In this blog 1, I try to predict the number of positive and negative reviews downloaded from IMDb based on sentiment by using different classification models.
Step 1. Import packages
Import necassary packages we need.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("IMDB Dataset.csv")
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import nltk
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer
from wordcloud import WordCloud,STOPWORDS
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize,sent_tokenize
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import spacy
import re,string,unicodedata
from nltk.tokenize.toktok import ToktokTokenizer
from nltk.stem import LancasterStemmer,WordNetLemmatizer
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression,SGDClassifier
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from textblob import TextBlob
from textblob import Word
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report,confusion_matrix,accuracy_score
import os
print(os.listdir("IMDB Dataset.csv"))
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')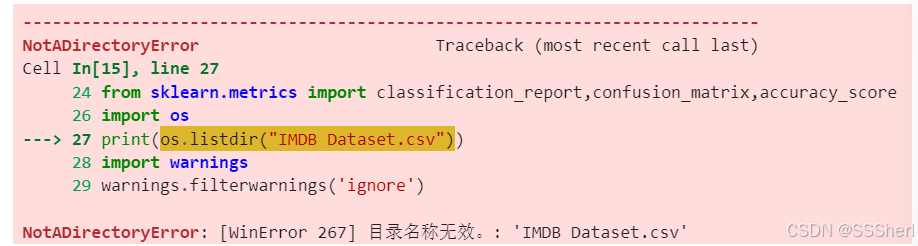
This part of the error can be ignored for the time being. You can then check whether the file exists, and if it does, do not process the error message above.
import os
import pandas as pd
# Check if the file exists
file_path = "IMDB Dataset.csv"
if os.path.isfile(file_path):
print(f"File '{file_path}' exists.")
else:
print(f"File '{file_path}' does not exist.")
# Load the file
data = pd.read_csv(file_path)
print(data.head())
Now we see the data file does exist. Let's run the step 2 together.
Step 2. Import the training data and data pre-processing
In this step, we would import the dataset and make pre-process of the dataset. The goal of the data pre-processing is to transform the raw text data into a form that the model can understand.
Data pre-processing:
1). Split the dataset;
2). Text normalization;
3). Remove html strips and noise text;
4). Text stemming;
5). Remove stopwords to English;
6). Normalized the training reviews.
imdb_data=pd.read_csv("IMDB Dataset.csv")
print(imdb_data.shape)
imdb_data.head(10)
(50000, 2) means dataset has 50000 rows and 2 columns.
The table shows first 10 rows.
#Check the summary of the dataset
imdb_data.describe()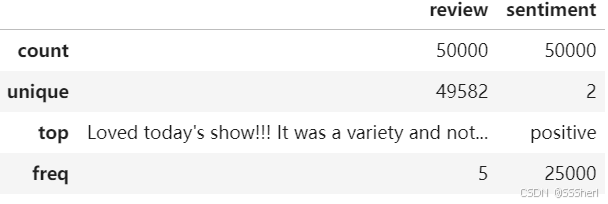
review: count=50000 means the total of 50000 reviews with no missing values. unique=49582 means there are 49582 unique reviews indicating duplication of reviews. top means the most frequent review. freq means the review is repeated 5 times.
sentiment: count=50000 means the total number of sentimental tags is 50000, with no missing values. unique=2 means there are 2 unique sentimental tags(positive and negative). top=positive means the most frequent positive tag is 'positive'. freq means the positive reviews are repeated 25000 times.
P.S. This dataset has the same number of positive and negative reviews.
#Sentiment count
imdb_data['sentiment'].value_counts()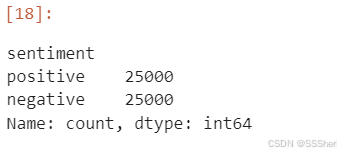
In sentiment column:
There were 25,000 reviews tagged 'Positive'. There were 25,000 reviews tagged 'Negative'.
The output Series name is 'count', indicating that this is the count result.
'dtype: int64' indicates that the result of the count is integer data.
1). Split the dataset
#Split the dataset
#Training dataset
train_reviews=imdb_data.review[:40000]
train_sentiments=imdb_data.sentiment[:40000]
#Testing dataset
test_reviews=imdb_data.review[40000:]
test_sentiments=imdb_data.sentiment[40000:]
print(train_reviews.shape,train_sentiments.shape)
print(test_reviews.shape,test_sentiments.shape)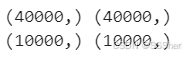
Training dataset: Number of reviews is 40000, number of tags is 40000.
Testing dataset: Number of reviews is 10000, number of tags is 10000.
2). Text normalization
#Text normalization
from nltk.tokenize.toktok import ToktokTokenizer
import nltk
# Initialize the tokenizer
tokenizer = ToktokTokenizer()
print("Tokenizer initialized:", tokenizer)
# Load the stopwords
nltk.download('stopwords') # Make sure the stopwords data is downloaded
stopword_list = nltk.corpus.stopwords.words('english')
print("First 10 stopwords:", stopword_list[:10])

The list of stopwords loaded from NLTK, with the first 10 words are: ['i', 'me', 'my', 'myself', 'we', 'our', 'ours', 'ourselves', 'you', "you're"].
3). Remove html strips and noise text
#Remove html strips and noise text
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
#1. Remove the html strips
def strip_html(text):
text = str(text)
if "<" in text and ">" in text:
soup = BeautifulSoup(text, "html.parser")
return soup.get_text()
else:
return text
#2. Remove the square brackets
def remove_between_square_brackets(text):
return re.sub('\\[[^]]*\\]', '', text)
#3. Remove the noisy text
def denoise_text(text):
text = strip_html(text)
text = remove_between_square_brackets(text)
return text
#Apply function on review column
imdb_data['review'] = imdb_data['review'].apply(denoise_text)#Removing special characters
#Define function for removing special characters
def remove_special_characters(text, remove_digits=True):
pattern=r'[^a-zA-z0-9\s]'
text=re.sub(pattern,'',text)
return text
#Apply function on review column
imdb_data['review']=imdb_data['review'].apply(remove_special_characters)
4). Text stemming
#Text stemming
def simple_stemmer(text):
ps=nltk.porter.PorterStemmer()
text= ' '.join([ps.stem(word) for word in text.split()])
return text
#Apply function on review column
imdb_data['review']=imdb_data['review'].apply(simple_stemmer)
This code uses Porter Stemmer (the Stemmer) to perform a Stemmer operation on each comment in the IMDB [' review' ] column.
5). Remove stopwords to English
#Remove stopwords to English
stop = set(stopwords. words('english'))
print(stop)
#removing the stopwords
def remove_stopwords(text, is_lower_case = False):
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(text)
tokens = [token.strip() for token in tokens]
if is_lower_case:
filtered_tokens = [token for token in tokens if token not in stopword_list]
else:
filtered_tokens = [token for token in tokens if token.lower() not in stopword_list]
filtered_text = ' '.join(filtered_tokens)
return filtered_text
#Apply function on review column
imdb_data['review'] = imdb_data['review'].apply(remove_stopwords)

These are the most frequent stopwords in the dataset.
6). Normalized the training reviews
#Normalized train reviews
norm_train_reviews=imdb_data.review[:40000]
norm_train_reviews[0]
#convert dataframe to string
#norm_train_string=norm_train_reviews.to_string()
#Spelling correction using Textblob
#norm_train_spelling=TextBlob(norm_train_string)
#norm_train_spelling.correct()
#Tokenization using Textblob
#norm_train_words=norm_train_spelling.words
#norm_train_words
The above code extracts the first 40,000 comments in the dataset, with [0] representing the text content of the first comment viewed. If you want to view other text content, you can do so by changing the number inside [].
#Access the 23158th comment
norm_train_reviews=imdb_data.review[:40000]
norm_train_reviews[23518]
Next we extract the last 40,000 comments of the dataset in the same way as above.
#Access the 49699th comment
norm_test_reviews=imdb_data.review[40000:]
norm_test_reviews[49699]
Encore
Data Pre-processing(extra method)
In this section, I'll cover some other ways to work with text. If there is something you need for your research, you can use it.
#Data Pre-processing(extra method)
#a.Extract review
import pandas as pd
import spacy
# Load the model
nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm")
# Load the csv file
data = pd.read_csv("IMDB Dataset.csv")
# Process the 1st review
doc = nlp(data['review'].iloc[0])
print(doc.text)
Above output it's a review of the TV series Oz which is the 1st review of all.
doc = nlp(data['review'].iloc[22])
print(doc.text)
This is the 22nd review.
#b. NER
#To extract the names of people and movies mentioned in the comments, and analyze their relationship with emotion
for ent in doc.ents:
print(ent.text, ent.label_) 
NER extracts named entities from the text and assign a label to each entity. If you want to know more NER labels, you could check this: https://github.com/explosion/spaCy/discussions/9147
If you don't have what you need here, you can search it in your browser.
#c. Emotion dictionary analysis
#Use a sentiment dictionary, such as VADER or AFINN, to give a direct sentiment score to the text
from vaderSentiment.vaderSentiment import SentimentIntensityAnalyzer
analyzer = SentimentIntensityAnalyzer()
score = analyzer.polarity_scores(norm_train_reviews[0])
print(score) # Output positive, neutral, negative and composite scores
![]()
neg(Nagative): Proportion of negative reviews. 'neg': 0.179 indicates that 17.9% of the text is prone to negative emotions.
neu(Neutral): Proportion of neutral reviews. 'neu': 0.709 indicates that 70.9% of the text is prone to neutral emotions.
pos(Positive): Proportion of positive reviews. 'pos': 0.112 indicates that 11.2% of the text is prone to positive emotions.
compound(Compound Score): Composite mood score, range [-1,1]. 1 means completely positive. -1 means completely negative of 0 indicates emotional neutral 'compound': -0.9363 means that the overall mood of the text is strongly negative.
#d. Feature extraction
import pandas as pd
from gensim.models import Word2Vec
# 1. Load comments from the CSV file
csv_file = "IMDB Dataset.csv"
data = pd.read_csv(csv_file)
# Set the comments to be stored in the“Review” column
reviews = data["review"].dropna().tolist() # Deletes a null value and converts it to a list
# 2. Split words
tokenized_reviews = [review.split() for review in reviews]
# 3. Train the Word2Vec model
w2v_model = Word2Vec(sentences=tokenized_reviews, vector_size=100, window=5, min_count=1)
# 4. Check whether the target word is in the vocabulary
word = "movie"
if word in w2v_model.wv:
word_vector = w2v_model.wv[word]
print(f"Vector for '{word}':\n", word_vector)
else:
print(f"The word '{word}' is not in the vocabulary.")
# 5. View the vocabulary of the model
vocab = list(w2v_model.wv.index_to_key)
print("\nVocabulary size:", len(vocab))
print("Sample words in vocabulary:", vocab[:10])
Vector for 'movie': Each vector represents the character of the word 'movie' in a 100-dimensional space, and the length of the vector is determined by the vector. Theectorses themselves are not intuitive, but they capture the semantic relationship between 'movie' and other word
Vocabulary size: This is the vocabulary size of the model, which is how many unique words the model remembers. Each word has a corresponding word vector.
Sample words in vocabulary: This is the first 10 words in the model vocabulary, sorted by frequency (from high to low).
Then there are the feature extraction, model training, and model evaluation sessions, which I will cover in Blog2.
Stay tuned!
I hope my sharing is helpful to you. ٩(❛ัᴗ❛ั⁎)




















 812
812

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








