(1)声明位于包test.exam中Point类,有坐标x、y两个私有成员变量,有一个返回与其它点的距离的方法,还有一个移动点的方法
package com.qst.fuxi;
public class Point {
double x;
double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x, double y) {
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public void movePoint(double dx,double dy) {
System.out.println("移动前的坐标为:"+this.x+this.y);
System.out.println("移动量:"+dx+dy);
this.x+=dx;
this.y+=dy;
System.out.println("移动后的坐标为:"+this.x+this.y);
}
}
测试函数
1、返回与其它点的距离
package com.qst.fuxi;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.*;
public class PointDemo {
Point p1;
Point p2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第一个点的x值x1");
Double x1 = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入第一个点的y值y1");
Double y1 = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入第二个点的x值x2");
Double x2 = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入第二个点的y值y2");
Double y2 = scanner.nextDouble();
Point p1 = new Point(x1, y1);
Point p2 = new Point(x2, y2);
PointDemo pd2= new PointDemo(p1,p2);
pd2.distance();
}
public void distance() {
Double a=Math.sqrt(Math.abs(p1.getX()-p2.getX())*Math.abs(p1.getX()-p2.getX())+Math.abs(p1.getY()-p2.getY())*Math.abs(p1.getY()-p2.getY()));
System.out.println(a);
}
public PointDemo() {
super();
}
public PointDemo(Point p1, Point p2) {
super();
this.p1 = p1;
this.p2 = p2;
}
public Point getP1() {
return p1;
public void setP1(Point p1) {
this.p1 = p1;
}
public Point getP2() {
return p2;
}
public void setP2(Point p2) {
this.p2 = p2;
}
}
2、移动点
package com.qst.fuxi;
public class PointMove {
public double x;
public double y;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point p1=new Point(1.0,2.0);
Point p2=new Point(3.0,4.0);
p1.movePoint(p2.x,p2.y);
}
}运行结果:

(2)声明一个位于包test.abc中的圆类,圆由圆心和半径组成,有一个计算面积的方法,利用1中的类实现圆类,写一个测试类用于测试1中的点类和2中的圆类
package com.qst.fuxi;
public class CircleArea {
// 成员变量
private int r; // 变量可以Scanner输入数据
private double PI = 3.14; // double接收
// 构造方法(无参构造方法)
public void Circle() {
}
public void setR(int r) {
this.r = r;
}
// 定义一个getArea方法将来求圆的面积
public void getArea() {
System.out.println("圆的面积为:" + (PI * r * r));
}
// 定义一个getGirth方法将来求圆的面积
public void getGirth() {
System.out.println("圆的周长为:" + (2 * PI * r));
}
}
测试函数
package com.qst.fuxi;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Circle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // 创建对象
System.out.println("请输入圆的半径为:");
int radius = sc.nextInt(); // 接收数据
CircleArea c = new CircleArea();
c.setR(radius);
c.getArea();
c.getGirth();
}
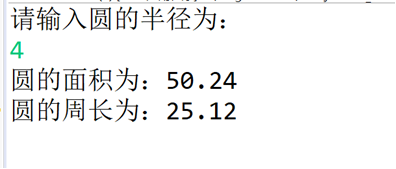
}运行结果:
(3)Person类有姓名属性,说出姓名方法,Student类除了有姓名,还有学号、专业和成绩属性及设置和输出成绩等方法,定义这两个类并用测试类进行测试
1、Person类
package text;
public class Person {
private String name;
//创建构造器
public Person(String name){
this.name = name;
}
//进行封装
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//建立一个talk方法对个人信息进行输出
public void talk(){
System.out.println("学生信息"+"\n学生姓名:"+name);
}
}
2、Student类
package text;
public class Student extends Person {
//添加student类的属性 学号 专业 成绩
private String sno;
private String major;
private double score;
//创建student类的构造器
public Student(String name,String sno,String major,double score){
super( name);
this.sno=sno;
this.major=major;
this.score = score;
}
//封装student类的属性
public String getsno() {
return sno;
}
public void setsno(String sno) {
this.sno=sno;
}
public String getmajor() {
return major;
}
public void setmajor(String major) {
this.major = major;
}
public double getscore() {
return score;
}
public void score(double score) {
this.score=score;
}
public static void sort(Student[] stus) {//数组方法
Student temp;
for (int i = 0; i<stus.length-1;i++) {//冒泡比较
for (int j=0;j<stus.length-i-1;j++) {
if (stus[j].score < stus[j+1].score) {
temp=stus[j];
stus[j]=stus[j+1];
stus[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
}
//重写talk()方法
public void talk() {
super.talk();
System.out.println("学号:"+sno);
System.out.println("专业:"+major);
System.out.println("成绩:"+score);
}
}
3、测试类
package text;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class studentInformation {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String [] args){
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入要录入的学生个数:");
int numStudent=new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
Student[] stus = new Student[numStudent];
//录入学生信息
System.out.println("按要求输入学生信息");
for(int i=0;i<numStudent;i++) {
System.out.print("依次输入第"+(i+1)+"个学生的姓名学号专业成绩:");
stus[i]=new Student(new Scanner(System.in).next(),new Scanner(System.in).next(),new Scanner(System.in).next(),new Scanner(System.in).nextDouble());
}
//调用排序方法
Student.sort(stus);
System.out.println("成绩录入完成,下面将按成绩的降序排序输出学生信息");
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------");
//按成绩降序输出学生信息
for (Student stu : stus) {
stu.talk();
}
}
}运行结果:


(4)编写一个复数类,具有实部、虚部成员变量,可以完成加、减、乘、获得实部和虚部等操作,并编写一个主类对其进行测试。
package complexTest;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Complex { // 复数类
double real; // 实部
double image; // 虚部
Complex(){ // 不带参数的构造方法
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double real = input.nextDouble();
double image = input.nextDouble();
Complex1(real,image);
}
public void Complex1( double real, double image) { // 供不带参数的构造方法调用
this.real = real;
this.image = image;
}
public Complex(double real,double image){ // 带参数的构造方法
this.real = real;
this.image = image;
}
public double getReal() {
return real;
}
public void setReal(double real) {
this.real = real;
}
public double getImage() {
return image;
}
public void setImage(double image) {
this.image = image;
}
Complex add(Complex a){ // 复数相加
double real2 = a.getReal();
double image2 = a.getImage();
double newReal = real + real2;
double newImage = image + image2;
Complex result = new Complex(newReal,newImage);
return result;
}
Complex sub(Complex a){ // 复数相减
double real2 = a.getReal();
double image2 = a.getImage();
double newReal = real - real2;
double newImage = image - image2;
Complex result = new Complex(newReal,newImage);
return result;
}
Complex mul(Complex a){ // 复数相乘
double real2 = a.getReal();
double image2 = a.getImage();
double newReal = real*real2 - image*image2;
double newImage = image*real2 + real*image2;
Complex result = new Complex(newReal,newImage);
return result;
}
public void print(){ // 输出
if(image > 0){
System.out.println(real + " + " + image + "i");
}else if(image < 0){
System.out.println(real + "" + image + "i");
}else{
System.out.println(real);
}
}
}
测试类
package complexTest;
public class ComplexTest { // 用于测试复数类
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("请用户输入第一个复数的实部和虚部:");
Complex data1 = new Complex();
System.out.println("请用户输入第二个复数的实部和虚部:");
Complex data2 = new Complex();
// 以下分别为加减乘
Complex result_add = data1.add(data2);
Complex result_sub = data1.sub(data2);
Complex result_mul = data1.mul(data2);
result_add.print();
result_sub.print();
result_mul.print();
}
}运行结果:

(5)定义一个抽象类Shape,该类有抽象方法area,圆形、矩形、梯形等均是一种Shape,也都有自己求area方法,定义这些类并写测试类进行测试
package area;
//抽象类
abstract class Shape
{
public abstract Double calculateShape();
}
//Rectangle类
class Rectangle extends Shape
{
private double length;
private double width;
public Rectangle(double length, double width)
{
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
public double getLength()
{
return length;
}public void setLength(double length)
{
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth()
{
return width;
}public void setWidth(double width)
{
this.width = width;
}
//继承Shape类,实现getArea()方法
public Double getArea()
{
return width*length;
}
public Double calculateShape() {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
return null;
}
}
//Circle类
class Circle extends Shape
{
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius)
{
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius()
{
return radius;
}
public void setR(double radius)
{
this.radius = radius;
}
//继承Shape类,实现getArea()方法
public Double getArea()
{
return Math.PI*radius*radius;
}
public Double calculateShape() {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
return null;
}
}
//trapezoid类
class Trapezoid extends Shape
{
private double high;
private double width1;
private double width2;
public Trapezoid(double high, double width1,double width2)
{
this.high =high;
this.width1 = width1;
this.width2 = width2;
}
public double getHigh()
{
return high;
}public void setHigh(double high)
{
this. high = high;
}
public double getWidth1()
{
return width1;
}public void setWidth1(double width1)
{
this.width1 = width1;
}
public double getWidth2()
{
return width2;
}public void setWidth2(double width2)
{
this.width2 = width2;
}
//继承Shape类,实现Area()方法
public Double getArea()
{
return (width1+width2)*high/2;
}
public Double calculateShape() {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
return null;
}
}
测试类
package area;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输出圆的半径:");
double radius=sc.nextDouble();
Circle circle=new Circle(radius);
System.out.println("半径为:"+circle.getRadius()+"的圆面积为:"+circle.getArea());
System.out.println("\n输出矩形的长和宽:");
double length=sc.nextDouble();
double width=sc.nextDouble();
Rectangle rectangle=new Rectangle(length,width);
System.out.println("长为:"+rectangle.getLength()+"宽为:"+rectangle.getWidth()+"的长方形面积为:"+rectangle.getArea());
System.out.println("\n输出梯形的高和上边、下边:");
double high=sc.nextDouble();
double width1=sc.nextDouble();
double width2=sc.nextDouble();
Trapezoid trapezoid=new Trapezoid(high,width1,width2);
System.out.println("高为:"+trapezoid.getHigh()+"上边为:"+trapezoid.getWidth1()+"下边为:"+trapezoid.getWidth2()+"的梯形面积为:"+trapezoid.getArea());
}
}
运行结果:






 本文通过一系列Java实验展示了对象、类、继承和包的使用。实验包括:创建位于不同包中的Point类,实现计算距离和移动方法;定义圆类并利用Point类实现;创建Person和Student类,展示继承和方法;实现复数类,完成复数运算;以及定义抽象类Shape和其子类(圆形、矩形、梯形),每个类都有计算面积的方法,并进行了测试验证。
本文通过一系列Java实验展示了对象、类、继承和包的使用。实验包括:创建位于不同包中的Point类,实现计算距离和移动方法;定义圆类并利用Point类实现;创建Person和Student类,展示继承和方法;实现复数类,完成复数运算;以及定义抽象类Shape和其子类(圆形、矩形、梯形),每个类都有计算面积的方法,并进行了测试验证。
















 1377
1377

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








