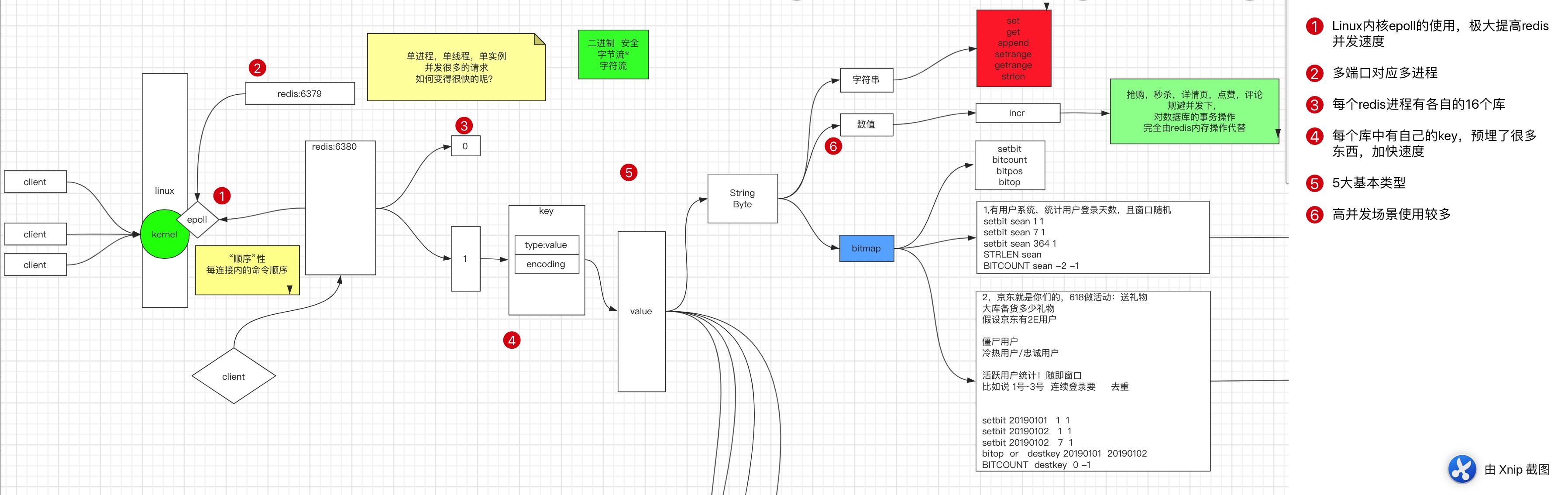
Redis的使用&redis-Value-string类型
redis-cli 进入客户端
[root@localhost ~]# redis-cli --help & redis-cli -h
redis-cli 6.0.6
Usage: redis-cli [OPTIONS] [cmd [arg [arg ...]]]
-h <hostname> Server hostname (default: 127.0.0.1).
-p <port> Server port (default: 6379).
-s <socket> Server socket (overrides hostname and port).
-a <password> Password to use when connecting to the server.
You can also use the REDISCLI_AUTH environment
variable to pass this password more safely
(if both are used, this argument takes predecence).
--user <username> Used to send ACL style 'AUTH username pass'. Needs -a.
--pass <password> Alias of -a for consistency with the new --user option.
--askpass Force user to input password with mask from STDIN.
If this argument is used, '-a' and REDISCLI_AUTH
environment variable will be ignored.
-u <uri> Server URI.
-r <repeat> Execute specified command N times.
-i <interval> When -r is used, waits <interval> seconds per command.
It is possible to specify sub-second times like -i 0.1.
-n <db> Database number.
-3 Start session in RESP3 protocol mode.
-x Read last argument from STDIN.
-d <delimiter> Multi-bulk delimiter in for raw formatting (default: \n).
-c Enable cluster mode (follow -ASK and -MOVED redirections).
--raw Use raw formatting for replies (default when STDOUT is
not a tty).
--no-raw Force formatted output even when STDOUT is not a tty.
--csv Output in CSV format.
--stat Print rolling stats about server: mem, clients, ...
--latency Enter a special mode continuously sampling latency.
If you use this mode in an interactive session it runs
forever displaying real-time stats. Otherwise if --raw or
--csv is specified, or if you redirect the output to a non
TTY, it samples the latency for 1 second (you can use
-i to change the interval), then produces a single output
and exits.
--latency-history Like --latency but tracking latency changes over time.
Default time interval is 15 sec. Change it using -i.
--latency-dist Shows latency as a spectrum, requires xterm 256 colors.
Default time interval is 1 sec. Change it using -i.
--lru-test <keys> Simulate a cache workload with an 80-20 distribution.
--replica Simulate a replica showing commands received from the master.
--rdb <filename> Transfer an RDB dump from remote server to local file.
--pipe Transfer raw Redis protocol from stdin to server.
--pipe-timeout <n> In --pipe mode, abort with error if after sending all data.
no reply is received within <n> seconds.
Default timeout: 30. Use 0 to wait forever.
--bigkeys Sample Redis keys looking for keys with many elements (complexity).
--memkeys Sample Redis keys looking for keys consuming a lot of memory.
--memkeys-samples <n> Sample Redis keys looking for keys consuming a lot of memory.
And define number of key elements to sample
--hotkeys Sample Redis keys looking for hot keys.
only works when maxmemory-policy is *lfu.
--scan List all keys using the SCAN command.
--pattern <pat> Useful with --scan to specify a SCAN pattern.
--intrinsic-latency <sec> Run a test to measure intrinsic system latency.
The test will run for the specified amount of seconds.
--eval <file> Send an EVAL command using the Lua script at <file>.
--ldb Used with --eval enable the Redis Lua debugger.
--ldb-sync-mode Like --ldb but uses the synchronous Lua debugger, in
this mode the server is blocked and script changes are
not rolled back from the server memory.
--cluster <command> [args...] [opts...]
Cluster Manager command and arguments (see below).
--verbose Verbose mode.
--no-auth-warning Don't show warning message when using password on command
line interface.
--help Output this help and exit.
--version Output version and exit.
Cluster Manager Commands:
Use --cluster help to list all available cluster manager commands.
Examples:
cat /etc/passwd | redis-cli -x set mypasswd
redis-cli get mypasswd
redis-cli -r 100 lpush mylist x
redis-cli -r 100 -i 1 info | grep used_memory_human:
redis-cli --eval myscript.lua key1 key2 , arg1 arg2 arg3
redis-cli --scan --pattern '*:12345*'
(Note: when using --eval the comma separates KEYS[] from ARGV[] items)
When no command is given, redis-cli starts in interactive mode.
Type "help" in interactive mode for information on available commands
and settings.
常用:
-h不加参数 显示help内容-h x.x.x.x连接指定ip参数-p xxx指定端口-a使用密码-n选择库名—raw触发当前编码集,进行格式化
库表结构
- 库:Redis 默认16个库
-n指定连接的库- 默认为
0号库 - select x 进行切换库
help使用
127.0.0.1:6379> help
redis-cli 6.0.6
To get help about Redis commands type:
"help @<group>" to get a list of commands in <group>
"help <command>" for help on <command>
"help <tab>" to get a list of possible help topics
"quit" to exit
To set redis-cli preferences:
":set hints" enable online hints
":set nohints" disable online hints
Set your preferences in ~/.redisclirc
help @命令组
-
例如help @generic
127.0.0.1:6379> help @generic DEL key [key ...] summary: Delete a key since: 1.0.0 DUMP key summary: Return a serialized version of the value stored at the specified key. since: 2.6.0 EXISTS key [key ...] summary: Determine if a key exists since: 1.0.0 EXPIRE key seconds summary: Set a key's time to live in seconds since: 1.0.0 EXPIREAT key timestamp summary: Set the expiration for a key as a UNIX timestamp since: 1.2.0 KEYS pattern summary: Find all keys matching the given pattern since: 1.0.0 MIGRATE host port key| destination-db timeout [COPY] [REPLACE] [AUTH password] [KEYS key] summary: Atomically transfer a key from a Redis instance to another one. since: 2.6.0 MOVE key db summary: Move a key to another database since: 1.0.0 OBJECT subcommand [arguments [arguments ...]] summary: Inspect the internals of Redis objects since: 2.2.3 -
help tab可以补全
-
keys * 显示所有key
-
FLUSHDB 清库,测试环境下使用
127.0.0.1:6379> keys * 1) "k380" 2) "k380:1" 127.0.0.1:6379> FlushDB OK 127.0.0.1:6379> keys * (empty array) 127.0.0.1:6379>
Value- 5种基本类型之字符串
1. 通用命令
help @
string命令组
Set
设置值
# 查看set帮助
127.0.0.1:6379> help set
SET key value [EX seconds|PX milliseconds] [NX|XX] [KEEPTTL]
summary: Set the string value of a key
since: 1.0.0
group: string
-
NX -> not x -> not exist 不存在的时候才去设置
-
使用场景:分布式锁。谁先成功谁就拿到锁了
-
127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 hello nx OK 127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 world nx (nil) 127.0.0.1:6379> get k1 "hello" -
只有k1无值的时候才会生效
-
-
XX -> exist 只能更新,无法赋值
-
127.0.0.1:6379> set k2 redis xx (nil) 127.0.0.1:6379> get k2 (nil)
-
del
该命令用于在 key 存在是删除 key。
127.0.0.1:6379> del k1
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "k2"
2) "orkey"
3) "andkey"
flushdb
FLUSHDB [ASYNC]
summary: Remove all keys from the current database
since: 1.0.0
group: server
flushall
FLUSHALL [ASYNC]
summary: Remove all keys from all databases
since: 1.0.0
group: server
mset/mget
批量设置,读取
127.0.0.1:6379> mset k3 a k4 b
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> mget k3 k4
1) "a"
2) "b"
127.0.0.1:6379>
1).字符型
append
追加字符串的值
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
"hello"
127.0.0.1:6379> append k1 " world"
(integer) 11
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
"hello world"
getrange
获取范围内的字符串
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
"hello world"
127.0.0.1:6379> getrange k1 6 10
"world"
-
位置从
0开始 -
反方向索引
-
127.0.0.1:6379> getrange k1 -5 -1 "world" -
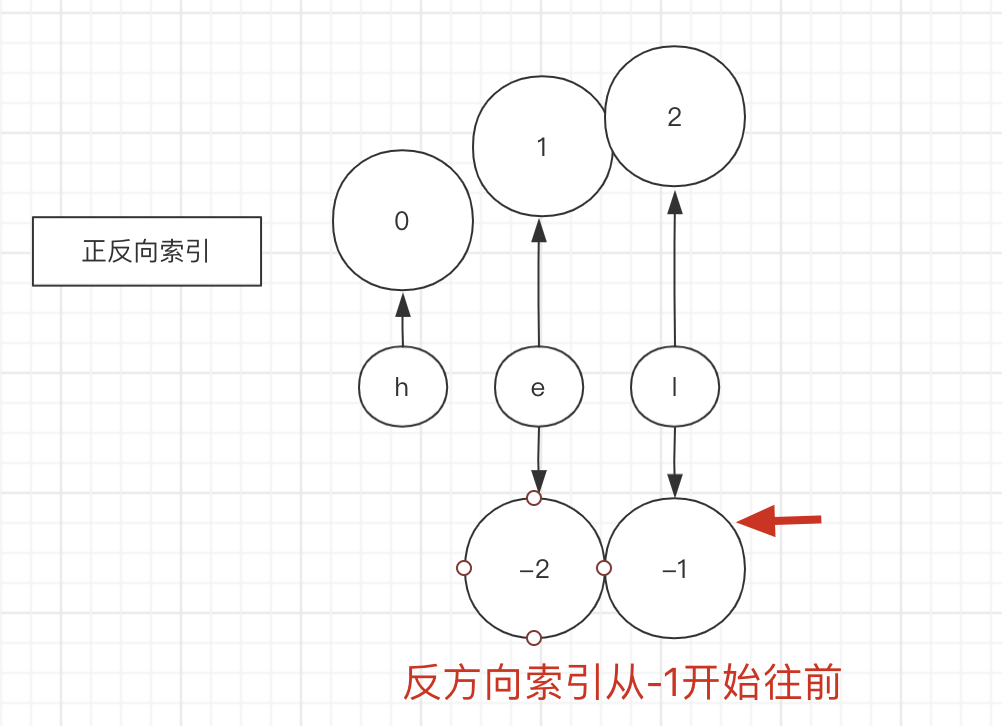
-
setrange
从指定位置开始set string值
127.0.0.1:6379> setrange k1 6 SeaSoonKeun
(integer) 17
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
"hello SeaSoonKeun"
strlen
返回字符串长度
127.0.0.1:6379> setrange k1 6 SeaSoonKeun
(integer) 17
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
"hello SeaSoonKeun"
127.0.0.1:6379> strlen k1
(integer) 17
type
查看key类型
127.0.0.1:6379> type k1
string
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
"hello SeaSoonKeun"
-
Key 中的 type 包含value 类型
-
Set 命令是 string 分组的,所以产生的数据都是 string类型的
127.0.0.1:6379> set k4 999 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get k4 "999" 127.0.0.1:6379> type k4 string127.0.0.1:6379> help set SET key value [EX seconds|PX milliseconds] [NX|XX] [KEEPTTL] summary: Set the string value of a key since: 1.0.0 group: string
object
子命令列表
127.0.0.1:6379> object help
1) OBJECT <subcommand> arg arg ... arg. Subcommands are:
2) ENCODING <key> -- Return the kind of internal representation used in order to store the value associated with a key.
3) FREQ <key> -- Return the access frequency index of the key. The returned integer is proportional to the logarithm of the recent access frequency of the key.
4) IDLETIME <key> -- Return the idle time of the key, that is the approximated number of seconds elapsed since the last access to the key.
5) REFCOUNT <key> -- Return the number of references of the value associated with the specified key.
-
object encoding key
显示key编码
127.0.0.1:6379> mget k1 k3 k4 1) "hello SeaSoonKeun" 2) "a" 3) "999" 127.0.0.1:6379> type k1 string 127.0.0.1:6379> type k3 string 127.0.0.1:6379> type k4 string 127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding k1 "raw" 127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding k3 "embstr" 127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding k4 "int"虽然key的type都是string类型,但是有不同的编码。redis这种
预埋设计,方便后面更加快速调用对应类型的方法进行计算,很大程度上提升了速度。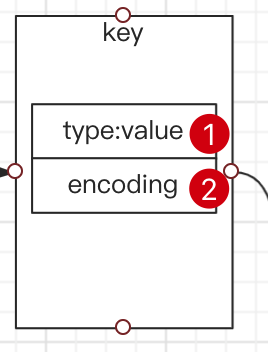
在此基础上,针对encoding是int类型的有下列方法:
# 加一 INCR key summary: Increment the integer value of a key by one since: 1.0.0 INCRBY key increment summary: Increment the integer value of a key by the given amount since: 1.0.0 INCRBYFLOAT key increment summary: Increment the float value of a key by the given amount since: 2.6.0 DECR key summary: Decrement the integer value of a key by one since: 1.0.0 DECRBY key decrement summary: Decrement the integer value of a key by the given number since: 1.0.0eg
127.0.0.1:6379> get k4 "999" 127.0.0.1:6379> 127.0.0.1:6379> INCR k4 (integer) 1000 127.0.0.1:6379> INCRBY k4 100 (integer) 1100 127.0.0.1:6379> DECR k4 (integer) 1099 127.0.0.1:6379> DECRBY k4 100 (integer) 999
一些方法会变掉key的类型,一些方法会提前固定编码
引申: 二进制安全 -> 字节流
编码并不会影响数据存储,因为是首先是按字节流完成的数据存储,然后redis为了自身方法更快速的计算,在key上加了encoding类型数据,也会随着方法的调用发生encoding编码的改变。
eg
- macos默认使用utf-8 编码集
- 在此编码集下,添加一个key。
127.0.0.1:6379> flushdb
OK
127.0.0.1:6379>
127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 我
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> STRLEN k1
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
"\xe6\x88\x91"
- 修改编码集为GBK
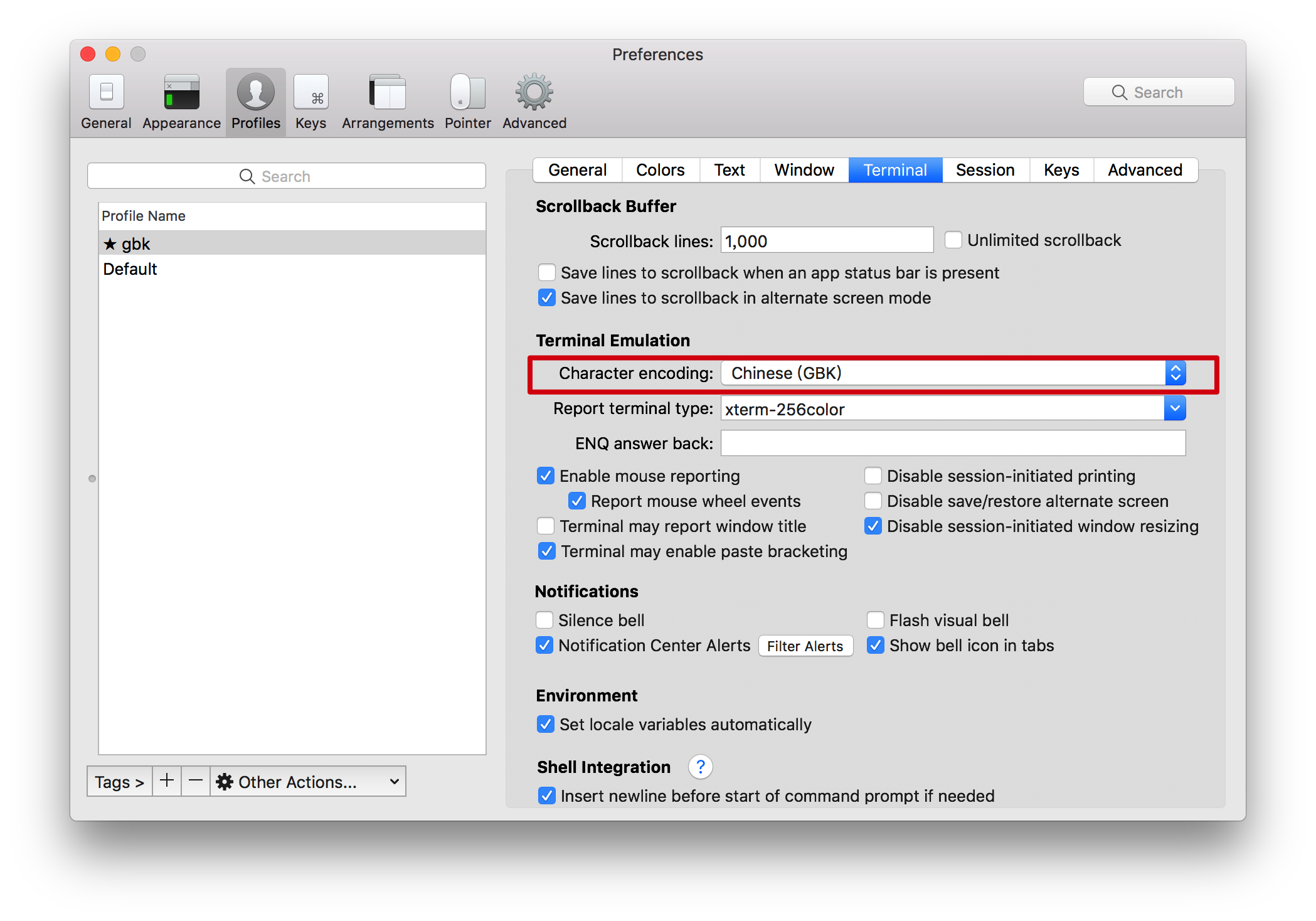
- 在此编码集下,添加一个相同的key。
[root@localhost ~]# redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> flushdb
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 我
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> strlen k1
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
"\xce\xd2"
结论:redis是按传递进来的字节进行存储,utf-8中占用三个字节,GBK占用二个字节。
redis是没有数据类型的,必须在用户端沟通好数据的编码和解码。
# redis utf-8编码下,格式化gbk编码的字节,出现乱码
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "k1"
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
"\xce\xd2"
127.0.0.1:6379> exit
[root@localhost ~]# redis-cli --raw
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
��
# redis gbk编码下,格式化gbk编码的字节,显示正常
[root@localhost ~]# redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
"\xce\xd2"
127.0.0.1:6379> exit
[root@localhost ~]# redis-cli --raw
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
我
getset
获取老值,赋值新值
127.0.0.1:6379> help GETSET
GETSET key value
summary: Set the string value of a key and return its old value
since: 1.0.0
group: string
127.0.0.1:6379> getset k1 hi
"hello SeaSoonKeun"
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1
"hi"
减少成本,避免两次请求造成不必要的通讯浪费。
引申:原子性操作。
触发原子,单线程不涉及肯定是原子的, 只有多笔操作的时候才会有原子的概念。
引申:内存
线性地址空间
2). 数值型:
集成了对数据类型常见的增减操作,如下所示。
INCR key
summary: Increment the integer value of a key by one
since: 1.0.0
INCRBY key increment
summary: Increment the integer value of a key by the given amount
since: 1.0.0
INCRBYFLOAT key increment
summary: Increment the float value of a key by the given amount
since: 2.6.0
DECR key
summary: Decrement the integer value of a key by one
since: 1.0.0
DECRBY key decrement
summary: Decrement the integer value of a key by the given number
since: 1.0.0
3). bitmap :
位图。BitMap 原本的含义是用一个比特位来映射某个元素的状态。由于一个比特位只能表示 0 和 1 两种状态,所以 BitMap 能映射的状态有限,但是使用比特位的优势是能大量的节省内存空间。
Redis 其实只支持 5 种数据类型,并没有 BitMap 这种类型,BitMap 底层是基于 Redis 的字符串类型实现的。
字节Byte = 8bit
BitMap 的 offset 值上限
但是需要注意,Redis 中字符串的最大长度是 512M,所以 BitMap 的 offset 值也是有上限的,其最大值是:
8 * 1024 * 1024 * 512 = 2^32
由于 C语言中字符串的末尾都要存储一位分隔符,所以实际上 BitMap 的 offset 值上限是:
(8 * 1024 * 1024 * 512) -1 = 2^32 - 1
BitMap 占用的空间,
就是底层字符串占用的空间。假如 BitMap 偏移量的最大值是 OFFSET_MAX,那么它底层占用的空间就是:
(OFFSET_MAX/8)+1 = 占用字节数
因为字符串内存只能以字节分配,所以上面的单位是字节。
SETBIT
SETBIT key offset value
summary: Sets or clears the bit at offset in the string value stored at key
since: 2.2.0
group: string
offset 代表二进制位 不是偏移量
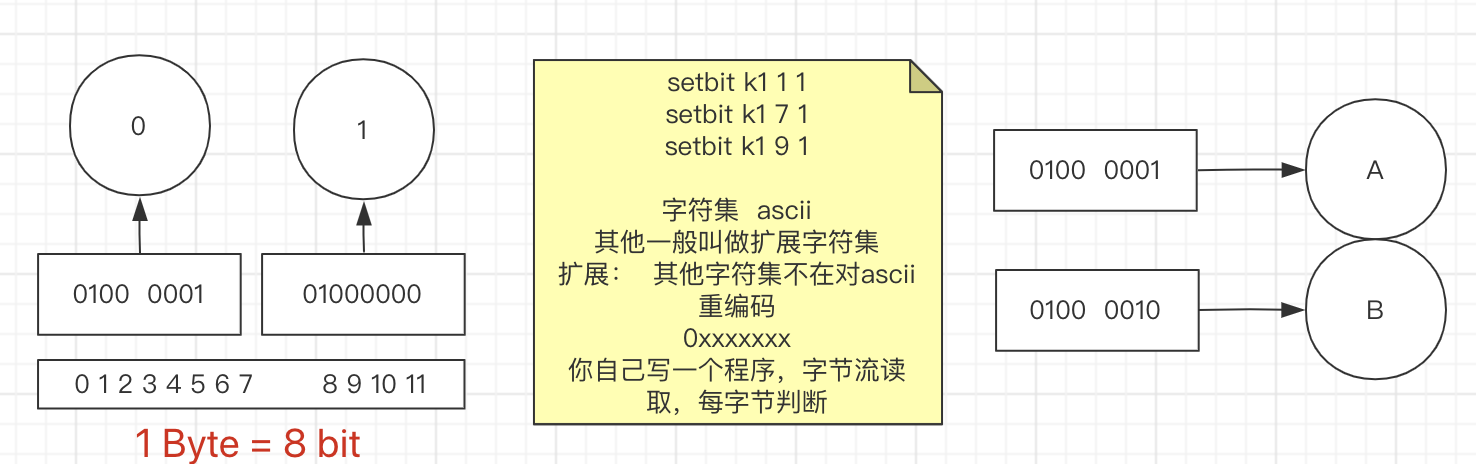
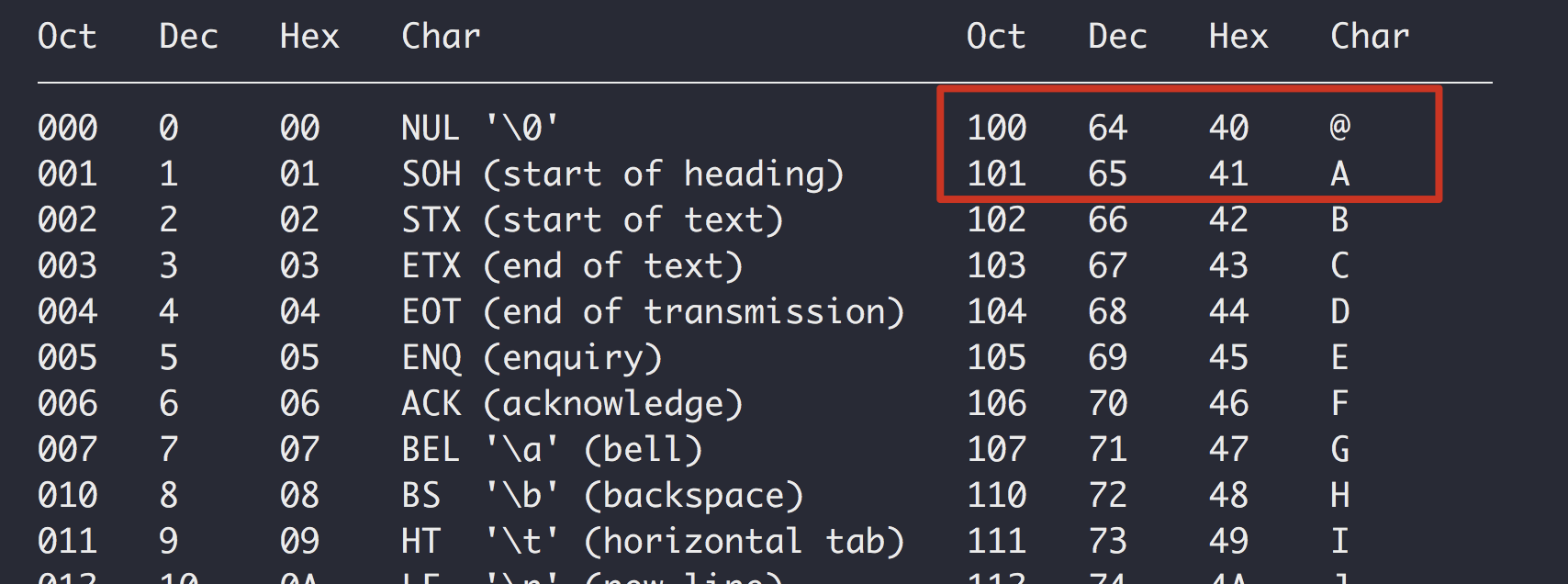
man ascii验证ascii码的值
127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT k4 1 1
0
127.0.0.1:6379> get k4
@
01000000
127.0.0.1:6379> SETBIT k4 9 1
0
127.0.0.1:6379> get k4
@@
01000000 01000000
BITCOUNT
# 获取指定范围内值为 1 的个数 # start 和 end 以字节为单位
BITCOUNT key [start end]
summary: Count set bits in a string
BITFIELD
高级命令
BITFIELD key [GET type offset] [SET type offset value] [INCRBY type offset increment] [OVERFLOW WRAP|SAT|FAIL]
summary: Perform arbitrary bitfield integer operations on strings
since: 3.2.0
BITOP
# result 计算的结果,会存储在该key中
# key1 … keyn 参与运算的key,可以有多个,空格分割,not运算只能一个key
# 当 BITOP 处理不同长度的字符串时,较短的那个字符串所缺少的部分会被看作 0。返回值是保存到 destkey 的字符串的长度(以字节byte为单位),和输入 key 中最长的字符串长度相等。
BITOP operation destkey key [key ...]
summary: Perform bitwise operations between strings
since: 2.6.0
BITPOS
# 返回指定key中第一次出现指定value(0/1)的位置
BITPOS key bit [start] [end]
summary: Find first bit set or clear in a string
since: 2.8.7
位图的应用场景
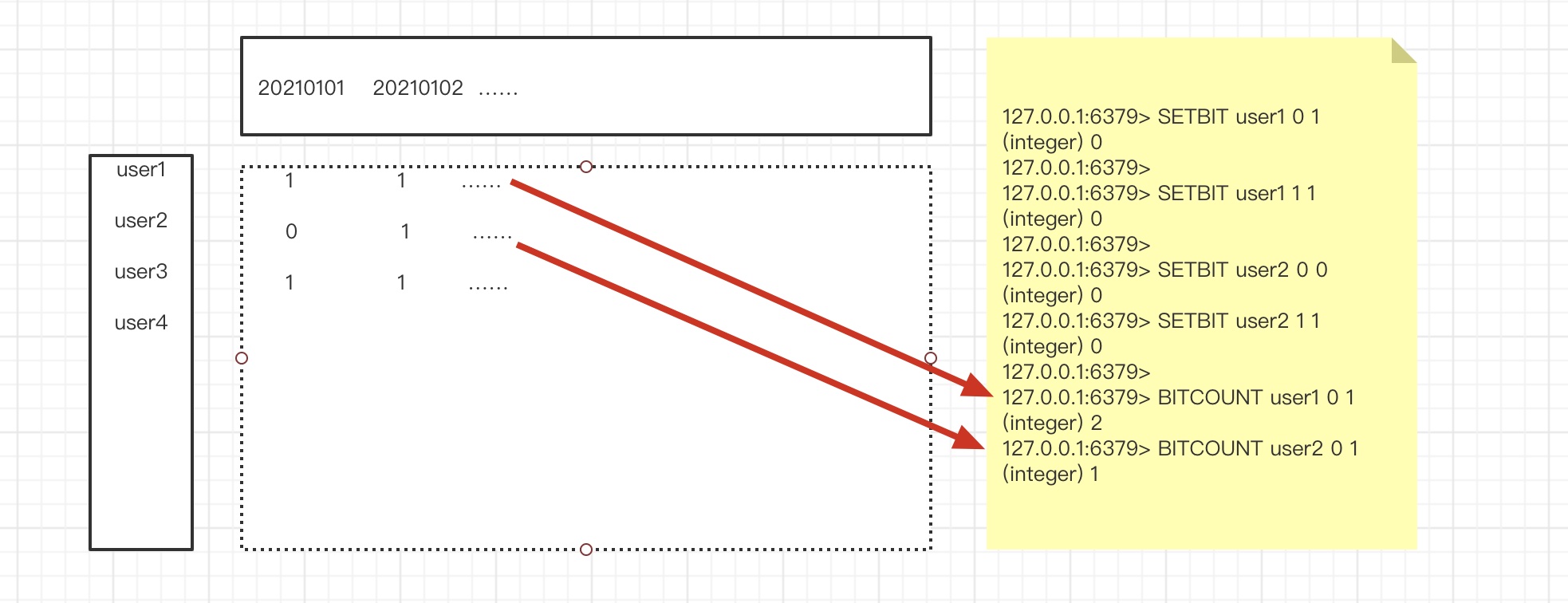
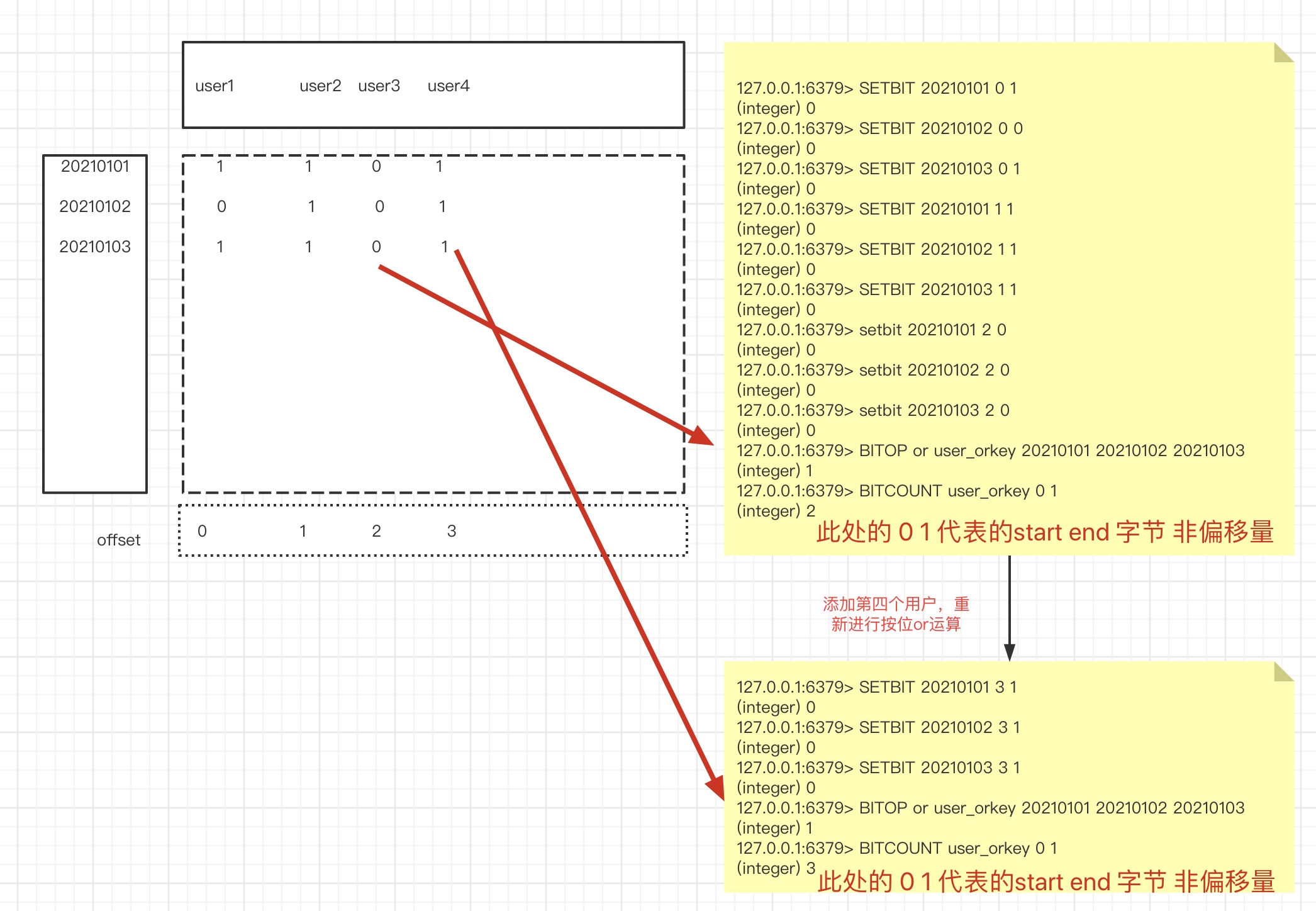
2. ###### 京东秒杀,统计某一时间段的活跃用户。
bitop
大库备货多少礼物
假设京东有2E用户
分为:僵尸用户,冷热用户/忠诚用户
活跃用户统计!随即窗口
比如说 1号~3号 连续登录要 去重





 本文详细介绍了Redis中Value-string类型的操作,包括SET、GET、DEL、FLUSHDB、MSET/MGET、APPEND、GETRANGE、SETRANGE、STRLEN、TYPE、INCR/DECR系列以及BITMAP相关的SETBIT和BITCOUNT等,还讨论了字符串编码和Redis的原子性与内存管理。
本文详细介绍了Redis中Value-string类型的操作,包括SET、GET、DEL、FLUSHDB、MSET/MGET、APPEND、GETRANGE、SETRANGE、STRLEN、TYPE、INCR/DECR系列以及BITMAP相关的SETBIT和BITCOUNT等,还讨论了字符串编码和Redis的原子性与内存管理。
















 2002
2002

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








