
背景
上周,某公司的产品经理提了一个需求:根据用户手机壳颜色来改变 App 主题颜色。可能是由于这天马行空的需求激怒了程序员,导致程序员和产品经理打了起来,最后双双被公司开除。
那如何实现这个功能呢?首先需要获取图像中的主色。
插一句题外话,作为程序员在桌面上还是要有一些必备的东西需要放的。

KMeans 算法
k-平均算法(英文:k-means clustering)源于信号处理中的一种向量量化方法,现在则更多地作为一种聚类分析方法流行于数据挖掘领域。k-平均聚类的目的是:把 n 个点(可以是样本的一次观察或一个实例)划分到k个聚类中,使得每个点都属于离他最近的均值(此即聚类中心)对应的聚类,以之作为聚类的标准。这个问题将归结为一个把数据空间划分为Voronoi cells的问题。
KMeans 算法思想为:给定n个数据点{x1,x2,…,xn},找到K个聚类中心{a1,a2,…,aK},使得每个数据点与它最近的聚类中心的距离平方和最小,并将这个距离平方和称为目标函数,记为Wn,其数学表达式为:

本文使用 KMeans 算法对图像颜色做聚类。
算法基本流程: 1、初始的 K 个聚类中心。 2、按照距离聚类中心的远近对所有样本进行分类。 3、重新计算聚类中心,判断是否退出条件: 两次聚类中心的距离足够小视为满足退出条件; 不退出则重新回到步骤2。
算法实现
public List<Scalar> extract(ColorProcessor processor) {// initialization the pixel dataint width = processor.getWidth();int height = processor.getHeight();byte[] R = processor.getRed();byte[] G = processor.getGreen();byte[] B = processor.getBlue();//Create random points to use a the cluster centerRandom random = new Random();int index = 0;for (int i = 0; i < numOfCluster; i++){int randomNumber1 = random.nextInt(width);int randomNumber2 = random.nextInt(height);index = randomNumber2 * width + randomNumber1;ClusterCenter cc = new ClusterCenter(randomNumber1, randomNumber2, R[index]&0xff, G[index]&0xff, B[index]&0xff);cc.cIndex = i;clusterCenterList.add(cc);}// create all cluster pointfor (int row = 0; row < height; ++row){for (int col = 0; col < width; ++col){index = row * width + col;pointList.add(new ClusterPoint(row, col, R[index]&0xff, G[index]&0xff, B[index]&0xff));}}// initialize the clusters for each pointdouble[] clusterDisValues = new double[clusterCenterList.size()];for(int i=0; i<pointList.size(); i++){for(int j=0; j<clusterCenterList.size(); j++){clusterDisValues[j] = calculateEuclideanDistance(pointList.get(i), clusterCenterList.get(j));}pointList.get(i).clusterIndex = (getCloserCluster(clusterDisValues));}// calculate the old summary// assign the points to cluster center// calculate the new cluster center// computation the delta value// stop condition--double[][] oldClusterCenterColors = reCalculateClusterCenters();int times = 10;while(true){stepClusters();double[][] newClusterCenterColors = reCalculateClusterCenters();if(isStop(oldClusterCenterColors, newClusterCenterColors)){break;}else{oldClusterCenterColors = newClusterCenterColors;}if(times > 10) {break;}times++;}//update the result imageList<Scalar> colors = new ArrayList<Scalar>();for(ClusterCenter cc : clusterCenterList) {colors.add(cc.color);}return colors;}private boolean isStop(double[][] oldClusterCenterColors, double[][] newClusterCenterColors) {boolean stop = false;for (int i = 0; i < oldClusterCenterColors.length; i++) {if (oldClusterCenterColors[i][0] == newClusterCenterColors[i][0] &&oldClusterCenterColors[i][1] == newClusterCenterColors[i][1] &&oldClusterCenterColors[i][2] == newClusterCenterColors[i][2]) {stop = true;break;}}return stop;}/*** update the cluster index by distance value*/private void stepClusters(){// initialize the clusters for each pointdouble[] clusterDisValues = new double[clusterCenterList.size()];for(int i=0; i<pointList.size(); i++){for(int j=0; j<clusterCenterList.size(); j++){clusterDisValues[j] = calculateEuclideanDistance(pointList.get(i), clusterCenterList.get(j));}pointList.get(i).clusterIndex = (getCloserCluster(clusterDisValues));}}/*** using cluster color of each point to update cluster center color** @return*/private double[][] reCalculateClusterCenters() {// clear the points nowfor(int i=0; i<clusterCenterList.size(); i++){clusterCenterList.get(i).numOfPoints = 0;}// recalculate the sum and total of points for each clusterdouble[] redSums = new double[numOfCluster];double[] greenSum = new double[numOfCluster];double[] blueSum = new double[numOfCluster];for(int i=0; i<pointList.size(); i++){int cIndex = (int)pointList.get(i).clusterIndex;clusterCenterList.get(cIndex).numOfPoints++;int tr = pointList.get(i).pixelColor.red;int tg = pointList.get(i).pixelColor.green;int tb = pointList.get(i).pixelColor.blue;redSums[cIndex] += tr;greenSum[cIndex] += tg;blueSum[cIndex] += tb;}double[][] oldClusterCentersColors = new double[clusterCenterList.size()][3];for(int i=0; i<clusterCenterList.size(); i++){double sum = clusterCenterList.get(i).numOfPoints;int cIndex = clusterCenterList.get(i).cIndex;int red = (int)(greenSum[cIndex]/sum);int green = (int)(greenSum[cIndex]/sum);int blue = (int)(blueSum[cIndex]/sum);clusterCenterList.get(i).color = new Scalar(red, green, blue);oldClusterCentersColors[i][0] = red;oldClusterCentersColors[i][0] = green;oldClusterCentersColors[i][0] = blue;}return oldClusterCentersColors;}/**** @param clusterDisValues* @return*/private double getCloserCluster(double[] clusterDisValues){double min = clusterDisValues[0];int clusterIndex = 0;for(int i=0; i<clusterDisValues.length; i++){if(min > clusterDisValues[i]){min = clusterDisValues[i];clusterIndex = i;}}return clusterIndex;}/**** @param p* @param c* @return distance value*/private double calculateEuclideanDistance(ClusterPoint p, ClusterCenter c){int pr = p.pixelColor.red;int pg = p.pixelColor.green;int pb = p.pixelColor.blue;int cr = c.color.red;int cg = c.color.green;int cb = c.color.blue;return Math.sqrt(Math.pow((pr - cr), 2.0) + Math.pow((pg - cg), 2.0) + Math.pow((pb - cb), 2.0));}
在 Android 中使用该算法来提取主色:
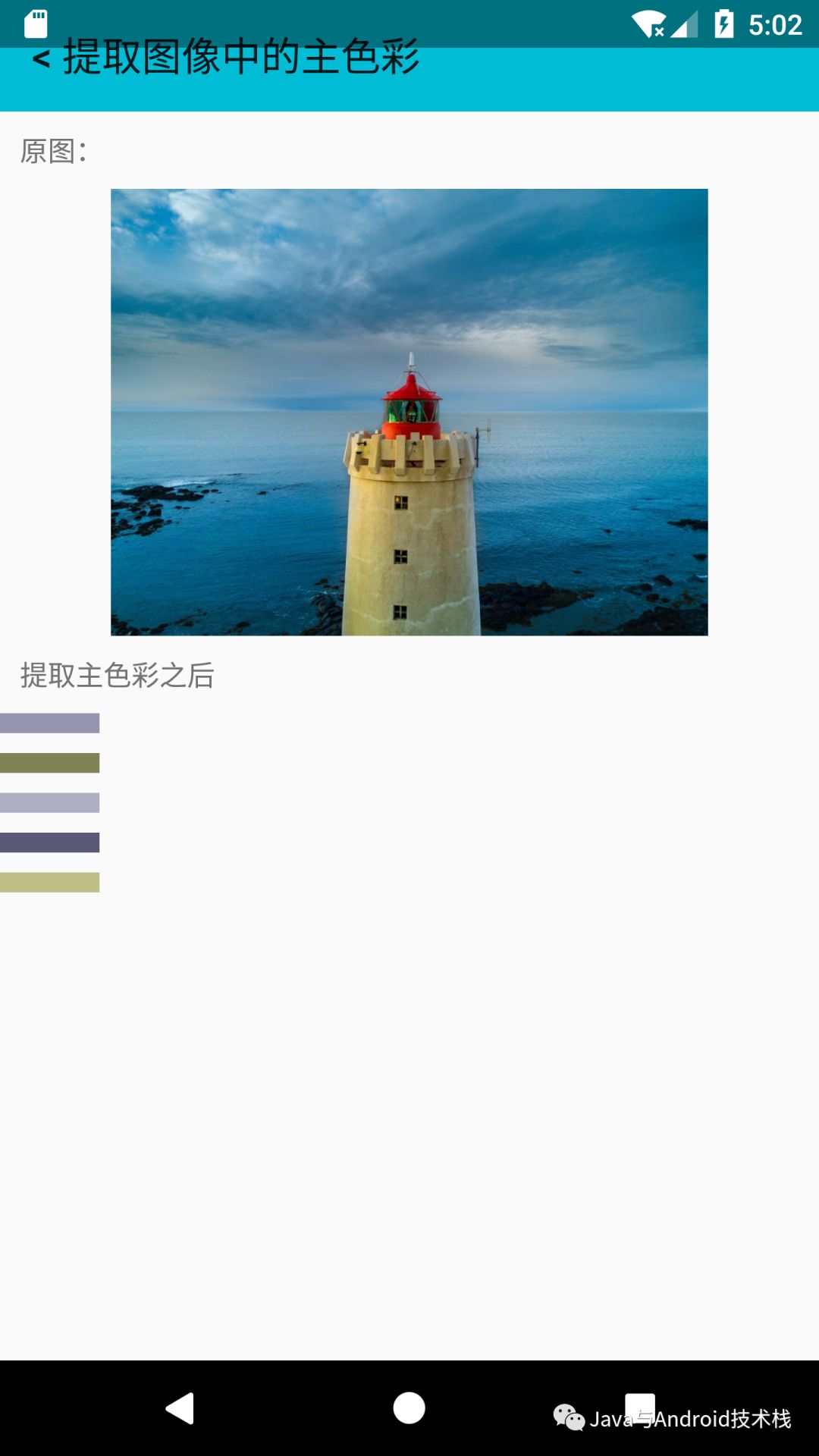
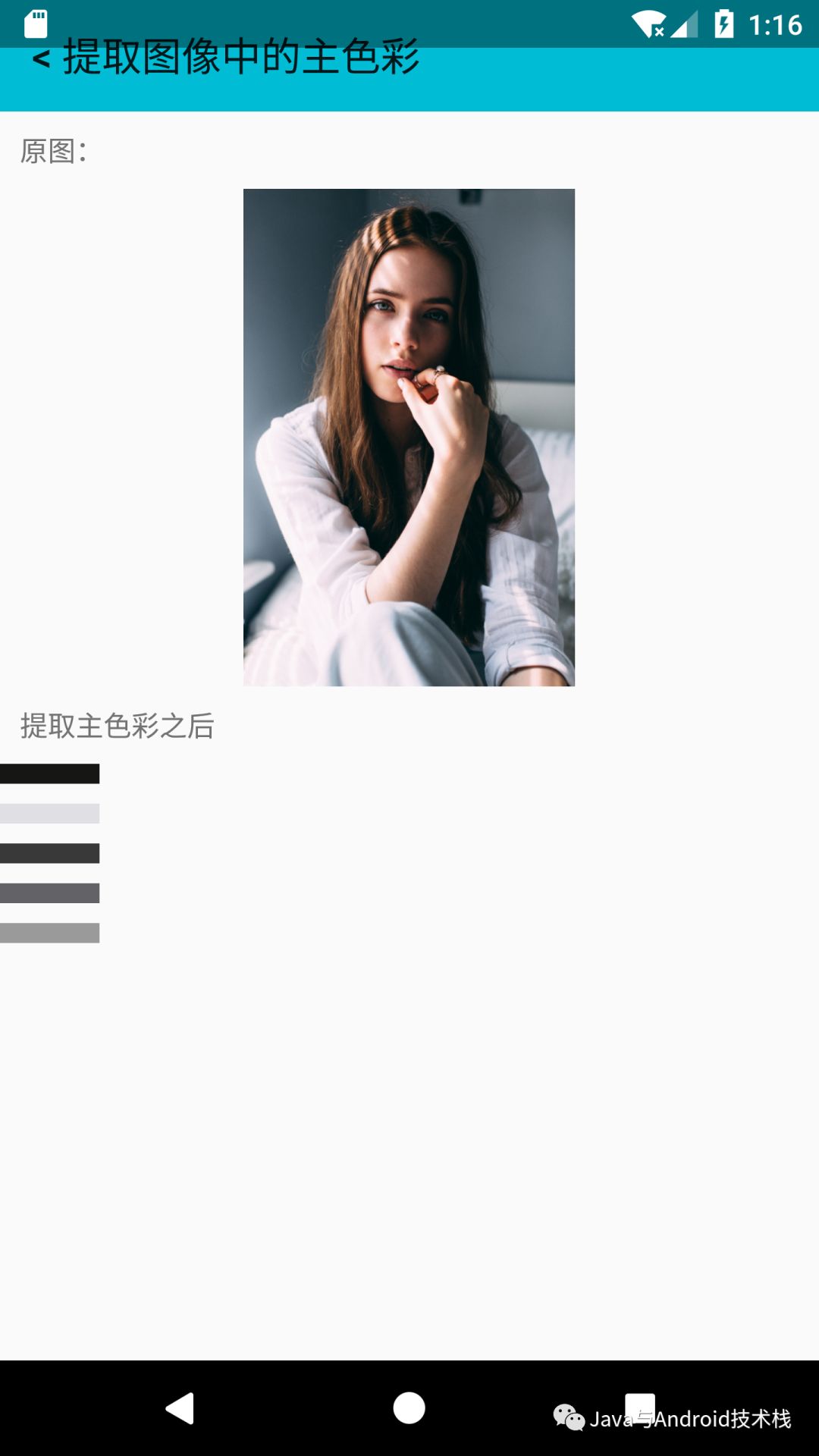
完整的算法实现可以在:https://github.com/imageprocessor/cv4j/blob/master/cv4j/src/main/java/com/cv4j/core/pixels/PrincipalColorExtractor.java 找到,它是一个典型的 KMeans 算法。
我们的算法中,K默认值是5,当然也可以自己指定。
以上算法目前在 demo 上耗时蛮久,不过可以有优化空间。例如,可以使用 RxJava 在 computation 线程中做复杂的计算操作然后切换回ui线程。亦或者可以使用类似 Kotlin 的 Coroutines 来做复杂的计算操作然后切换回ui线程。
总结
提取图像中的主色,还有其他算法例如八叉树等,在 Android 中也可以使用 Palette 的 API来实现。
cv4j(https://github.com/imageprocessor/cv4j) 是gloomyfish(http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/jia20003)和我一起开发的图像处理库,纯java实现,我们已经分离了一个Android版本和一个Java版本。
如果您想看该系列先前的文章可以访问下面的文集: https://www.jianshu.com/nb/10401400
最后提醒一句,作为程序员,还是要多健身。
关注【Java与Android技术栈】
更多精彩内容请关注扫码:





 这篇博客探讨了如何利用KMeans算法提取图像的主要颜色,以满足将App主题色与手机壳颜色匹配的需求。虽然这是一个有趣但颇具挑战性的任务,文章通过介绍KMeans算法的基本原理和在Android中的实现,提供了实现这一功能的思路。还提到了可以使用RxJava或Kotlin的Coroutines优化计算性能,并推荐了cv4j图像处理库。最后,作者建议程序员们关注健康,保持健身习惯。
这篇博客探讨了如何利用KMeans算法提取图像的主要颜色,以满足将App主题色与手机壳颜色匹配的需求。虽然这是一个有趣但颇具挑战性的任务,文章通过介绍KMeans算法的基本原理和在Android中的实现,提供了实现这一功能的思路。还提到了可以使用RxJava或Kotlin的Coroutines优化计算性能,并推荐了cv4j图像处理库。最后,作者建议程序员们关注健康,保持健身习惯。
















 2922
2922

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








