通讯录
实现一个通讯录系统含有:添加,删除,查找,展示,退出等功能。
思路
- 创建一个person结构体包含
name;phone;age 等信息;还需一个结构体指针 - 因为要以链表的方法(动态内存开辟)来写,所以在结构细中还需要一个结构体指针来存储下一个结构体变量的地址,这样就可以连续不断的找到下一个人的信息
struct Person{
char name[16];
char phone[11];
short age;
struct Person *next; //结构体指针,存储下一个结构体变量的地址
};- 用字符数组存储电话号码,因为电话号码的每位都是0~9,用字符数组足以
画一个图帮助理解
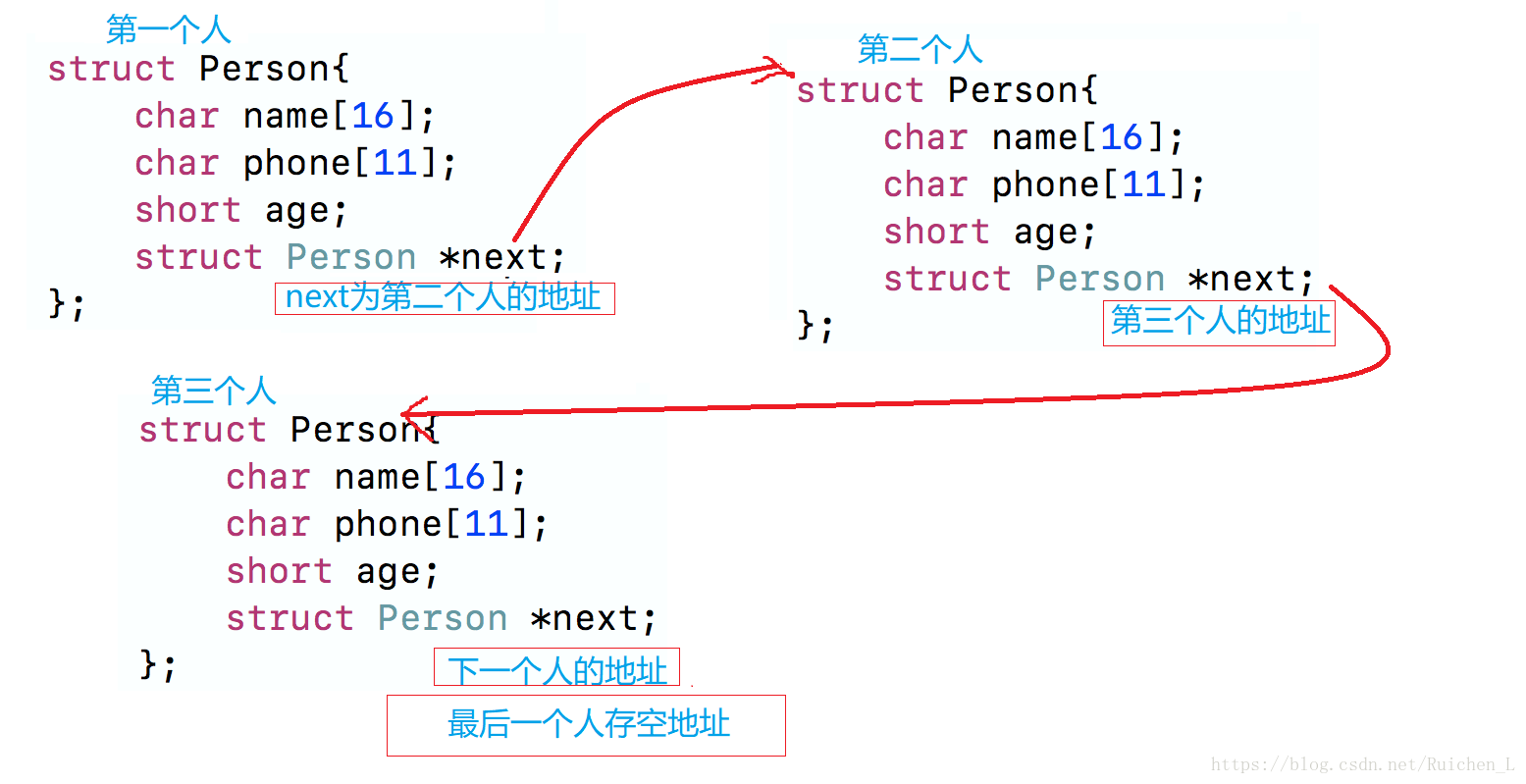
- 这样一直延续,最后一个结构体内存空地址,这样就将分散的每个结构体变量连了起来,这就是链表。
代码
框架
int main()
{
int choice = 0;
struct Person *head = NULL; //保存最开始的结构体变量地址
do
{
menu(); //展菜单函数
printf("请输入指令:");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch (choice) {
case 1:
//添加
init(&head);
break;
case 2:
//展示
show(head);
break;
case 3:
//查找
find(head);
break;
case 4:
//删除
delete(&head);
break;
case 0:
//退出
printf("已退出!\n");
default:
break;
}
}while (choice);
return 0;
}
展示菜单
void show(const struct Person *ph)
{
while (ph != NULL)
{
printf("name:%s\n",ph->name);
printf("phone:%s\n",ph->phone);
printf("age:%hd\n",ph->age);
ph = ph->next;
}
}添加功能
- 动态开辟一个person结构体变量,将本次开辟的地址放到上一次中,结构体内的next存下一次开辟的地址。
- 因为要改变head指向的内容所以需要用二级指针
void init(struct Person **ph)
{
struct Person *p = malloc(sizeof(struct Person));
printf("name:");
scanf("%s",p->name);
printf("phone:");
scanf("%s",p->phone);
fflush(stdin);
printf("age:");
//fflush(stdin);
scanf("%hd",&p->age);
p->next = NULL;
if (*ph == NULL)
//ph为空说明本次就是第一次开辟,所以将head改为p
{
*ph = p;
}
else
{
struct Person *tmp = *ph;
//循环找到结尾的结构体变量,即next为空的那个。
while (tmp->next != NULL){
tmp = tmp->next;}
//将next改为本次的p,将上一次的结尾和这次连起来
tmp->next = p;
}
}展示功能
void show(const struct Person *ph)
{
while (ph != NULL)
{
printf("name:%s\n",ph->name);
printf("phone:%s\n",ph->phone);
printf("age:%hd\n",ph->age);
ph = ph->next;
}
}查找功能
int find(struct Person *ph)
{
char name[16];
printf("请输入要查找的姓名:");
scanf("%s",name);
while (ph != NULL)
{
if (strcmp( ph->name, name) == 0 )
{
printf("name:%s\n",ph->name);
printf("phone:%s\n",ph->phone);
printf("age:%hd\n",ph->age);
return 1;
}
ph = ph->next;
}
printf("查无此人\n");
return 0;
}删除功能
int delete(struct Person **ph)
{
char name[16];
struct Person *p1 = *ph;
struct Person *p2 = NULL;
printf("请输入要删除的姓名:");
scanf("%s",name);
while (p1 != NULL)
{
if (strcmp( p1->name, name) == 0 )
{
break;
}
p2 = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
}
if (p2 == NULL)
{
*ph = p1->next;
free(p1);
}
else
{
p2->next = p1->next;
free(p1);
}
return 0;
}
整体代码及结果展示
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Person{
char name[16];
char phone[11];
short age;
struct Person *next;
};
void init(struct Person **ph)
{
struct Person *p = malloc(sizeof(struct Person));
printf("name:");
scanf("%s",p->name);
printf("phone:");
scanf("%s",p->phone);
fflush(stdin);
printf("age:");
//fflush(stdin);
scanf("%hd",&p->age);
p->next = NULL;
if (*ph == NULL)
{
*ph = p;
}
else
{
struct Person *tmp = *ph;
while (tmp->next != NULL){
tmp = tmp->next;}
tmp->next = p;
}
}
void show(const struct Person *ph)
{
while (ph != NULL)
{
printf("name:%s\n",ph->name);
printf("phone:%s\n",ph->phone);
printf("age:%hd\n",ph->age);
ph = ph->next;
}
}
int find(struct Person *ph)
{
char name[16];
printf("请输入要查找的姓名:");
scanf("%s",name);
while (ph != NULL)
{
if (strcmp( ph->name, name) == 0 )
{
printf("name:%s\n",ph->name);
printf("phone:%s\n",ph->phone);
printf("age:%hd\n",ph->age);
return 1;
}
ph = ph->next;
}
printf("查无此人\n");
return 0;
}
int delete(struct Person **ph)
{
char name[16];
struct Person *p1 = *ph;
struct Person *p2 = NULL;
printf("请输入要删除的姓名:");
scanf("%s",name);
while (p1 != NULL)
{
if (strcmp( p1->name, name) == 0 )
{
break;
}
p2 = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
}
if (p2 == NULL)
{
*ph = p1->next;
free(p1);
}
else
{
p2->next = p1->next;
free(p1);
}
return 0;
}
void menu()
{
printf("+------------------------+\n");
printf("+ 通讯录系统 +\n");
printf("+ 1.添加 2.展示 +\n");
printf("+ 3.查找 4.删除 +\n");
printf("+ 0.退出 +\n");
printf("+------------------------+\n");
}
int main()
{
int choice = 0;
struct Person *head = NULL;
do
{
menu();
printf("请输入指令:");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch (choice) {
case 1:
//添加
init(&head);
break;
case 2:
//展示
show(head);
break;
case 3:
//查找
find(head);
break;
case 4:
//删除
delete(&head);
break;
case 0:
//退出
printf("已退出!\n");
default:
break;
}
}while (choice);
return 0;
}结果
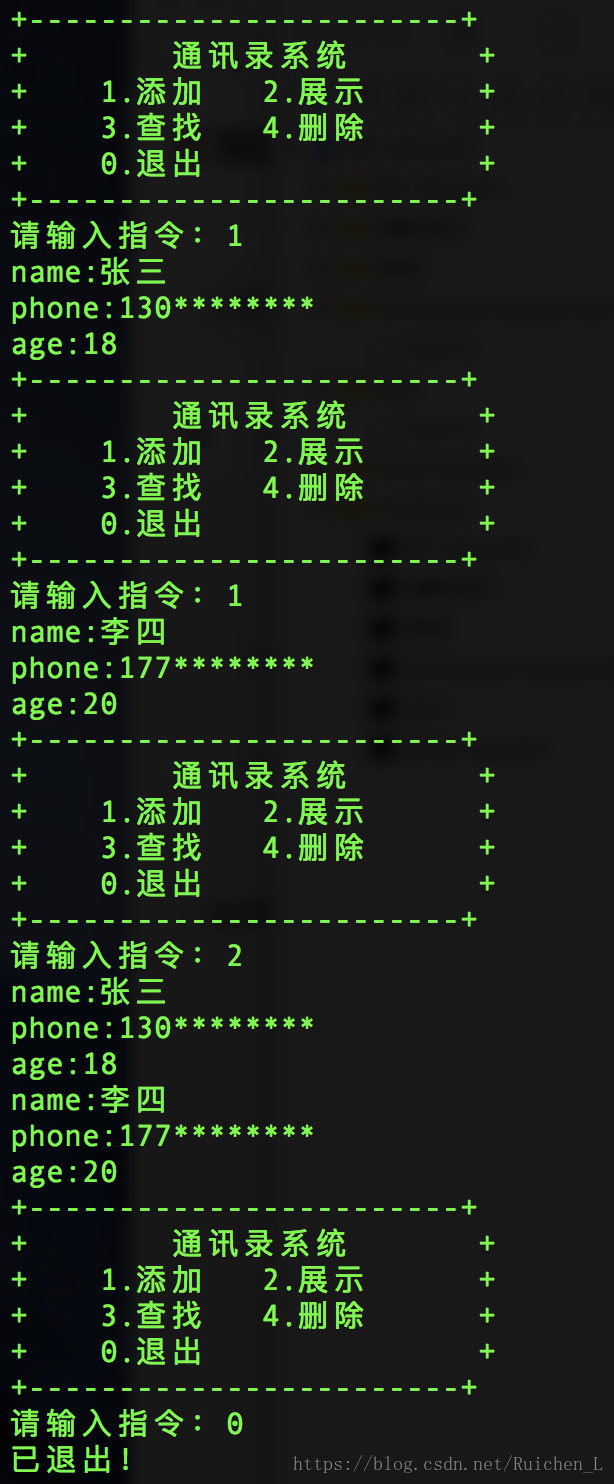





 本文介绍了一个使用单链表实现的简单通讯录系统,包括添加、展示、查找和删除联系人的功能,并提供了完整的代码示例。
本文介绍了一个使用单链表实现的简单通讯录系统,包括添加、展示、查找和删除联系人的功能,并提供了完整的代码示例。
















 5916
5916

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








