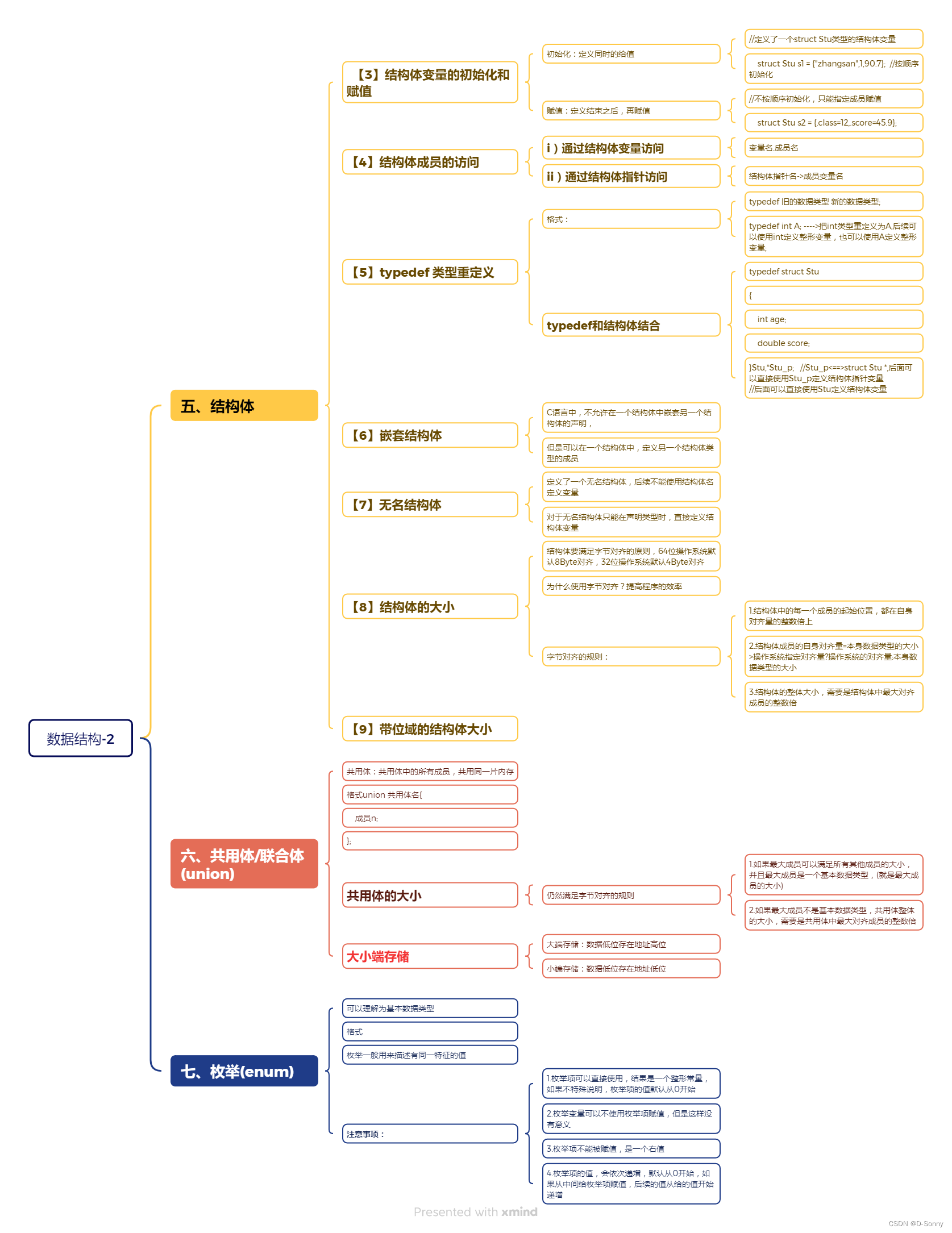
1.求结构体大小
struct data{
char t1; //1
char t2; //1
unsigned short t3;//2 //4
unsigned long t4;//8
};//16
struct data{
char t1;//1 //3
int t2;//4
short t3;//2 //2
};//12
struct s1
{
char c1;//1 //3
int i;//4
char c2;//1 //3
};//12
struct s2
{
char c1;//1
char c2;//1 //2
int i;//4
};//8
typedef struct Test
{
short a;//2 //6
struct
{
int b; //4 //4
double c;//8
char d;//1 //7
}p;//8
int e;//4 //4
}Test;//40
typedef struct Test
{
short a;//2 //6
struct
{
int b;//4 //4
double c[10];//80
char d;//1 //7
};//8
int e;//4 //4
}Test;//112
struct C{
char b;//1 //3
int a;//4
short c;//2 //2
};//12
struct C {
char a;//1
char b[3];//3
char c;//1
};//5
typedef struct
{
int b;//4
char a;//1 //3
long e;//8
char c;//1
float d;//4 //3
double t;//8
}node;//32
2.枚举练习题
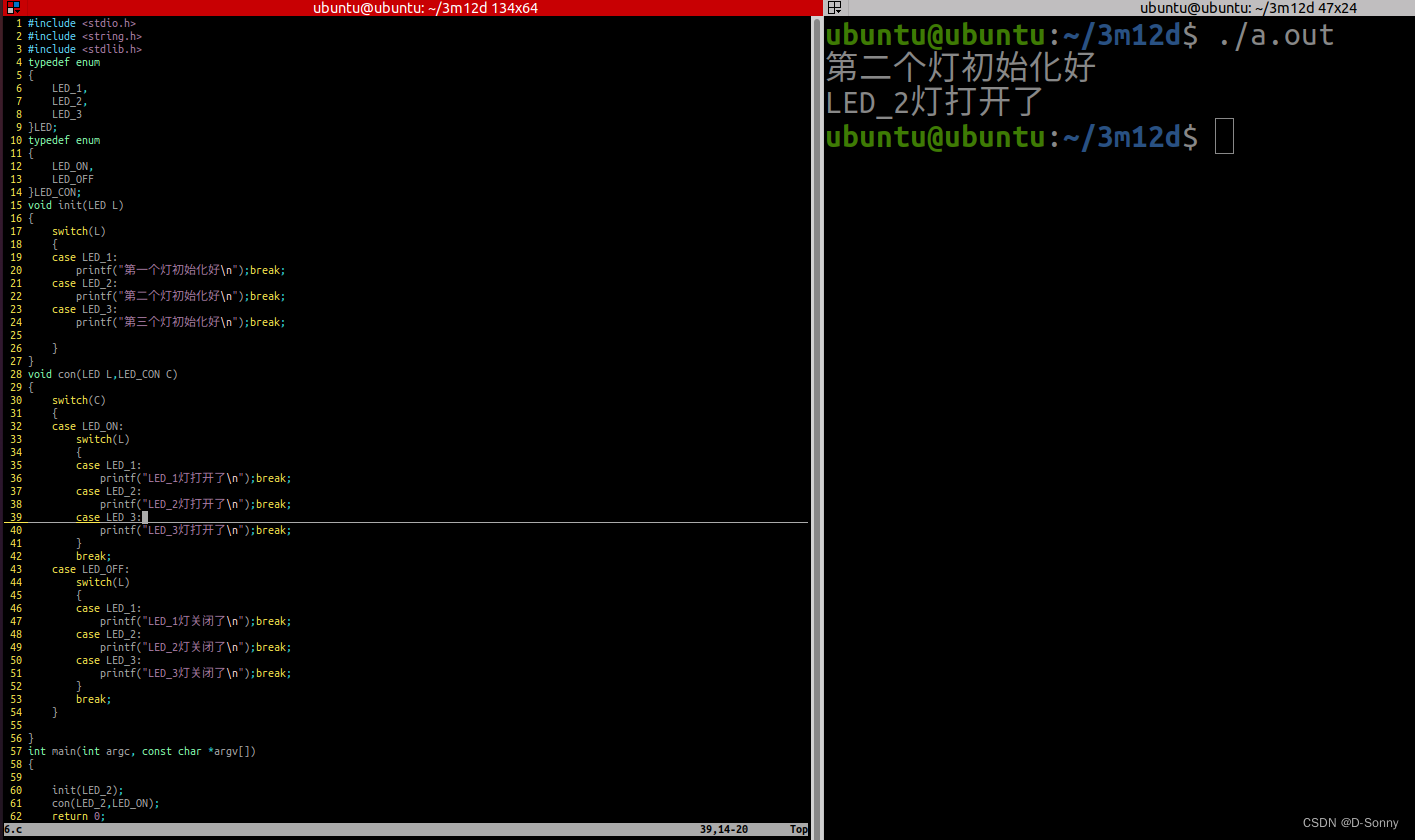
已知有三盏灯,LED_1,LED_2,LED_3,每盏灯有两种状态LED_ON,LED_OFF,现有两个函数void init(enum LED L)灯的初始化函数;void con(enum LED L,enum LED_CON C),在主函数内完成三盏灯的初始化和控制操作。
3.三种验证大小端存储的代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef enum
{
LED_1,
LED_2,
LED_3
}LED;
typedef enum
{
LED_ON,
LED_OFF
}LED_CON;
void init(LED L)
{
switch(L)
{
case LED_1:
printf("第一个灯初始化好\n");break;
case LED_2:
printf("第二个灯初始化好\n");break;
case LED_3:
printf("第三个灯初始化好\n");break;
}
}
void con(LED L,LED_CON C)
{
switch(C)
{
case LED_ON:
switch(L)
{
case LED_1:
printf("LED_1灯打开了\n");break;
case LED_2:
printf("LED_2灯打开了\n");break;
case LED_3:
printf("LED_3灯打开了\n");break;
}
break;
case LED_OFF:
switch(L)
{
case LED_1:
printf("LED_1灯关闭了\n");break;
case LED_2:
printf("LED_2灯关闭了\n");break;
case LED_3:
printf("LED_3灯关闭了\n");break;
}
break;
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
init(LED_2);
con(LED_2,LED_ON);
return 0;
}
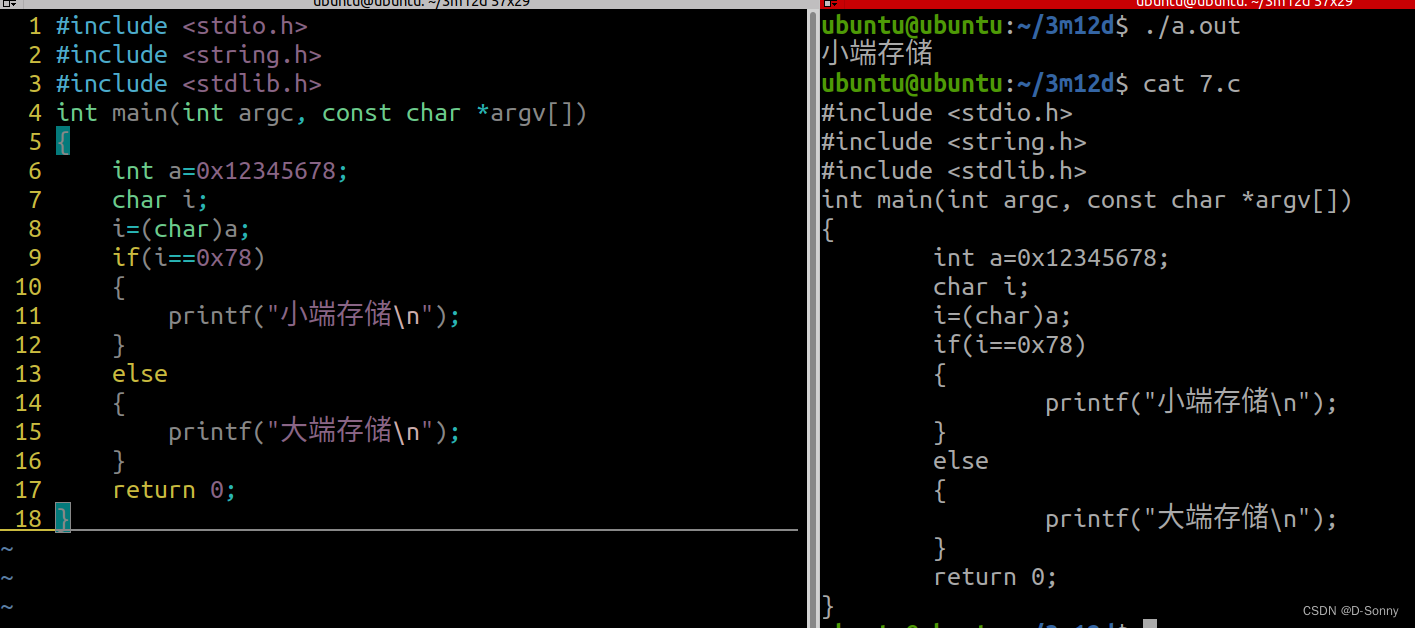
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int a=0x12345678;
char i;
i=(char)a;
if(i==0x78)
{
printf("小端存储\n");
}
else
{
printf("大端存储\n");
}
return 0;
}
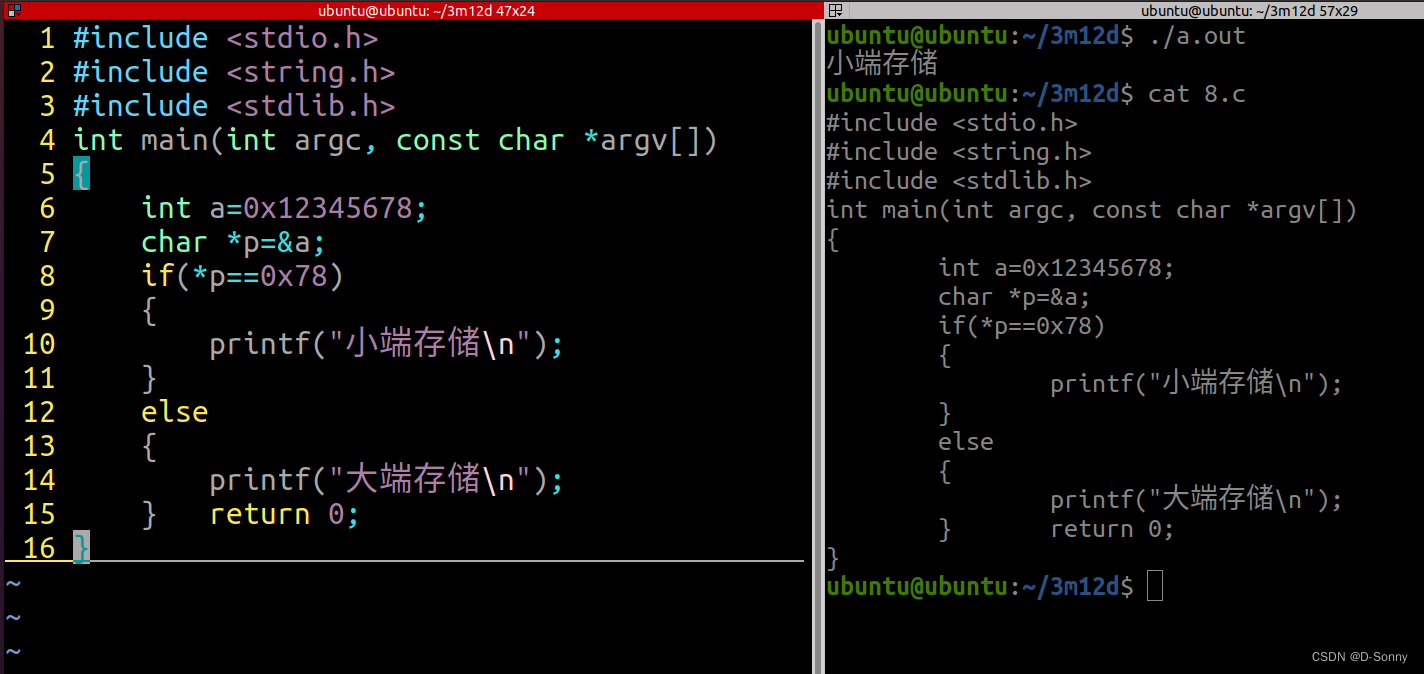
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int a=0x12345678;
char *p=&a;
if(*p==0x78)
{
printf("小端存储\n");
}
else
{
printf("大端存储\n");
}
return 0;
}
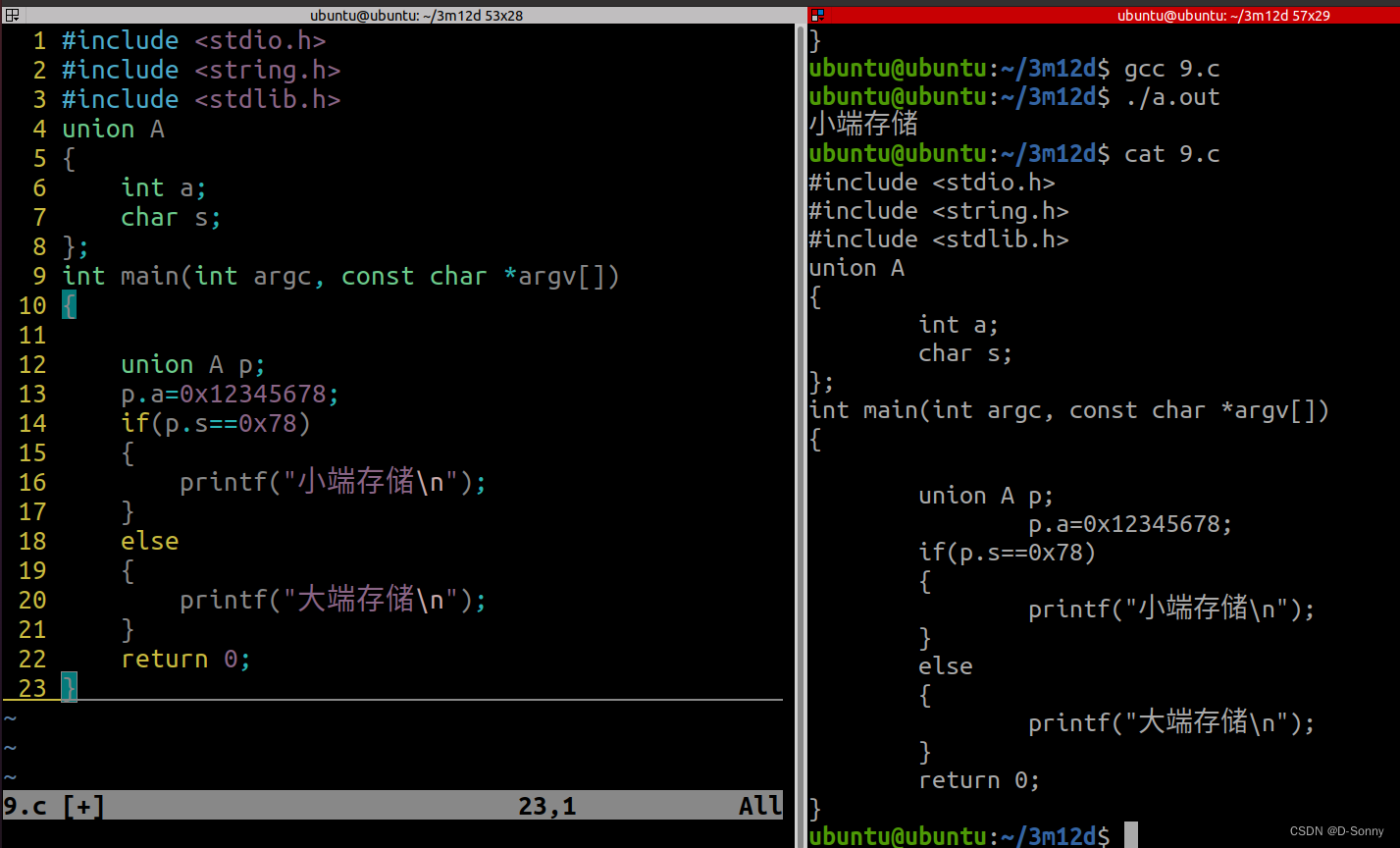
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
union A
{
int a;
char s;
};
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
union A p;
p.a=0x12345678;
if(p.s==0x78)
{
printf("小端存储\n");
}
else
{
printf("大端存储\n");
}
return 0;
}




 文章讲述了C语言中结构体大小计算、枚举类型使用、初始化函数和灯控制,以及验证数据存储(大端/小端)的示例。
文章讲述了C语言中结构体大小计算、枚举类型使用、初始化函数和灯控制,以及验证数据存储(大端/小端)的示例。
















 3632
3632

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








