Hystrix框架简介
Hystrix翻译成中文是“豪猪”的意思。豪猪身上长满了刺,能保护自己不受天敌的伤害,代表了一种防御机制。因此Hystrix 的logo也是定义成了豪猪。

假设有如下场景:
比如我们现在有3个业务调用,分别是查询订单、查询商品、查询用户,且这三个业务请求都是依赖第三方服务—订单服务、商品服务、用户服务。三个服务均是通过RPC调用。当查询订单服务,假如线程阻塞了,这个时候后续有大量的查询订单请求过来,那么容器中的线程数量则会持续增加直至CPU资源耗尽,整个服务对外不可用,集群环境下就是雪崩。
Hystrix核心功能

线程隔离
- 正常情况下,tomcat或其他容器的线程对外提供服务,接收用户请求。
- Hystrix线程隔离的做法是:将tomcat线程处理的任务转交给Hystrix内部的线程去执行,这样tomcat线程就可以去做其他事情了。当Hystrix的线程将任务执行完后,将执行结果返回给tomcat线程。
信号量隔离
信号量的资源隔离只是起到一个开关的作用,例如,服务X的信号量大小为10,那么同时只允许10个tomcat的线程(此处是tomcat的线程,而不是服务X的独立线程池里面的线程)来访问服务X,其他的请求就会被拒绝,从而达到限流保护的作用。
线程隔离和信号量隔离对比


降级策略
- 当请求出现了异常,超时,或者服务不可用的时候,一般情况你会怎么做?返回空,抛异常给调用方还是什么都不做?
- Hystrix可以让你自定义降级策略。当发生异常的时候,返回你事先定义好的策略。比如空对象/默认值
熔断技术
- 一般是指软件系统中,由于某些原因使得服务出现了过载现象,为防止造成整个系统故障,从而采用的一种保护措施,所以很多地方把熔断亦称为过载保护。很多时候刚开始可能只是系统出现了局部的、小规模的故障,然而由于种种原因,故障影响的范围越来越大,最终导致了全局性的后果。
- 如果某个目标服务调用慢或者有大量超时,此时,熔断该服务的调用,对于后续调用请求,不在继续调用目标服务,直接返回,快速释放资源。如果目标服务情况好转则恢复调用。
请求缓存
- 将请求缓存下来,当后续有相同的请求到来的时候,直接返回缓存中的响应,从而避免直接对服务进行调用,增加服务的压力
- 比如根据用户id查询用户信息,根据商品id查询商品信息等,查询全国所有城市的邮编。这类实体的属性不会频繁的变动。
请求合并
将相同类型的请求合并成一次调用,而不是分别调用服务提供方,目的是降低服务提供方的压力。


Hystrix demo
HelloWorld demo:
public class CommandHelloWorld extends HystrixCommand<String> {
private final String name;
public CommandHelloWorld(String name) {
super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ExampleGroup"));
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected String run() {
return "Hello " + name + "!";
}
public static class UnitTest {
@Test
public void testSynchronous() {
assertEquals("Hello World!", new CommandHelloWorld("World").execute());
assertEquals("Hello Bob!", new CommandHelloWorld("Bob").execute());
}
@Test
public void testAsynchronous1() throws Exception {
assertEquals("Hello World!", new CommandHelloWorld("World").queue().get());
assertEquals("Hello Bob!", new CommandHelloWorld("Bob").queue().get());
}
@Test
public void testAsynchronous2() throws Exception {
Future<String> fWorld = new CommandHelloWorld("World").queue();
Future<String> fBob = new CommandHelloWorld("Bob").queue();
assertEquals("Hello World!", fWorld.get());
assertEquals("Hello Bob!", fBob.get());
}
@Test
public void testObservable() throws Exception {
Observable<String> fWorld = new CommandHelloWorld("World").observe();
Observable<String> fBob = new CommandHelloWorld("Bob").observe();
// blocking
assertEquals("Hello World!", fWorld.toBlocking().single());
assertEquals("Hello Bob!", fBob.toBlocking().single());
// non-blocking
// - this is a verbose anonymous inner-class approach and doesn't do assertions
fWorld.subscribe(new Observer<String>() {
@Override
public void onCompleted() {
System.out.println("onCompleted here");
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
@Override
public void onNext(String v) {
System.out.println("onNext: " + v);
}
});
// non-blocking
// - also verbose anonymous inner-class
// - ignore errors and onCompleted signal
fBob.subscribe(new Action1<String>() {
@Override
public void call(String v) {
System.out.println("onNext: " + v);
}
});
// non-blocking
// - using closures in Java 8 would look like this:
// fWorld.subscribe((v) -> {
// System.out.println("onNext: " + v);
// })
// - or while also including error handling
// fWorld.subscribe((v) -> {
// System.out.println("onNext: " + v);
// }, (exception) -> {
// exception.printStackTrace();
// })
// More information about Observable can be found at https://github.com/Netflix/RxJava/wiki/How-To-Use
}
}
}上例中execute()方法是通过同步的方式执行任务;queue()方法是通过异步的防止执行任务。
new Observer<String>() { @Override public void onCompleted() { System.out.println("onCompleted here"); } @Override public void onError(Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } @Override public void onNext(String v) { System.out.println("onNext: " + v); } }
是对任务注册的回调事件。onCompleted是在任务执行完的时候回调,onError是在出现异常时候回调,onNext是获取结果后回调。三者的执行顺序是:onNext/onError完成之后最后回调onCompleted。
线程隔离和信号量隔离的demo:
package com.example.demo.hystrixdemo.isolation;
import com.netflix.hystrix.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
*
* 测试线程池隔离策略
* 设置线程池里的线程数=3,然后循环>3次和<3次,最后查看当前所有线程名称
*
*/
public class HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest extends HystrixCommand<String> {
private final String name;
public HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest(String name) {
// super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ThreadPoolTestGroup"));
super(Setter.withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ThreadPoolTestGroup"))
.andCommandKey(HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey("testCommandKey"))
.andThreadPoolKey(HystrixThreadPoolKey.Factory.asKey("ThreadPoolTest"))
.andCommandPropertiesDefaults(
HystrixCommandProperties.Setter()
.withExecutionTimeoutInMilliseconds(5000)
)
.andThreadPoolPropertiesDefaults(
HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter()
.withCoreSize(3) // 配置线程池里的线程数
)
);
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected String run() throws Exception {
/*---------------会触发fallback的case-------------------*/
// int j = 0;
// while (true) {
// j++;
//// return "a";
// }
// 除零异常
// int i = 1/0;
// 主动抛出异常
// throw new HystrixTimeoutException();
// throw new RuntimeException("this command will trigger fallback");
// throw new Exception("this command will trigger fallback");
// throw new HystrixRuntimeException(FailureType.BAD_REQUEST_EXCEPTION, commandClass, message, cause, fallbackException);
/*---------------不会触发fallback的case-------------------*/
// 被捕获的异常不会触发fallback
// try {
// throw new RuntimeException("this command never trigger fallback");
// } catch(Exception e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// HystrixBadRequestException异常由非法参数或非系统错误引起,不会触发fallback,也不会被计入熔断器
// throw new HystrixBadRequestException("HystrixBadRequestException is never trigger fallback");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + name);
return name;
}
@Override
protected String getFallback() {
return "fallback: " + name;
}
public static class UnitTest {
@Test
public void testSynchronous() throws IOException {
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
try {
// assertEquals("fallback: Hlx", new HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest("Hlx").execute());
// System.out.println("===========" + new HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest("Hlx").execute());
//占有线程池中的线程
Future<String> future = new HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest("get available thread" + i).queue();
//强制阻塞
// System.out.println("future返回:" + future.get());
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("run()抛出HystrixBadRequestException时,被捕获到这里" + e.getCause());
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
// assertEquals("fallback: Hlx", new HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest("Hlx").execute());
System.out.println("===========" + new HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest(" not get available thread" + i).execute());
// Future<String> future = new HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest("Hlx1"+i).queue();
// System.out.println("===========" + future);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("run()抛出HystrixBadRequestException时,被捕获到这里" + e.getCause());
}
}
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2000);
}catch(Exception e) {}
System.out.println("------开始打印现有线程---------");
Map<Thread, StackTraceElement[]> map=Thread.getAllStackTraces();
for (Thread thread : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(thread.getName());
}
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println("thread num: " + map.size());
// int numExecuted = HystrixRequestLog.getCurrentRequest().getAllExecutedCommands().size();
// System.out.println("num executed: " + numExecuted);
}
}
}package com.example.demo.hystrixdemo.isolation;
import com.example.demo.hystrixdemo.HelloWorldHystrixCommand;
import com.netflix.hystrix.*;
import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommandProperties.ExecutionIsolationStrategy;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 测试信号量隔离策略
* 默认执行run()用的是主线程,为了模拟并行执行command,这里我们自己创建多个线程来执行command
* 设置ExecutionIsolationSemaphoreMaxConcurrentRequests为3,意味着信号量最多允许执行run的并发数为3,超过则触发降级,即不执行run而执行getFallback
* 设置FallbackIsolationSemaphoreMaxConcurrentRequests为1,意味着信号量最多允许执行fallback的并发数为1,超过则抛异常fallback execution rejected
*/
public class HystrixCommand4SemaphoreTest extends HystrixCommand<String> {
private final String name;
public HystrixCommand4SemaphoreTest(String name) {
super(Setter.withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("SemaphoreTestGroup"))
.andCommandKey(HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey("SemaphoreTestKey"))
.andThreadPoolKey(HystrixThreadPoolKey.Factory.asKey("SemaphoreTestThreadPoolKey"))
.andCommandPropertiesDefaults( // 配置信号量隔离
HystrixCommandProperties.Setter()
.withExecutionIsolationStrategy(ExecutionIsolationStrategy.SEMAPHORE) // 信号量隔离
.withExecutionIsolationSemaphoreMaxConcurrentRequests(3)
.withFallbackIsolationSemaphoreMaxConcurrentRequests(1)
)
// 设置了信号量隔离后,线程池配置将变无效
// .andThreadPoolPropertiesDefaults(
// HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter()
// .withCoreSize(13) // 配置线程池里的线程数
// )
);
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected String run() throws Exception {
return "run(): name=" + name + ",线程名是" + Thread.currentThread().getName();
}
@Override
protected String getFallback() {
return "getFallback(): name=" + name + ",线程名是" + Thread.currentThread().getName();
}
public static class UnitTest {
@Test
public void testSynchronous() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int j = i;
// 自主创建线程来执行command,创造并发场景
// @Override
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
// 这里执行两类command:HystrixCommand4SemaphoreTest设置了信号量隔离、HelloWorldHystrixCommand未设置信号量
System.out.println("-----------" + new HelloWorldHystrixCommand("HelloWorldHystrixCommand" + j).execute());
System.out.println("===========" + new HystrixCommand4SemaphoreTest("HystrixCommand4SemaphoreTest" + j).execute()); // 被信号量拒绝的线程从这里抛出异常
System.out.println("-----------" + new HelloWorldHystrixCommand("HelloWorldHystrixCommand" + j).execute()); // 被信号量拒绝的线程不能执行到这里
});
thread.start();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// try {
// TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2000);
// }catch(Exception e) {}
// System.out.println("------开始打印现有线程---------");
// Map<Thread, StackTraceElement[]> map = Thread.getAllStackTraces();
// for (Thread thread : map.keySet()) {
// System.out.println(thread.getName());
// }
// System.out.println("thread num: " + map.size());
// System.in.read();
Thread.sleep(4000);
}
}
}降级策略demo:
/**
*
* 以下四种情况将触发getFallback调用:
* 1)run()方法抛出非HystrixBadRequestException异常
* 2)run()方法调用超时
* 3)熔断器开启拦截调用
* 4)线程池/队列/信号量是否跑满
*
* 实现getFallback()后,执行命令时遇到以上4种情况将被fallback接管,不会抛出异常或其他
*/
public class HystrixFallback4ExceptionTest extends HystrixCommand<String> {
private final String name;
public HystrixFallback4ExceptionTest(String name) {
super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("FallbackGroup"));
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected String run() throws Exception {
/*---------------会触发fallback的case-------------------*/
// 无限循环,实际上属于超时
// int j = 0;
// while (true) {
// j++;
// }
// 除零异常
// int i = 1/0;
// 主动抛出异常
// throw new HystrixTimeoutException();
// throw new RuntimeException("this command will trigger fallback");
// throw new Exception("this command will trigger fallback");
// throw new HystrixRuntimeException(FailureType.BAD_REQUEST_EXCEPTION, commandClass, message, cause, fallbackException);
/*---------------不会触发fallback的case-------------------*/
// 被捕获的异常不会触发fallback
// try {
// throw new RuntimeException("this command never trigger fallback");
// } catch(Exception e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// HystrixBadRequestException异常由非法参数或非系统错误引起,不会触发fallback,也不会被计入熔断器
throw new HystrixBadRequestException("HystrixBadRequestException is never trigger fallback");
// return name;
}
@Override
protected String getFallback() {
return "fallback: " + name;
}
public static class UnitTest {
@Test
public void testSynchronous() throws IOException {
try {
System.out.println(new HystrixFallback4ExceptionTest("ExceptionTest").execute());
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("run()抛出HystrixBadRequestException时,会被捕获到这里" + e.getCause());
}
// System.in.read();
}
}
}
package com.example.demo.hystrixdemo.fallback;
import com.netflix.hystrix.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
*
* 设置线程池里的线程数=3,然后循环>3次和<3次,最后查看当前所有线程名称
*
*/
public class HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest extends HystrixCommand<String> {
private final String name;
public HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest(String name) {
// super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ThreadPoolTestGroup"));
super(Setter.withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("ThreadPoolTestGroup"))
.andCommandKey(HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey("testCommandKey"))
.andThreadPoolKey(HystrixThreadPoolKey.Factory.asKey("ThreadPoolTest"))
.andCommandPropertiesDefaults(
HystrixCommandProperties.Setter()
.withExecutionTimeoutInMilliseconds(5000)
)
.andThreadPoolPropertiesDefaults(
HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter()
.withCoreSize(3) // 配置线程池里的线程数
)
);
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected String run() throws Exception {
/*---------------会触发fallback的case-------------------*/
// int j = 0;
// while (true) {
// j++;
//// return "a";
// }
// 除零异常
// int i = 1/0;
// 主动抛出异常
// throw new HystrixTimeoutException();
// throw new RuntimeException("this command will trigger fallback");
// throw new Exception("this command will trigger fallback");
// throw new HystrixRuntimeException(FailureType.BAD_REQUEST_EXCEPTION, commandClass, message, cause, fallbackException);
/*---------------不会触发fallback的case-------------------*/
// 被捕获的异常不会触发fallback
// try {
// throw new RuntimeException("this command never trigger fallback");
// } catch(Exception e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// HystrixBadRequestException异常由非法参数或非系统错误引起,不会触发fallback,也不会被计入熔断器
// throw new HystrixBadRequestException("HystrixBadRequestException is never trigger fallback");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + name);
return name;
}
@Override
protected String getFallback() {
return "fallback: " + name;
}
public static class UnitTest {
@Test
public void testSynchronous() throws IOException {
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
try {
// assertEquals("fallback: Hlx", new HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest("Hlx").execute());
// System.out.println("===========" + new HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest("Hlx").execute());
//占有线程池中的线程
Future<String> future = new HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest("get available thread" + i).queue();
//强制阻塞
// System.out.println("future返回:" + future.get());
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("run()抛出HystrixBadRequestException时,被捕获到这里" + e.getCause());
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
// assertEquals("fallback: Hlx", new HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest("Hlx").execute());
System.out.println("===========" + new HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest(" not get available thread" + i).execute());
// Future<String> future = new HystrixCommand4ThreadPoolTest("not get available thread" + i).queue();
// System.out.println("===========" + future.get());
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("run()抛出HystrixBadRequestException时,被捕获到这里" + e.getCause());
}
}
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2000);
}catch(Exception e) {}
System.out.println("------开始打印现有线程---------");
Map<Thread, StackTraceElement[]> map=Thread.getAllStackTraces();
for (Thread thread : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(thread.getName());
}
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println("thread num: " + map.size());
// int numExecuted = HystrixRequestLog.getCurrentRequest().getAllExecutedCommands().size();
// System.out.println("num executed: " + numExecuted);
}
}
}package com.example.demo.hystrixdemo.fallback;
import com.netflix.hystrix.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
/**
*
* CircuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold设置为3,意味着10s内请求超过3次就触发熔断器
* run()中无限循环使命令超时进入fallback,执行3次run后,将被熔断,进入降级,即不进入run()而直接进入fallback
* 如果未熔断,但是threadpool被打满,仍然会降级,即不进入run()而直接进入fallback
*/
public class HystrixCommand4CircuitBreakerTest extends HystrixCommand<String> {
private final String name;
public HystrixCommand4CircuitBreakerTest(String name) {
super(Setter.withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("CircuitBreakerTestGroup"))
.andCommandKey(HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey("CircuitBreakerTestKey"))
.andThreadPoolKey(HystrixThreadPoolKey.Factory.asKey("CircuitBreakerTest"))
.andThreadPoolPropertiesDefaults( // 配置线程池
HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter()
.withCoreSize(200) // 配置线程池里的线程数,设置足够多线程,以防未熔断却打满threadpool
)
.andCommandPropertiesDefaults( // 配置熔断器
HystrixCommandProperties.Setter()
.withCircuitBreakerEnabled(true)
.withCircuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold(3)
.withCircuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage(80)
// .withCircuitBreakerForceOpen(true) // 置为true时,所有请求都将被拒绝,直接到fallback
// .withCircuitBreakerForceClosed(true) // 置为true时,将忽略错误
// .withExecutionIsolationStrategy(ExecutionIsolationStrategy.SEMAPHORE) // 信号量隔离
// .withExecutionTimeoutInMilliseconds(5000)
)
);
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected String run() throws Exception {
System.out.println("running run():" + name);
int num = Integer.valueOf(name);
if(num % 2 == 0 && num < 10) { // 直接返回
return name;
} else { // 无限循环模拟超时
int j = 0;
while (true) {
j++;
}
}
// return name;
}
@Override
protected String getFallback() {
return "CircuitBreaker fallback: " + name;
}
public static class UnitTest {
@Test
public void testSynchronous() throws IOException {
for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
try {
System.out.println("===========" + new HystrixCommand4CircuitBreakerTest(String.valueOf(i)).execute());
// try {
// TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);
// }catch(Exception e) {}
// Future<String> future = new HystrixCommand4CircuitBreakerTest("Hlx"+i).queue();
// System.out.println("===========" + future);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("run()抛出HystrixBadRequestException时,被捕获到这里" + e.getCause());
}
}
System.out.println("------开始打印现有线程---------");
Map<Thread, StackTraceElement[]> map=Thread.getAllStackTraces();
for (Thread thread : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(thread.getName());
}
System.out.println("thread num: " + map.size());
System.in.read();
}
}
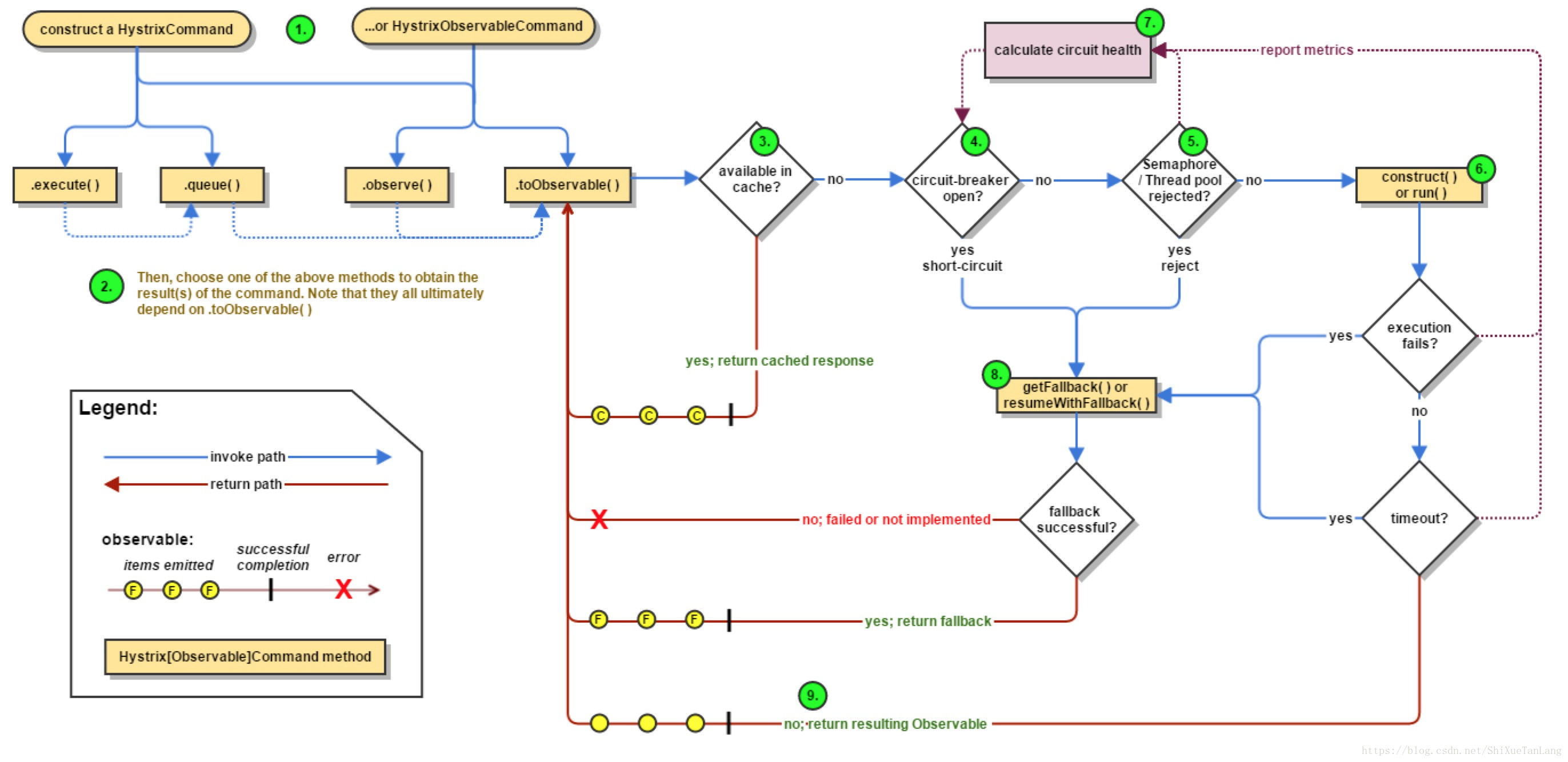
}Hystrix执行流程图:
请求合并的demo:
package com.example.demo.hystrixdemo.collapsing;
import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCollapser;
import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommand;
import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommandGroupKey;
import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommandKey;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Sample {@link HystrixCollapser} that automatically batches multiple requests to execute()/queue()
* into a single {@link HystrixCommand} execution for all requests within the defined batch (time or size).
*/
public class HelloWorldHystrixCollapser extends HystrixCollapser<List<String>, String, Integer> {
private final Integer key;
public HelloWorldHystrixCollapser(Integer key) {
this.key = key;
}
@Override
public Integer getRequestArgument() {
return key;
}
// 创建一个批量请求命令
@Override
protected HystrixCommand<List<String>> createCommand(final Collection<CollapsedRequest<String, Integer>> requests) {
return new BatchCommand(requests); // 把批量请求传给command类
}
// 把批量请求的结果和对应的请求一一对应起来
@Override
protected void mapResponseToRequests(List<String> batchResponse, Collection<CollapsedRequest<String, Integer>> requests) {
int count = 0;
for (CollapsedRequest<String, Integer> request : requests) {
request.setResponse(batchResponse.get(count++));
}
}
// command类
private static final class BatchCommand extends HystrixCommand<List<String>> {
private final Collection<CollapsedRequest<String, Integer>> requests;
private BatchCommand(Collection<CollapsedRequest<String, Integer>> requests) {
super(Setter.withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("CollepsingGroup"))
.andCommandKey(HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey("CollepsingKey")));
this.requests = requests;
}
@Override
protected List<String> run() {
ArrayList<String> response = new ArrayList<String>();
// 处理每个请求,返回结果
for (CollapsedRequest<String, Integer> request : requests) {
// artificial response for each argument received in the batch
response.add("ValueForKey: " + request.getArgument() + " thread:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
return response;
}
}
}package com.example.demo.hystrixdemo.collapsing;
import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixEventType;
import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixInvokableInfo;
import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixRequestLog;
import com.netflix.hystrix.strategy.concurrency.HystrixRequestContext;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue;
/**
* 相邻两个请求可以自动合并的前提是两者足够“近”:启动执行的间隔时间足够小,默认10ms
*
*/
public class HystrixCommand4RequestCollapsingTest {
@Test
public void testCollapser() throws Exception {
HystrixRequestContext context = HystrixRequestContext.initializeContext();
try {
Future<String> f1 = new HelloWorldHystrixCollapser(1).queue();
Future<String> f2 = new HelloWorldHystrixCollapser(2).queue();
// System.out.println(new HelloWorldHystrixCollapser(1).execute()); // 这条很可能会合并到f1和f2的批量请求中
// System.out.println(new HelloWorldHystrixCollapser(1).execute()); // 由于上面有IO打印,这条很可能不会合并到f1和f2的批量请求中
Future<String> f3 = new HelloWorldHystrixCollapser(3).queue();
Future<String> f4 = new HelloWorldHystrixCollapser(4).queue();
Future<String> f5 = new HelloWorldHystrixCollapser(5).queue();
// f5和f6,如果sleep时间够小则会合并,如果sleep时间够大则不会合并,默认10ms
// TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
Future<String> f6 = new HelloWorldHystrixCollapser(6).queue();
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + " : " + f1.get());
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + " : " + f2.get());
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + " : " + f3.get());
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + " : " + f4.get());
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + " : " + f5.get());
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + " : " + f6.get());
// 下面3条都不在一个批量请求中
// System.out.println(new HelloWorldHystrixCollapser(7).execute());
// System.out.println(new HelloWorldHystrixCollapser(8).queue().get());
// System.out.println(new HelloWorldHystrixCollapser(9).queue().get());
// note:numExecuted表示共有几个命令执行,1个批量多命令请求算一个,这个实际值可能比代码写的要多,因为due to non-determinism of scheduler since this example uses the real timer
int numExecuted = HystrixRequestLog.getCurrentRequest().getAllExecutedCommands().size();
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + " : " + "num executed: " + numExecuted);
int numLogs = 0;
for (HystrixInvokableInfo<?> command : HystrixRequestLog.getCurrentRequest().getAllExecutedCommands()) {
numLogs++;
// assert the command is the one we're expecting
// assertEquals("CollepsingKey", command.getCommandKey().name());
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() + " : " + command.getCommandKey().name() + " => command.getExecutionEvents(): " + command.getExecutionEvents());
// confirm that it was a COLLAPSED command execution
// assertTrue(command.getExecutionEvents().contains(HystrixEventType.COLLAPSED));
assertTrue(command.getExecutionEvents().contains(HystrixEventType.SUCCESS));
}
assertEquals(numExecuted, numLogs);
} finally {
context.shutdown();
}
}
}hystrix支持N个请求自动合并为一个请求,这个功能在有网络交互的场景下尤其有用,比如每个请求都要网络访问远程资源,如果把请求合并为一个,将使多次网络交互变成一次,极大节省开销。重要一点,两个请求能自动合并的前提是两者足够“近”,即两者启动执行的间隔时长要足够小,默认为10ms,即超过10ms将不自动合并。
以demo为例,我们连续发起多个queue请求,依次返回f1~f6共6个Future对象,根据打印结果可知f1~f5同处一个线程,说明这5个请求被合并了,而f6由另一个线程执行,这是因为f5和f6中间隔了一个sleep,超过了合并要求的最大间隔时长。请求熔断的demo:
package com.example.demo.hystrixdemo.circuitbreak;
import com.netflix.hystrix.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
/**
*
* CircuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold设置为3,意味着10s内请求超过3次就触发熔断器
* run()中无限循环使命令超时进入fallback,执行3次run后,将被熔断,进入降级,即不进入run()而直接进入fallback
* 如果未熔断,但是threadpool被打满,仍然会降级,即不进入run()而直接进入fallback
*/
public class HystrixCommand4CircuitBreakerTest extends HystrixCommand<String> {
private final String name;
public HystrixCommand4CircuitBreakerTest(String name) {
super(Setter.withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("CircuitBreakerTestGroup"))
.andCommandKey(HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey("CircuitBreakerTestKey"))
.andThreadPoolKey(HystrixThreadPoolKey.Factory.asKey("CircuitBreakerTest"))
.andThreadPoolPropertiesDefaults( // 配置线程池
HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter()
.withCoreSize(200) // 配置线程池里的线程数,设置足够多线程,以防未熔断却打满threadpool
)
.andCommandPropertiesDefaults( // 配置熔断器
HystrixCommandProperties.Setter()
.withCircuitBreakerEnabled(true)
.withCircuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold(3)
.withCircuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage(80)
// .withCircuitBreakerForceOpen(true) // 置为true时,所有请求都将被拒绝,直接到fallback
// .withCircuitBreakerForceClosed(true) // 置为true时,将忽略错误
// .withExecutionIsolationStrategy(ExecutionIsolationStrategy.SEMAPHORE) // 信号量隔离
// .withExecutionTimeoutInMilliseconds(5000)
)
);
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected String run() throws Exception {
System.out.println("running run():" + name);
int num = Integer.valueOf(name);
if(num % 2 == 0 && num < 10) { // 直接返回
return name;
} else { // 无限循环模拟超时
int j = 0;
while (true) {
j++;
}
}
// return name;
}
@Override
protected String getFallback() {
return "CircuitBreaker fallback: " + name;
}
public static class UnitTest {
@Test
public void testSynchronous() throws IOException {
for(int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
try {
System.out.println("===========" + new HystrixCommand4CircuitBreakerTest(String.valueOf(i)).execute());
// try {
// TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);
// }catch(Exception e) {}
// Future<String> future = new HystrixCommand4CircuitBreakerTest("Hlx"+i).queue();
// System.out.println("===========" + future);
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("run()抛出HystrixBadRequestException时,被捕获到这里" + e.getCause());
}
}
System.out.println("------开始打印现有线程---------");
Map<Thread, StackTraceElement[]> map=Thread.getAllStackTraces();
for (Thread thread : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(thread.getName());
}
System.out.println("thread num: " + map.size());
}
}
}以demo为例,我们通过withCircuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold配置10s内请求数超过3个时熔断器开始生效,通过withCircuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage配置错误比例>80%时开始熔断,然后for循环执行execute()触发run(),在run()里,如果name是小于10的偶数则正常返回,否则超时,通过多次循环后,超时请求占所有请求的比例将大于80%,就会看到后续请求都不进入run()而是进入getFallback(),因为不再打印"running run():" + name了。
请求缓存的demo:
package com.example.demo.hystrixdemo.cache;
import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommand;
import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommandGroupKey;
import com.netflix.hystrix.strategy.concurrency.HystrixRequestContext;
import org.junit.Test;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertFalse;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue;
/**
* cache只有同在一个context中才生效
* 通过HystrixRequestContext.initializeContext()初始化context,通过shutdown()关闭context
*/
public class HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest extends HystrixCommand<Boolean> {
private final int value;
private final String value1;
protected HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest(int value, String value1) {
super(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("RequestCacheCommandGroup"));
this.value = value;
this.value1 = value1;
}
// 返回结果是cache的value
@Override
protected Boolean run() {
return value == 0 || value % 2 == 0;
}
// 构建cache的key
@Override
protected String getCacheKey() {
return String.valueOf(value) + value1;
}
public static class UnitTest {
@Test
public void testWithoutCacheHits() {
HystrixRequestContext context = HystrixRequestContext.initializeContext();
try {
assertTrue(new HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest(2,"HLX").execute());
assertFalse(new HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest(1,"HLX").execute());
assertTrue(new HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest(0,"HLX").execute());
assertTrue(new HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest(58672,"HLX").execute());
} finally {
context.shutdown();
}
}
@Test
public void testWithCacheHits() {
HystrixRequestContext context = HystrixRequestContext.initializeContext();
try {
HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest command2a = new HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest(2,"HLX");
HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest command2b = new HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest(2,"HLX");
HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest command2c = new HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest(2,"HLX1");
assertTrue(command2a.execute());
// this is the first time we've executed this command with the value of "2" so it should not be from cache
assertFalse(command2a.isResponseFromCache());
assertTrue(command2b.execute());
// this is the second time we've executed this command with the same value so it should return from cache
assertTrue(command2b.isResponseFromCache());
assertTrue(command2c.execute());
assertFalse(command2c.isResponseFromCache());
} finally {
context.shutdown();
}
// start a new request context
context = HystrixRequestContext.initializeContext();
try {
HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest command3a = new HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest(2,"HLX");
HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest command3b = new HystrixCommand4RequestCacheTest(2,"HLX");
assertTrue(command3a.execute());
// this is a new request context so this should not come from cache
assertFalse(command3a.isResponseFromCache());
// 从command3a.execute()执行中得到的cache
command3b.execute();
assertTrue(command3b.isResponseFromCache());
} finally {
context.shutdown();
}
}
}
}
以demo的testWithCacheHits()为例,command2a、command2b、command2c同处一个context,前两者的cache key都是2HLX(见getCacheKey()),所以command2a执行完后把结果缓存,
command2b执行时就不走run()而是直接从缓存中取结果了,而command2c的cache key是2HLX1,无法从缓存中取结果。此外,通过isResponseFromCache()可检查返回结果是否来自缓存。
源码地址:
https://github.com/PerseveranceForever/hystrix_demo.git





 本文详细介绍了Hystrix框架的功能特性,包括线程隔离、信号量隔离、降级策略、熔断技术、请求缓存、请求合并等。并通过具体代码示例展示了这些特性的使用方法。
本文详细介绍了Hystrix框架的功能特性,包括线程隔离、信号量隔离、降级策略、熔断技术、请求缓存、请求合并等。并通过具体代码示例展示了这些特性的使用方法。
















 2142
2142

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








