"遥不可及的声明"正确的代码出现红波浪线"unreachable statement",为鼠标放上去的提示; 意思是->在程序中,一条语句的执行不可能被到达。
通常发生在这种情况下是因为程序中存在一个永远不会为假的条件语句,或者因为在程序的其他地方已经使用了 return, break, continue 等语句终止了程序的执行。
例如:
以及:
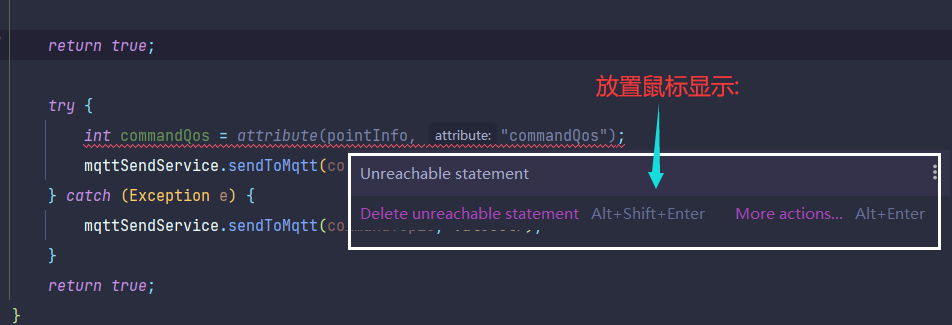
这里就是因为在这块代码前面使用了return,导致程序有永远不可能到达这里所导致的
需要明确的是:“unreachable statement” 表示 编译级错误,不是警告,意味着编译器能明确判断:某行代码永远没有机会被执行,必须修复才能运行。核心原因是「代码执行流被提前终止」或「条件永远无法满足」
一、最常见场景(按发生频率排序)
场景 1:return/throw 语句后有代码(执行流被提前终止)
return(返回结果)或 throw(抛出异常)会直接终止当前方法的执行,后续代码永远走不到。
错误示例:
public String getUserName() {
return "yang"; // 执行到这里,方法直接返回,后续代码永远不执行
System.out.println("方法结束"); // 红波浪线:unreachable statement
}
// 抛异常同理
public void checkParam(String param) {
if (param == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数不能为空"); // 抛出异常后,方法终止
System.out.println("检查结束"); // 红波浪线:不可达
}
}
修复方案:
删除 return/throw 后的冗余代码,或调整语句顺序(把需要执行的代码放在前面):
public String getUserName() {
System.out.println("方法结束"); // 调整顺序,先执行打印
return "yang"; // 最后返回
}
public void checkParam(String param) {
if (param == null) {
System.out.println("参数为空,准备抛异常"); // 先执行必要逻辑
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数不能为空");
}
}
场景 2:if(永远为true) 等条件后有代码(条件分支永远无法进入)
如果条件是「编译期就能确定的常量 true」(如 if(true)、if(1==1)),那么 else 分支或条件后的代码永远不可达。
错误示例:
public void testCondition() {
if (true) { // 条件永远为true,必然进入这个分支
System.out.println("进入if分支");
return;
}
// 以下代码永远走不到(if分支已经return,且else不存在)
System.out.println("条件结束"); // 红波浪线:unreachable statement
}
// 同理:else分支永远无法进入
public void testElse() {
int num = 10;
if (num > 5) { // 编译期可确定num=10>5,永远为true
System.out.println("num大于5");
} else {
System.out.println("num小于等于5"); // 红波浪线:不可达
}
}
修复方案:
- 若条件是故意写死的(如调试):删除冗余的
else或条件后代码; - 若条件需要动态判断:把「常量条件」改为「变量条件」(如
if(num > 5)中num是动态传入的):
public void testCondition(String type) {
if ("A".equals(type)) { // 动态条件(type由外部传入,不确定值)
System.out.println("进入A分支");
return;
}
// 此时else分支或后续代码是可达的
System.out.println("进入默认分支");
}
场景 3:while(true) 无 break 的循环后有代码(循环永远不退出)
while(true) 是「无限循环」,如果循环内部没有 break/return/throw 终止循环,循环后的代码永远执行不到。
错误示例:
public void infiniteLoop() {
while (true) { // 无限循环,无退出条件
System.out.println("循环中...");
}
// 循环永远不结束,后续代码不可达
System.out.println("循环退出"); // 红波浪线:unreachable statement
}
修复方案:
- 若循环需要退出:在循环内添加
break(满足条件时退出); - 若循环确实无限(如服务监听线程):删除循环后的冗余代码:
public void infiniteLoopWithBreak() {
int count = 0;
while (true) {
System.out.println("循环中...");
count++;
if (count >= 10) {
break; // 满足条件退出循环,后续代码可达
}
}
System.out.println("循环退出"); // 正常执行,无错误
}
场景 4:break/continue 语句后有代码(循环内执行流终止)
break(跳出循环)或 continue(跳过当前循环次)会终止当前循环逻辑,循环体内后续代码不可达。
错误示例:
public void loopTest() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (i == 2) {
break; // 跳出整个循环,循环体内后续代码不可达
System.out.println("i等于2"); // 红波浪线:unreachable statement
}
System.out.println("i=" + i);
}
}
// continue同理
public void continueTest() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
continue; // 跳过当前次循环,后续代码不执行
System.out.println("偶数"); // 红波浪线:不可达
}
}
}
修复方案:
删除 break/continue 后的冗余代码,或调整逻辑顺序:
public void loopTest() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (i == 2) {
System.out.println("i等于2"); // 先执行逻辑,再break
break;
}
System.out.println("i=" + i);
}
}
场景 5:死代码块(永远无法进入的代码块)
代码块被「永远为 false 的条件」包裹,或处于不可达的分支中。
错误示例:
public void deadCode() {
boolean flag = false;
if (flag) { // flag是false,且没有任何地方修改它,代码块永远不执行
System.out.println("进入flag分支"); // 红波浪线:unreachable statement
}
// 更明显的情况:条件是常量false
if (1 == 2) { // 编译期确定为false
System.out.println("永远不会执行"); // 红波浪线
}
}
修复方案:
- 若代码块无用:直接删除;
- 若需要执行:修正条件(如把
flag改为动态赋值,或修正判断逻辑):
public void deadCode(String status) {
boolean flag = "active".equals(status); // 动态条件(status由外部传入)
if (flag) {
System.out.println("进入flag分支"); // 可达(当status="active"时执行)
}
}
二、快速排查步骤(30 秒定位问题)
- 看红波浪线位置:找到标红的代码行;
- 往上找 “终止语句”:查看红波浪线之前的代码,是否有
return/throw/break/continue; - 检查条件是否 “恒成立 / 恒不成立”:如果红波浪线在
if/while分支后,看条件是否是「常量值」(如true/false、1==1); - 删除 / 调整代码:冗余代码直接删除,需要执行的代码调整到「终止语句」之前,或修正条件为动态判断。
三、特殊注意:Lambda / 匿名内部类中的不可达
在 Lambda 或匿名内部类中,若捕获的变量是「final 或 effectively final」(未被重新赋值),也可能出现不可达:
public void lambdaTest() {
boolean isFinish = true;
new Thread(() -> {
if (isFinish) { // isFinish是final(未重新赋值),恒为true
System.out.println("线程结束");
return;
}
System.out.println("线程运行中"); // 红波浪线:不可达
}).start();
}
修复:把 isFinish 改为可动态修改(如用 AtomicBoolean),或删除冗余代码。
总结
“unreachable statement” 的核心是「编译器判定代码 “没用”」,修复原则只有一个:确保每一行代码都有 “被执行到的可能”。按以下优先级处理:
- 优先删除标红的冗余代码(最常见情况);
- 若代码需要执行:调整
return/break位置,或把「常量条件」改为「动态条件」; - 避免写
while(true)无退出的循环,或if(true)死分支(调试时用完及时删除)。

























 793
793

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








