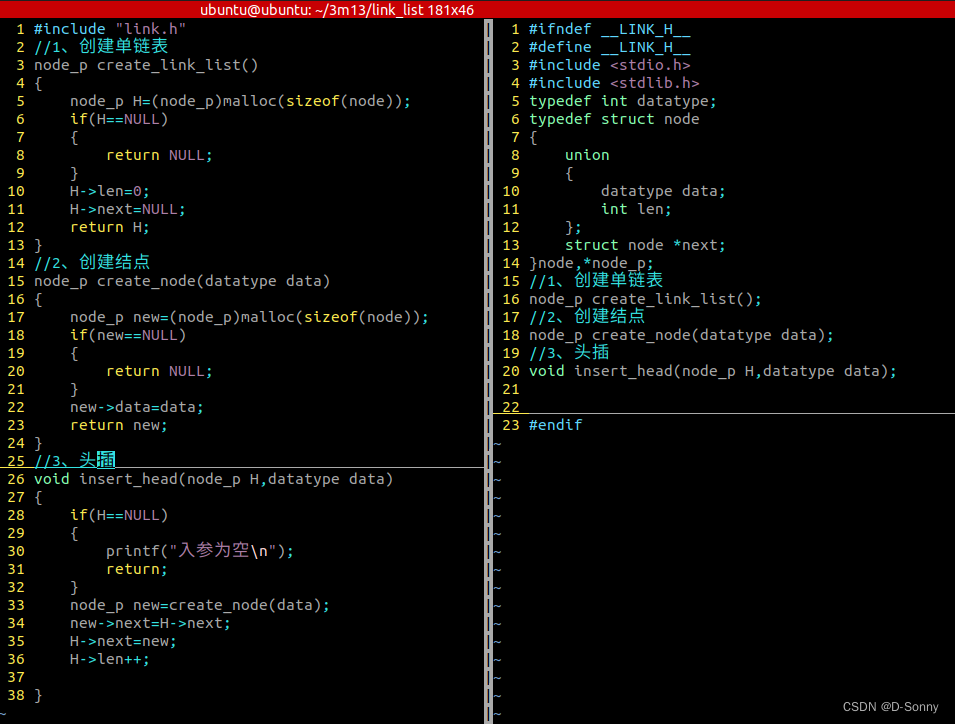
链表创建、结点创建、单向链表的头插
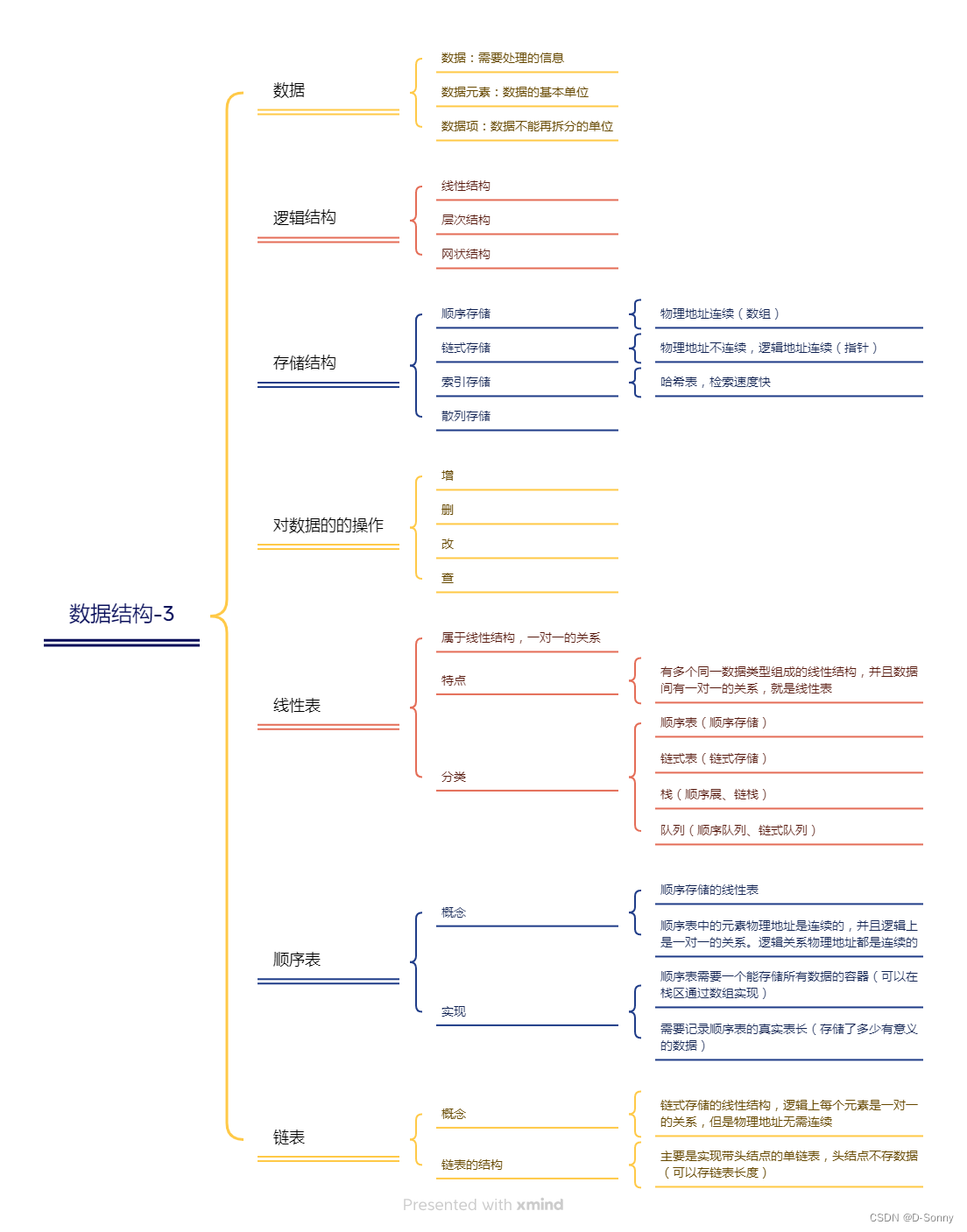
#ifndef __FUN_H__
#define __FUN_H__
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX 7
typedef int datatype;
typedef struct
{
datatype data[MAX];
int len;
}seq_list,*seq_p;
//1、在堆区申请顺序表的空间
seq_p create_seq_list();
//2、判空
int empty_seq(seq_p L);
//3、判满
int full_seq(seq_p L);
//4、头插
void insert_head(seq_p L,datatype data);
//5、输出
void show_seq(seq_p L);
//6、尾插
void insert_tail(seq_p L,datatype data);
//7、头删
void dele_head(seq_p L);
//8、尾删
void dele_tail(seq_p L);
//9、按位置查找返回元素的值
int search_pos(seq_p L,int pos);
//10、按位置查找,并更改数据的值
void updata_pos(seq_p L,int pos,int new_data);
//11、按位置插入
void insert_pos(seq_p L,int pos,datatype data);
//12、按位置删除
void dele_pos(seq_p L,int pos);
//13、按值查找元素,返回下标
int search_data(seq_p L,datatype key);
//14、清空顺序表
void clean_seq(seq_p L);
//15、释放顺序表(释放堆区申请的空间)
void free_seq(seq_p *L);
//16、顺序表去重
void dele(seq_p L);
#endif
#include "fun.h"
int main()
{
seq_p L=create_seq_list();
insert_head(L,90);
insert_head(L,60);
insert_head(L,20);
insert_head(L,80);
insert_head(L,20);
insert_head(L,80);
show_seq(L);
dele(L);
putchar(10);
show_seq(L);
return 0;
}
#include "fun.h"
//1、在堆区申请顺序表的空间
seq_p create_seq_list()
{
seq_p L = (seq_p)malloc(sizeof(seq_list));
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("空间申请失败\n");
return NULL;
}
L->len=0;
return L;
}
//2、判空
int empty_seq(seq_p L)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空\n");
return -1;
}
return L->len ==0? 1:0;
}
//3、判满
int full_seq(seq_p L)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("表已满,请检查\n");
return -1;
}
return L->len ==MAX? 1:0;
}
//4、头插
void insert_head(seq_p L,datatype data)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空,请检查\n");
return ;
}
if(full_seq(L))
{
printf("表已满,不能插入\n");
return;
}
for(int i=L->len-1;i>=0;i--)
{
L->data[i+1]=L->data[i];
}
L->data[0]=data;
L->len++;
}
//5、输出
void show_seq(seq_p L)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空\n");
return;
}
for (int i=0;i<L->len;i++)
{
printf("%d\n",L->data[i]);
}
}
//6、尾插
void insert_tail(seq_p L,datatype data)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空\n");
return;
}
if(full_seq (L))
{
printf("表已满\n");
return;
}
L->data[L->len]=data;
L->len++;
}
//7、头删
void dele_head(seq_p L)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空\n");
return;
}
for(int i=1;i<L->len;i++)
{
L->data[i-1]=L->data[i];
}
L->len--;
}
//8、尾删
void dele_tail(seq_p L)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空\n");
return;
}
if(empty_seq (L))
{
printf("表为空,不需要尾删\n");
return;
}
L->len--;
}
//9、按位置查找返回元素的值
int search_pos(seq_p L,int pos)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空\n");
return -1;
}
if(pos<0||pos>L->len-1)
{
printf("位置不合理,重新输入\n");
return 0;
}
printf("%d\n",L->data[pos]);
return L->data[pos];
}
//10、按位置查找,并更改数据的值
void updata_pos(seq_p L,int pos,int new_data)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空\n");
return;
}
if(pos<0||pos>L->len-1)
{
printf("位置不合理,重新输入\n");
return;
}
L->data[pos]=new_data;
}
//11、按位置插入
void insert_pos(seq_p L,int pos,datatype data)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空\n");
return;
}
if(full_seq(L))
{
printf("表已满\n");
return;
}
if(pos<0||pos>L->len)
{
printf("位置不合理,重新输入\n");
return;
}
for(int i=L->len-1;i>pos-1;i--)
{
L->data[i+1]=L->data[i];
}
L->len++;
L->data[pos]=data;
}
//12、按位置删除
void dele_pos(seq_p L,int pos)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空\n");
return ;
}
if(pos<0||pos>L->len-1)
{
printf("位置不合理,重新输入\n");
return;
}
for(int i=pos+1;i<=L->len-1;i++)
{
L->data[i-1]=L->data[i];
}
L->len--;
/* for(int i=pos;i<L->len-1;i++)
{
L->data[i]=L->data[i+1];
}
L->len--;*/
}
//13、按值查找元素,返回下标
int search_data(seq_p L,datatype key)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空\n");
return -1;
}
for(int i=0;i<L->len;i++)
{
if(key==L->data[i])
{
return i;
}
}
printf("没有该值,请检查\n");
}
//14、清空顺序表
void clean_seq(seq_p L)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空\n");
return;
}
L->len=0;
}
//15、释放顺序表(释放堆区申请的空间)
void free_seq(seq_p *L)
{
if(L==NULL||*L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空,请检查\n");
return;
}
clean_seq(*L);
free(*L);
*L=NULL;
}
//16、顺序表去重
void dele(seq_p L)
{
if(L==NULL)
{
printf("入参为空\n");
return ;
}
for(int i=0;i<L->len-2;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<L->len-1;j++)
{
if(L->data[i]==L->data[j])
{
dele_pos(L,j);
}
}
}
}




















 3632
3632

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








